If you decide to make lighting in your house using spots, one of the main steps that you need to do correctly is to calculate their exact number for the ceiling. There are several basic calculation methods - using a formula, using or relying on the optimal value. Next, we will tell readers of the site how to calculate the number of spotlights in a room.
Method No. 1 – Generally Accepted Standard
There has long been a so-called optimal lighting level for one square meter of a room. According to the generally accepted standard, 20 W of power must be calculated per 1 m2. This method cannot be called the most accurate and recommended, but still, if you are too lazy to carry out calculations using formulas, you can simply rely on these numbers.
For example, if you have a 3*4 living room (12 squares), then you need to collect so many spotlights so that their total power is at least 240 W.
Method No. 2 – Formula
You can also find out how many spots are required by calculating the area of the room. Calculation formula as follows:
N=(S*W)/P;
- N – required number of spots;
- S – room area, m2;
- W – specific power of the luminous flux, (W/m2);
- P – power of one spotlight.
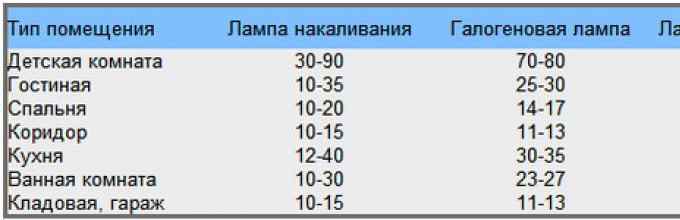
The first question that will arise is “where can I get the value of W?” This is a tabular value that helps us choose the appropriate illumination for the room. To calculate the number of spotlights, use this table:
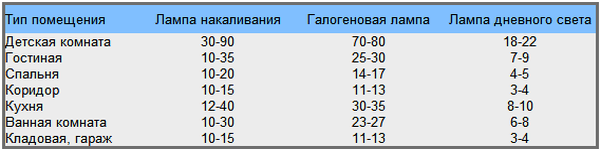
If you decide to install LED bulbs, then use the following values:
Please note that this formula is only suitable for rough household calculations because it does not take into account the height of the ceiling, its material (suspended, suspended or slatted), type of lighting (main or additional), decoration and color of the walls and other important factors. You can also accept your wattage density by choosing brighter or dimmer light bulbs in your kitchen, bathroom or living room!
N = (10*1)/5= 2 pieces;
As you can see, according to the calculation, we need 2 spots for normal
We suggest you figure out how to implement it correctly lighting calculation depending on the type and size of the room.
The degree of illumination of a surface is usually expressed in Lux (Lx), and the amount of luminous flux emanating from a certain light source is measured in Lumens (Lm). We will produce illumination level calculation in two stages:
- the first stage is to determine the total amount of luminous flux required for the room;
- second stage - based on the data obtained from the first stage - calculation of the required number of LED lamps taking into account their power.
Stage No. 1 of calculation.
To easily calculate the required number of lamps, use the Calculator for calculating the number of lamps.
The formula = X * Y * Z calculates the required luminous flux (Lumen) in this case:
- X is the established norm for illumination of an object depending on the type of room. The standards are given in Table No. 1,
- Y - corresponds to the area of the room in square meters,
- Z - coefficient of correction of values depending on the height of the ceilings in the room. For ceiling heights from 2.5 to 2.7 meters, the coefficient is equal to one; from 2.7 to 3 meters, the coefficient corresponds to 1.2; from 3 to 3.5 meters the coefficient is 1.5; 3.5 to 4.5 meters the coefficient is 2.
Table No. 1 "Illumination standards for office and residential buildings according to SNiP"
Stage No. 2 of calculation.
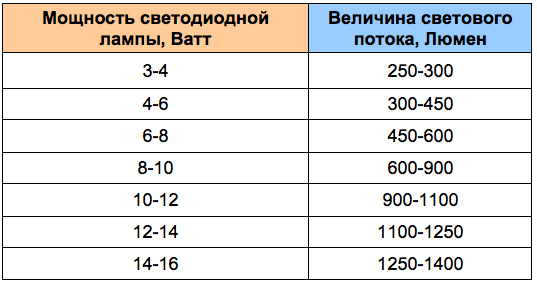
Having received the necessary data on the amount of luminous flux, we can calculate the required number of LED lamps and their power. Table No. 2 shows the power values of LED lamps and the corresponding luminous flux indicators. So, we divide the luminous flux value obtained at stage No. 1 by the luminous flux value in lumens for the selected lamp. As a result, we have the required number of LED lamps of a certain power for the room.
Table No. 2 "Luminous flux values of LED lamps of different power"
Example of lighting calculation.
150 (X) * 20 (Y) * 1 (Z) = 3000 Lumens.
Now, according to table No. 2, we select a lamp that will fit into the installed lighting fixtures and with which we want to illuminate our room. Suppose we take all 10 Watt lamps with a luminous flux of 800 Lumens, then to illuminate our room with such LED lamps we will need at least 3000/800 = 3.75 light bulbs. As a result of mathematical rounding, we get 4 light bulbs of 10 watts each.
It is important to remember that it is desirable to achieve uniform light distribution in the room. To do this, it is better to have several light sources. If you are planning to create artistic lighting with multiple ceiling mounted fixtures, we recommend using 8 LED bulbs of 5 watts each and evenly distributing them across the ceiling.
Please note that we took the SNiP standards adopted in our country as the basis for our calculations. Since these standards were developed and adopted a long time ago, many of our clients say that the level of lighting according to these standards is low for them and the light is clearly not enough. Therefore, we recommend increasing these standards by 1.5-2 times while installing several switches, dividing them by zones of the room and by the number of lamps. This will allow you to turn on some of the lamps and get soft, not very bright lighting, and, if necessary, turn on full bright lighting.
The concept of lighting calculation, like any other technical calculation, implies the performance of certain mathematical operations that combine the lighting parameters of lighting devices (their number, power, quantity, location in the room, etc.) with the resulting light indicators (illuminance, brightness, and so on) resulting from their work.
