In this article we will introduce you to how to properly make a wooden floor on ceiling beams with your own hands, and also tell you about general procedure holding events of this type.
Let us immediately note that wooden beam floors are used, as a rule, only in private country house construction and are installed either between floors or between a room and an attic. This type of floors has a number of advantages not only in comparison with standard reinforced concrete blocks, but also in relation to monolithic floors.

These benefits are as follows:
- wooden floors are easy to erect and do not require any additional technical means (a truck crane, for example, or special concreting equipment) for their arrangement;
- they are much lighter than their counterparts made from well-known building materials;
- When using such floors, the foundation of the building can be somewhat lighter.
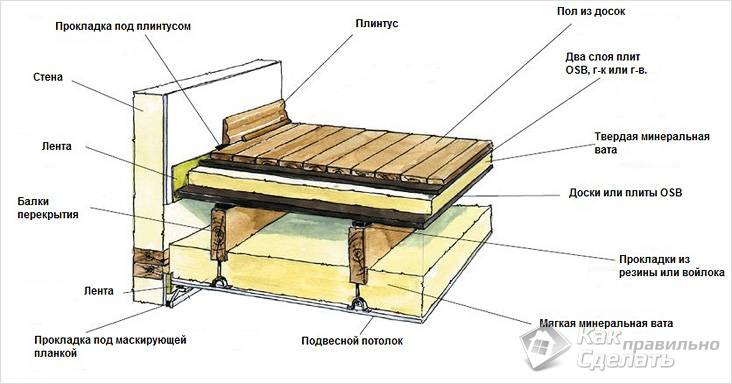
In addition, it should be noted the relatively low cost and high speed of installation of this structural element. The only disadvantages of floors of this class include their high fire hazard and the possibility of destruction by bark beetles. In addition, they are characterized by lower concrete structures, sound insulation, they are sensitive to changes in ambient temperature and humidity.
True, you can always eliminate these disadvantages if you use special impregnations that significantly reduce these risks.
Main characteristics of beam floors

Conventional solid wood is used to make floor beams. More durable glued samples are used with the same success, the length of which can be increased to 15 meters. The material from which beams are made can be either coniferous or hardwood. The distance between adjacent beams should not exceed one meter. Beams with a length of 2.5-4 meters (with a ratio of height to width of their cross-section of 1.4:1) are considered the most optimal for spans of typical household buildings.
The choice of beam section in the most general case is determined by the load for which the given floor must be designed. In order to increase bearing capacity In such structures, beams are usually laid along a short wall.
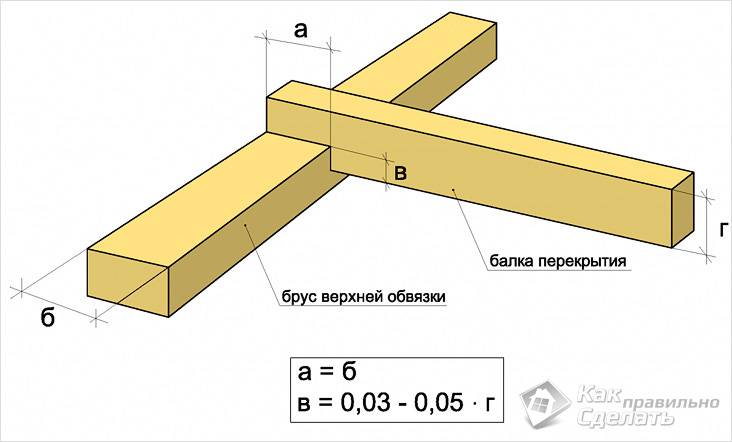
As a design option for such beams, you can consider the case when they are simply sheathed with boards on the upper side. The lower parts of the beams, open for public viewing, contribute to the creation of a certain style in the design of a given room. If you wish, you can also sheathe them and make a standard suspended ceiling.
The correct solution to the basic question “how to properly make a wooden floor?” also includes a limitation regarding the maximum length of beams.
The length of the floor beam between residential floors should not exceed 5 meters, while for floors between the residential floor and the attic this figure can reach 6 meters.
Floor installation

Installation of floor beams is usually carried out in the following order:
- Before laying the finished beam in a wall niche, its ends are wrapped in two layers of roofing material, and the length of the waterproofing layer is chosen with a margin (but not less than 25 cm). After