The number of such parameters and indicators can be very diverse, which is why the number of lighting problems is also large. Calculations can be conditionally divided into direct ones - when the parameters of lighting devices are determined according to given lighting technical indicators, and verification - during the solution of which, with known parameters, the expected value of the indicators is determined.
The methods of calculation can also be quite varied. This is, first of all, determined by the nature of the problems being solved: lighting fixtures or devices can be point, linear or two-dimensional; their light distribution can be circularly symmetrical, have two, one or no planes of symmetry; illuminated surfaces can be vertical, inclined or horizontal; the interest of the calculation may lie in determining the largest, smallest or average value of lighting indicators, and so on.
At the same time, to solve the same specific problem, quite often different authors of calculation methods propose different ways, but in practice only a few proposals are used.
Different methods and methods of calculation differ in the degree of accuracy of the calculation results.
Of course, first of all, the accuracy of calculations is of interest to design engineers working in design organizations, since the objects of their activity are public and administrative buildings, industrial premises, roads, recreation parks and others. That is, those objects in which the a large number of of people. In such cases, in Lately use special paid or free programs(computer-aided design systems (CAD)), in which the engineer draws a drawing of the illuminated object, selects the necessary lighting devices available in the program database, placing them around the object manually or automatically, and makes calculations. Sometimes calculations are made manually using a calculator using well-known methods.
For the vast majority of people living in individual houses or apartments and interested in the issue of ensuring standardized illumination of residential and non-residential rooms, it is enough to make an approximate calculation of room lighting or calculation of street lighting and determine the required number of lamps to achieve it. Such lighting calculations can be performed using specialized online illumination calculators. Such calculators are now common on the Internet, on the websites of lighting equipment manufacturers.
Let's get acquainted with the listed tools for calculating illumination.
Online lighting calculation
The expression itself - “online calculation”, indicates that the necessary calculations are made on the Internet, or rather on the pages of sites that have such a service. The number of such sites is quite large. If you enter search queries like: - "Online calculation of room illumination" or - "Calculation of lighting calculator online" in the line of the most popular search engines "Yandex" or "Google", then the search engines will return about a dozen such sites. The most well-known include the websites of lighting equipment manufacturing companies, such as Ardatovsky Lighting Plant OJSC and Lighting Technologies. You can also note the very interesting website “Online Calculator”, which is entirely dedicated to the topic of online calculations and contains on its pages a huge number of calculators from different fields of science and human activity in general. Such calculations are absolutely free.
Figure 1. Form for calculating the number of lamps of the Ardatov Lighting Plant
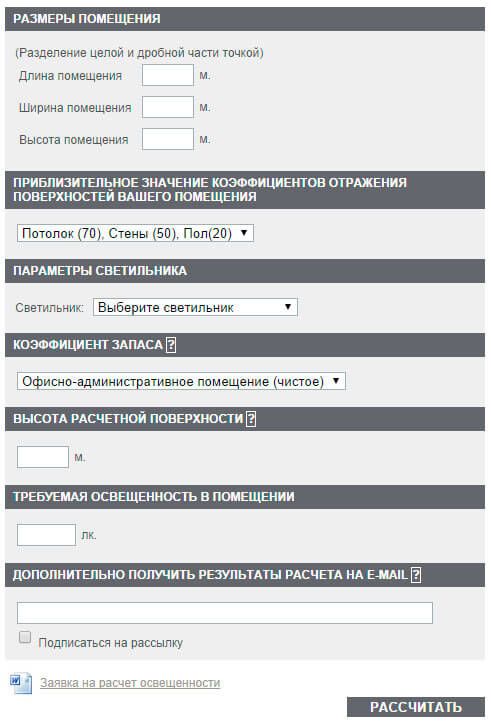
Figure 2. Calculation form for the number of lamps from the Lighting Technologies company
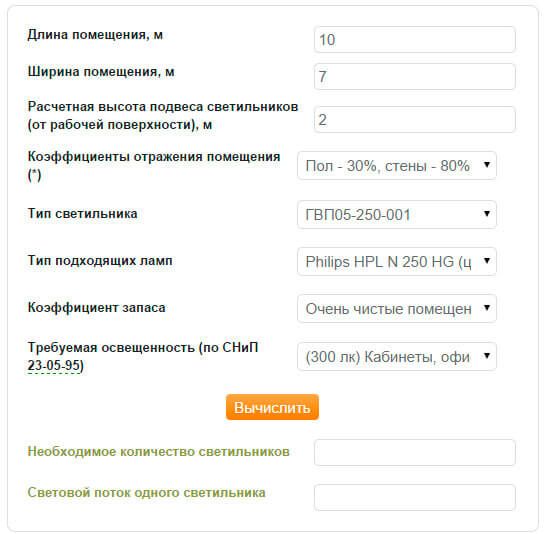
Figure 3. Form for calculating the number of luminaires and the luminous flux of one luminaire on the "Online calculator" website
As can be seen from the figures, the result of the calculation of all calculators is the required number of lamps for a certain room with given dimensions. During the calculation, a minimum number of parameters is also specified, without which the calculation will be impossible. This is the reflectance of room surfaces (walls, ceilings, floors); parameters of the luminaire, or rather its type, since by selecting the type of luminaire, all parameters of the luminaire (light distribution curves, luminous flux and others) are automatically applied in the calculation; type of lamps; required room illumination; safety factor (a value that takes into account the decrease in the efficiency of the lamp and luminaire); height of the lamp suspension and height of the calculated surface.
Illumination calculation programs
In addition to online calculations, there are stand-alone programs based on operating system Windows.
The first program of this kind that I discovered on the Internet is the “Formula of Light” program, developed by the lighting company “Electro”. The program resembles online calculators and is no different from them in functionality.
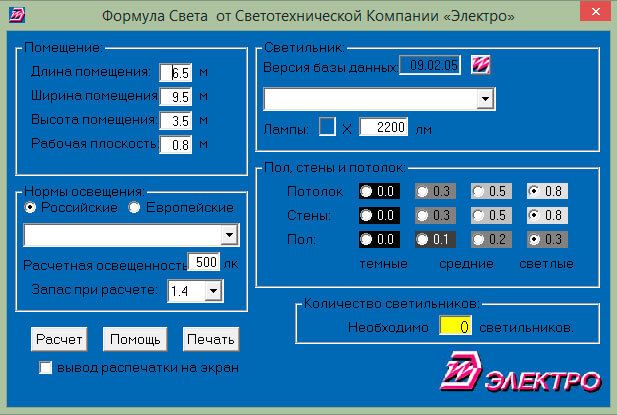
Figure 4. Working form of the "Formula of Light" program
The specified parameters in the calculation are: room dimensions; required level of illumination; safety factor; lamp type; reflection coefficient. That is, all those that are specified during online calculations. The result of the calculation is the number of lamps required to create the room illumination level specified in the task. Quite modest.
It is worth noting that the program has not been supported for a long time and the database of lighting devices is very outdated.

Figure 5. Calculation result in the "Formula of Light" program
In my opinion, the program is useful for those who do not have the opportunity to connect to the Internet. Although at the moment such people probably won’t be found anymore.
The next, more interesting program that gives more accurate calculation results is Beroes OS 1.1. This program allows you to calculate lighting in buildings and structures using two methods: the specific power method and the luminous flux utilization factor method. In addition, it is possible to check the calculation results using the point method and the method of calculation from luminous lines, followed by correction of the number of lamps and their placement. The program is intended for design organizations and students educational institutions involved in the calculation of artificial lighting of buildings and structures.
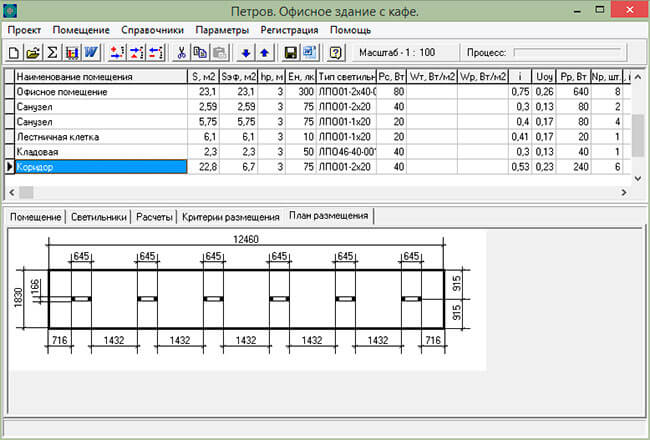
Figure 6. View of the main form of the Beroes OS 1.1 program
The program project is the equivalent of a separate calculation of artificial lighting for a building or structure that can have an unlimited number of rooms. The program allows you to manage any number of projects by creating, opening, deleting and copying them.
At first glance the program is a bit complicated. In any case, I was not able to immediately add the required lamp and lamp to it after creating a new project in order to calculate their total number. But the program's capabilities are impressive. The program is distributed free of charge.
Computer-aided design systems
CAD "Compass"
Similar calculation results can be obtained using the "KOMPAS. Power supply: ES/EM" application included in the universal computer-aided design (CAD) system "Compass-Graph". The application allows you not only to automatically arrange lighting devices, calculate illumination and, as a result, obtain a clear visual picture of the propagation of the luminous flux in the form of luminous intensity curves, but also to complete the entire project in terms of power electrical equipment (EM), internal electric lighting (EL) and power supply (ES). ).

Figure 7. Plan for arrangement of equipment, electrical panels, connection of electrical receivers to switchgears, cable routing
Figure 8. Calculation of the number of lamps using the utilization coefficient method of Aizenberg Yu.B.

Figure 9. Viewing the construction in three-dimensional space of lamps and cable routes
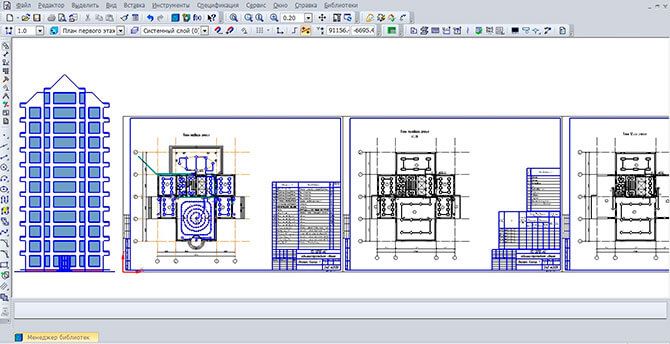
Figure 10. Layout of equipment and electrical wiring

Figure 11. Single-line design diagram
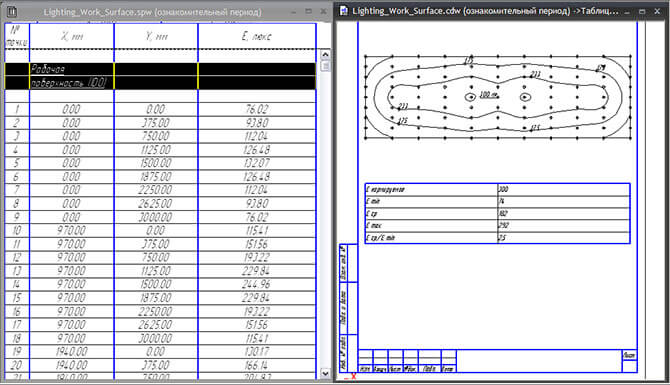
Figure 12. Table of indoor illumination values and isoluxes, giving a clear picture of the illumination distribution
The only drawback is that the illumination calculation is performed only for a rectangular area. That is, if you built a room whose shape is different from a rectangle or square, then the calculation will be made within a rectangular area, the length of the sides of which is equal to the maximum length of the walls of the room. Accordingly, the results differ slightly from the actual ones. But they are quite satisfying building regulations and rules for handing over a facility after construction or reconstruction. My opinion is that this program is best used to calculate the lighting of a production facility.
CAD "DIALux"
And finally, we’ll briefly talk about the masterpiece of all lighting design programs, the computer-aided design system for professional lighting DIALux. CAD was developed by the engineering company DIAL GmbH, whose main activity is measurement, testing, auditing, as well as checking the compliance of light sources, lighting devices, hardware and software with standards.
CAD DIALux is distributed free of charge, so its most latest version can be downloaded from the official website by anyone www.dial.de. DIALux is completely Russified, so most users should not have any particular difficulties in mastering it.
The DIALux functionality allows you to calculate lighting as interior spaces buildings and outdoor facilities, such as playgrounds, sports facilities, open warehouses, highways and others.
If you are working in DIALux for the first time, then you can use the assistant, which offers several options for the complexity of the layout of the illuminated object.
Figure 13. DIALux dialog box

Figure 14. Window for selecting project creation assistants
DIALux Light is the most in a simple way input of initial data and consists of four stages:
- input of design information;
- survey of room geometry, design parameters and choice of lamps. It should be noted that with the help of this assistant it is possible to build only rectangular and L-shaped rooms;
- placement of luminaires with calculation and indication of results;
- setting print options and printing calculation results.
Figure 15. DIALux Light window for entering project information

Figure 16. DIALux Light window for entering initial data
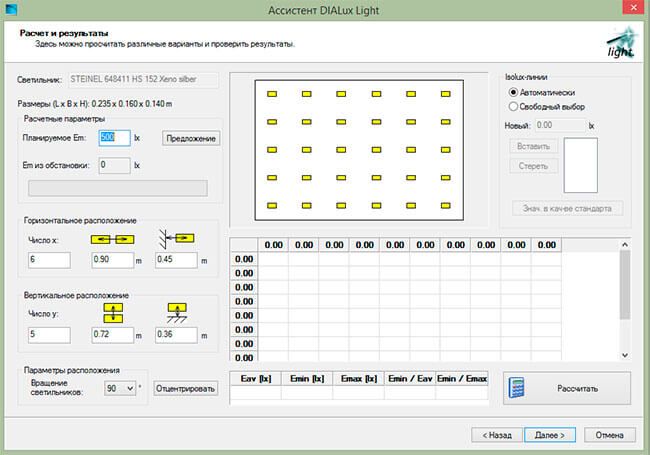
Figure 17. DIALux Light window for changing calculation conditions
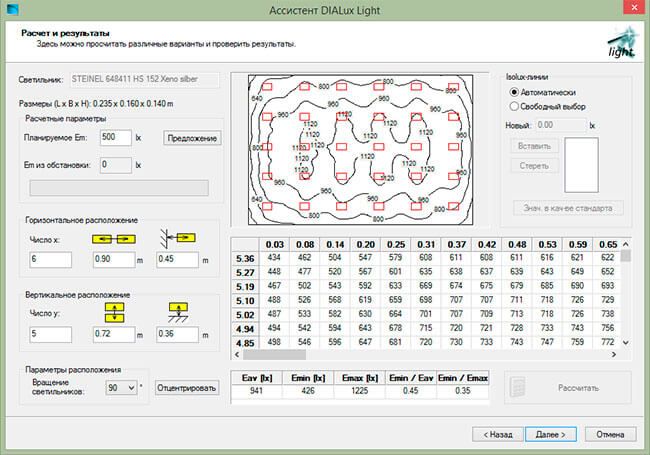
Figure 18. DIALux Light window with calculation results
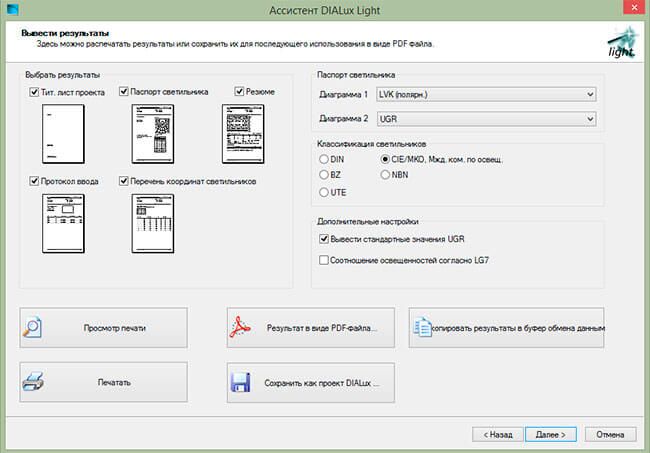
Figure 19. DIALux Light window for determining how calculation results are displayed
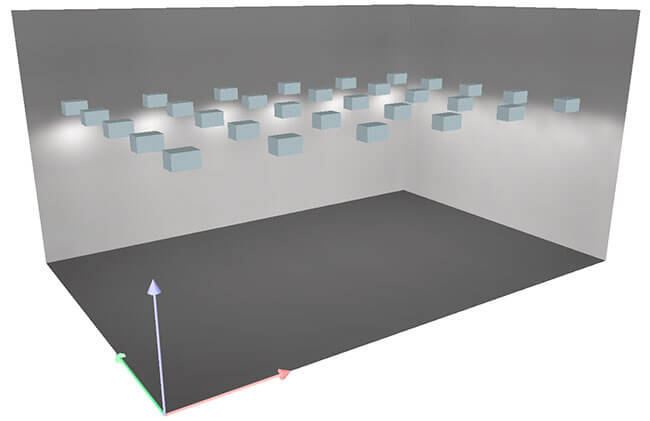
Figure 20. Three-dimensional model resulting from calculations in DIALux Light
The second method of entering initial data in the assistant allows you to quickly complete standard room layouts. In terms of the method of entering initial data, it is no more complicated than DIALux Light, but unlike it, it allows you to build rooms of a polygonal shape, that is, having complex shape walls and corners.
The third input method is identical to the second, but for some reason is designed for more experienced users. Although it is not superior in complexity or functionality.
And finally, using the fourth method of entering initial data, you can quickly compose an object for street (outdoor) lighting. Here, just like in DIALux Light, you need to go through three main stages:
- setting a road profile and other information;
- setting criteria fields and corresponding illumination classes;
- selection and placement of lamps.
To demonstrate the capabilities of CAD, I will provide several images with calculation results, which were taken from the Freelance website:

Figure 21. Example of calculating the lighting of a sports hall
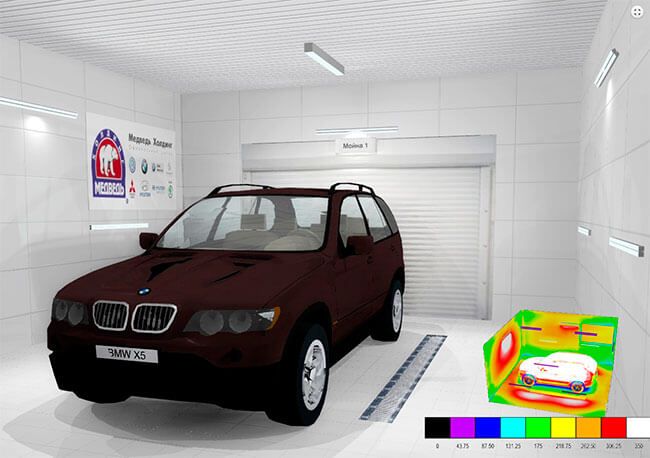

Figure 22. Example of calculating car wash lighting

Figure 23. Example of calculation of lighting for a Nissan car showroom

Figure 24. Example of calculating lighting for a clothing store

Figure 25. Example of calculating lighting for a restaurant entrance

Figure 26. An example of calculating the illumination of the external walls of a residential building


Figure 28. Example of calculating the lighting of a hotel room (top view)

Figure 29. Example of calculating the lighting of a hotel room

Figure 30. Example of calculating the lighting of a hotel room
Since October 2012, a new CAD system DIALux evo has become available, designed not only for calculating indoor and outdoor lighting, but also for architectural design generally. The main advantage of the new package is that in one project you can simultaneously create both external objects (roads, bridges, sidewalks, sports facilities, buildings, landscaping, etc.) and the internal layout of premises, including furniture and household appliances.
Figure 31. DIALux evo dialog box
When calculating the lighting of this CAD system, even the photometric properties of the glass are taken into account. This advantage is especially important when the room where the calculation is made has panoramic glazing.
In general, the user interface of the package itself looks more functional and intuitive. Here are examples of working windows and images obtained as a result of working in DIALux evo:

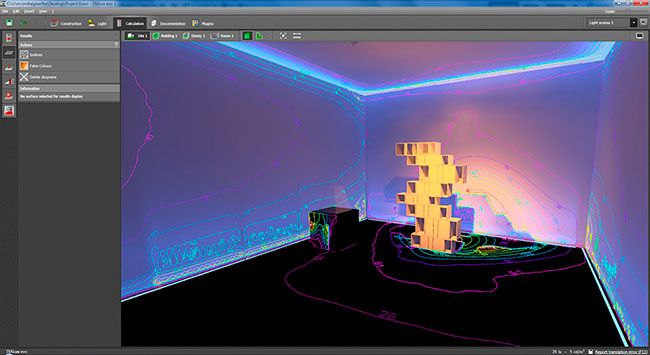


In addition to DIALux, there are other computer-aided design systems that have similar functionality and are distributed free of charge, or shareware, for example, RELUX, but, in my opinion, DIALux deserves the closest attention. The package has been developed for quite some time and is constantly being improved and updated. Its main advantage over other CAD systems designed for calculating lighting and visualizing the resulting results in the form of a three-dimensional image is that it is completely translated by the developers into Russian.
So, if you need to quickly “estimate” what level of illumination will be provided when using certain types of lighting devices, use online calculators. If you have free time, desire to build 3D model your home and visually evaluate the effect of using a specific lighting device located in a particular place, I advise you to use the CAD system DIALux or DIALux evo.
3.6666666666667 Rating 3.67 (3 votes)
In the evening, with the onset of twilight, and if the windows are in an unfavorable position, during the day, you have to turn on the lamps, and the question arises: how to calculate room illumination to save on electricity and not sit in the dark.
1 How to calculate the illumination of a room correctly?
Comfort in the house is not only a pleasant microclimate, a pleasing interior and a crackling fireplace in the corner. When creating coziness, the correct distribution of lamps is of great importance in order to provide lighting that does not tire the eyes or soft twilight. IN big room zoning with the help of light sources is possible; in a small room, distributing them according to height levels may be sufficient, for example: a floor lamp, sconce and chandelier. But, in any case, you must insert the most suitable light bulb into each device. You will have to choose it from a dozen different options, so that it does not turn out to be too bright or dull.
Illumination calculator
Indicate the dimensions of the room and lighting fixtures.When choosing the optimal level of room lighting, you should rely on factors such as the presence or absence of mirrors, the color scheme of the room, the color of the furniture (dark or light). Even the height of the ceilings will play a certain role when choosing light bulbs for a chandelier. You should also remember that the lighting must correspond to the purpose of the room. In the bedroom the best option the light will be dim; in the office, a bright light bulb will only be needed in the area desk, in the living room it is better to use different variants. The illumination power is usually taken at square meter, an example can be seen in the table below.

Generally accepted standards of illumination at the height of the ceiling of the room no more than 3 m
The simplest way to calculate the illumination of a room is the formula P = (p . S)/N, wherein p is the specific power, usually taken to be 20 W/m2, S– area of the room, and N– number of lamps. However, this formula will only give an approximate figure and will not reliably show the need to add or, conversely, reduce the brightness of the light. To begin with, the power density for each room is different, and can vary depending on what type of light bulb is inserted into the socket. You can verify this by looking at the table.
2 What should be taken into account when calculating the required brightness of lamps?
So, we looked at the simplest method for calculating the possible illumination power in a room. But, again, this is the total power. You can screw in 2 bulbs of 100 W or 4 bulbs of 50, distributing them over a wider front. What will change? Number of light sources. It is logical that by placing a two-armed and very bright chandelier in the center of the room, sitting with your back to it at the table, you will see your shadow on the work surface. And it’s easy to guess that placing 4 lamps with a total power identical to the previous option in different areas of the room, including the work area, will give a much greater effect.
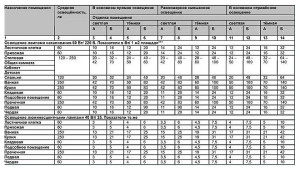
Before calculating the number of lamps, you should take into account the height of the ceiling and working surface. Above is a table of room lighting brightness standards for ceilings up to 3 meters. What if they are much higher? Then the same indicators should be multiplied by 1.5, and after 4 meters - by 2. Ideally, natural light sources should also be taken into account in the calculations, that is, but it is hardly possible to recalculate the number of lumens penetrating through them. But for lamps this is quite feasible if you use the table.
|
Source |
Power |
Light flow |
Average service life |
| Incandescent lamp warm white light |
15 |
90 |
1000 |
| Halogen lamp 12 V warm white light |
20 |
340 |
2000 - 4000 |
| Halogen lamp 220 V warm white light |
100 |
1650 |
2000 - 4000 |
| Luminiscent lamp warm white light cool white light neutral white light |
4 |
120 |
7500 - 8500 |
| Mercury lamp warm white light neutral white light |
50 |
2000 |
8000 - 12000 |
| Sodium lamp yellow light |
35 |
2000 |
8000 - 10000 |
| Metal halide lamp warm white light cool white light |
39 |
3000 |
6000 - 9000 |

Therefore, let’s pay attention not to external factors, but to internal ones, that is, to the light of the lamps and its interaction with the finish. Matte finishes on furniture and walls tend to absorb light rays, while glossy finishes are known to reflect them. It's the same with colors; darker ones require brighter lighting and vice versa. The specific power from the formula given earlier must be taken based on all the listed factors, and the following table will help with this.
|
Room |
Average power |
Direct lighting |
Mixed lighting |
Indirect lighting |
|||||||||
|
Decoration of the premises |
|||||||||||||
|
light |
dark |
light |
dark |
light |
dark |
||||||||
|
For incandescent lamps |
|||||||||||||
| Hallway | |||||||||||||
| Office, living room | |||||||||||||
| Bedroom | |||||||||||||
| Bathroom, kitchen | |||||||||||||
| Pantry | |||||||||||||
| Basement, attic | |||||||||||||
| Hallway, staircase | |||||||||||||
| Bathroom, kitchen, living room | |||||||||||||
| Pantry, basement, attic | |||||||||||||
3 How to calculate the number of lamps per room?
So, we know the height of the ceiling, let’s say 3.2 meters, in our office we have a table 80 centimeters high. How to determine how many light sources are needed? There's no way around this anymore simple method, and therefore we will use a more complex option, which will require a number of formulas. And you will have to operate in addition to Watts with such units of measurement as lux and lumen. First of all, we calculate the area of the room using the standard method S=a.b, Where a And b– lengths of adjacent sides of the room. Let's say the required value is 12 m 2.

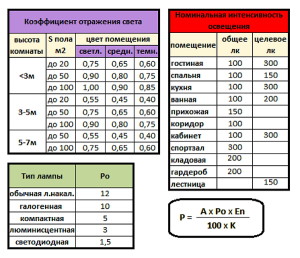
Next, we need to find out the utilization factor of the lighting fixture, for which we need the room index and the reflectance coefficients of various surfaces. The formula to obtain the first indicator is as follows: φ=S/((h1 - h2) ∙ (a + b)). Here two new variables are added, h1 And h2, representing the height from the ceiling to the floor and from the ceiling to the illuminated working surface of the table. As for the coefficients, they depend on what material the surface is made of and what texture it has. Suitable values can be selected from the table.
|
Nature of the reflective surface |
Reflection coefficient r, % |
| Surfaces made of highly reflective materials; white marble | |
| Whitewashed ceiling; whitewashed walls with windows covered with white curtains; white faience tiles | |
| Wallpaper white, cream, light yellow | |
| Whitewashed walls with uncurtained windows; whitewashed ceiling in damp rooms; clean concrete and light wood ceiling; light pine wood | |
| Wood plywood | |
| Light oak tree | |
| Concrete ceiling in dirty rooms; wooden ceiling; concrete walls with windows; walls covered with paper light wallpaper; gray surfaces | |
| Wallpaper dark | |
| Walls and ceilings in rooms with a lot of dark dust; continuous glazing without curtains; red brick not plastered; walls with dark wallpaper | |
| Red brick | |
| Window glass (thickness 1-2 mm) |
It is usually customary to take reflectance coefficients for the ceiling, walls and floor (they are converted to decimal fractions, that is, a value of 50 corresponds to 0.5). Based on them and the result of calculating the room index, it is not difficult to find another variable - the lighting use index U, which we will need for further calculations. The next coefficient is determined from tables, which differ significantly depending on the use of a particular brand of lamp. Let's take, for example, lamps with type KSS M, that is wide range lighting within 180 degrees of maximum brightness radiation. This is just an ordinary household light bulb.
|
U value, % |
||||||||||||
|
With r ceiling = 0.7, r walls = 0.5, r floor = 0.3 and φ equal to: |
With r ceiling = 0.7, r walls = 0.5, r floor = 0.1 and φ equal to: |
|||||||||||
| 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.25 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.25 | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
| M | 35 | 50 | 61 | 73 | 83 | 95 | 34 | 47 | 56 | 66 | 75 | 86 |
|
With r ceiling = 0.7, r walls = 0.3, r floor = 0.1 and φ equal to: |
With r ceiling = 0.5, r walls = 0.5, r floor = 0.3 and φ equal to: |
|||||||||||
| 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.25 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.25 | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
| M | 26 | 36 | 46 | 56 | 67 | 80 | 32 | 45 | 55 | 67 | 74 | 84 |
|
With r ceiling = 0.5, r walls = 0.5, r floor = 0.1 and φ equal to: |
With r ceiling = 0.5, r walls = 0.3, r floor = 0.1 and φ equal to: |
|||||||||||
| 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.25 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.25 | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
| M | 31 | 43 | 53 | 63 | 72 | 80 | 23 | 36 | 45 | 56 | 65 | 75 |
|
With r ceiling = 0.3, r walls = r floor = 0.1 and φ equal to: |
With r ceiling = r walls = r floor = 0.1 and φ equal to: |
|||||||||||
| 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.25 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.25 | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
| M | 17 | 29 | 38 | 46 | 58 | 67 | 16 | 28 | 38 | 45 | 55 | 65 |
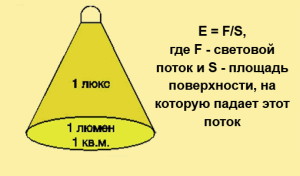
Having learned the meaning U, then substitute it into the formula N=(E∙S∙100∙K h)/(U∙n∙F l). We have new variables in the numerator: E– minimum illumination, expressed in lux (lx), and K z– safety factor taken into account based on the aging of light bulbs during operation. The latter is, in fact, a constant that can be found in SNiP, but on average this figure corresponds to 1.5 for fluorescent lamps and 1.3 for incandescent lamps. The denominator is unknown to us n– the number of light sources in the electrical appliance and F l– radiation from one lamp, expressed in lumes (lm). The minimum illumination value is calculated using the formula E = F l /S. Using all the parameters given in the tables, as well as the results of secondary formulas, find the number of lamps N the room will not be difficult.
No matter how many bulbs there are in a chandelier, it will not be able to illuminate the entire room; there will definitely be darker areas somewhere, so it is wiser to distribute the lighting sources throughout the room.
We all live in houses with artificial lighting, since not all rooms in the house can be illuminated window openings. And here the question arises, how many lighting fixtures are needed in order to feel comfortable anywhere in the apartment?
Lighting in the house
As you know, properly created lighting allows a person to spend time comfortably and at the same time maintain his health. Therefore, in order to do everything according to the rules, it is necessary to calculate the number of lamps that each specific room needs. You will learn how to do this from this article.
Why count?
Many people believe that such calculations are not necessary. But they are deeply mistaken. According to the lighting standards, which are given in a number of regulations, each room, depending on its purpose, has its own specific level of lighting.
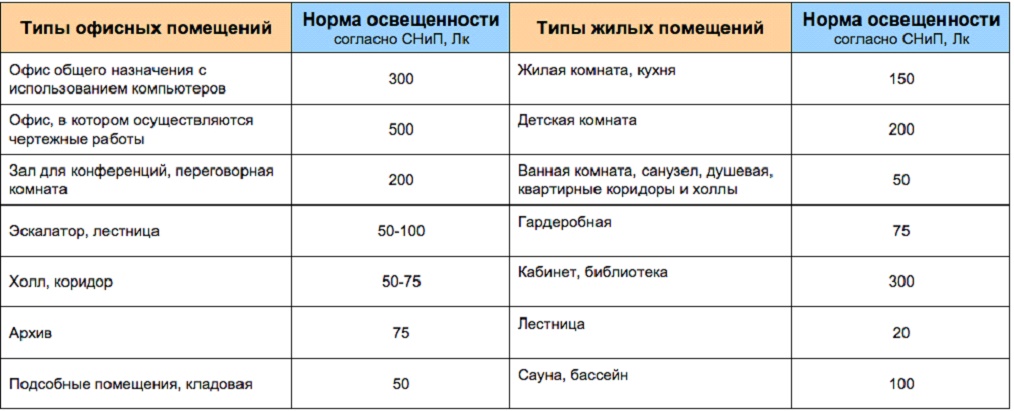
Light level table
Established standards should be used to determine the number of not only light bulbs, but also lamps (chandeliers, LED or spotlights, etc.).
Note! In regulations, lighting levels for residential premises are set to minimum standards. Therefore, if necessary, in some cases they can be varied somewhat.
If such standards are not taken into account, then staying in a room with an improperly organized level of illumination will lead to a deterioration in human health, especially in terms of the visual, nervous and immune systems. The person will begin to get tired much faster and become more irritable and nervous. This development of events can be caused not only by an incorrectly selected number of lighting devices, but also by uneven light from light bulbs and their incorrectly selected technical parameters.
How to proceed?
The required number of lighting fixtures (especially for spotlights and LED lamps) should be calculated for each room in the house or apartment. This is explained by the fact that they all have their own purpose, their own dimensions and their own illumination level standards in accordance with accepted requirements.
Particular attention in this matter should be paid to the nursery and kitchen. Industrial and office rooms also fall under the category of increased attention. The importance of lighting here is due to the fact that this is where people stay for a long time. Therefore, an incorrectly selected number of lamps in this situation will cause more significant harm to people’s health.
Anyone can calculate the number of lamps for any room. To do this, you just need to know the calculation algorithm, as well as those parameters that affect the final result.

Variety of models
Today, people are increasingly giving preference to spot and LED devices, installing them as main or combined lighting. Therefore, in this article we will look at the principles of calculating LED and spotlights for any room.
First calculation option
When determining the number of LED devices, the method of the coefficient of luminous flux emitted by the light source is used.
Note! This method is suitable for counting the number of any types of lighting fixtures, not just the LED version. It is also suitable for any type of room.

LED model
The essence of this method is to calculate the coefficient for the room, which is based on its size, as well as the reflective properties of surfaces (ceiling, floor and walls).
To make calculations using this method, you need to know the following parameters:
- a is the length of the room;
- b – its width;
- h1 – ceiling height.
You will also need the following indicators:
- lighting fixture utilization factor;
- light reflection coefficients from the surface of the ceiling, walls and floor;
- design height - the distance between work surface(hp) and lamp;
- type of light bulb used;
- power of light bulbs used;

Types of light bulbs
- lighting standards.
All these parameters can be found out from the relevant regulations for each specific premises.
The calculation algorithm includes the following steps:
- determining the area of the room. To do this, multiply the width (b) by the length (a);
- calculate the room index φ = S / (h - Кз) * (a + b);
Note! To calculate the room index you will need to know the following indicators:
- S – room area;
- h – its height;
- Кз – previously calculated safety factor;
- a and b are the width and length of the room.
- then we determine the coefficient for using the device. This indicator can be found from the serialization tables of lighting products. To do this, you need to know the room index and reflection coefficient.
Now everything is ready to determine the required number of lighting fixtures using the formula:
N = (E x S) / (U x n x Fl x Kz)
The values from the formula are deciphered as follows:
- E – required illumination for the horizontal plane (Lx);
- S – area (m2);
- U – coefficient of application of the lighting device;
- n is the number of light bulbs screwed into one product;
- Fl – luminous flux indicated for one lamp (Lm);
- Кз – safety factor. This coefficient determines the decrease in the brightness of the light bulb due to wear and/or contamination of the lighting elements, as well as contamination of the space of the illuminated surfaces.
After this, we determine the utilization factor of the device. We insert all the obtained values into the formula and read the final result.
The resulting number represents the optimal number of luminaires required to create a high-quality level of illumination for a particular room.
Second calculation option
Here we will consider the option of determining the number of point devices.

Point model
To carry out all the necessary calculations, you need to do the following algorithm:
- determine the area of the room for which further calculations will be carried out;
- We determine the power of light bulbs that are used for lighting. It is this indicator that is most important for determining the number of spotlights;
Note! The distribution of light sources is carried out according to the rule: per 1 sq. m. of area that needs to be illuminated, you should use a 20 W light bulb. Thus, if the lamp power in an existing lamp is approximately 35 W, then by 1.5 sq. m. it will be necessary to install one lighting fixture with such a light source.
- the distance between such spotlights should be approximately 30 cm. At the same time, there should be approximately 20 cm from the corner of the wall to the nearest light source.
Based on the above algorithm, you can easily calculate the number of spotlights for any size.
In a situation where spotlights will be placed only as additional lighting, then their number can be reduced somewhat. In addition, it would be rational to place spotlights in a specific area as local lighting.
It must be remembered that the lighting standard for this kind of lighting devices must be increased by approximately 15-20%. This should be done in a situation where they act as the main lighting.
Interior

Interior
The last thing to consider in such calculations is the color scheme of the interior. This parameter must be taken into account if you want to get optimal lighting. The darker the situation, the brighter the light sources should be. The power here needs to be increased by 1.5-2 times. In addition, you can slightly increase the number of lamps themselves.
As you can see, the calculations are not that complicated, but they are necessary for your comfortable stay in any room of the house.
 Making an original bio-fireplace on your own
Making an original bio-fireplace on your own
 Proper lighting in the corridor, compliance with standards
Proper lighting in the corridor, compliance with standards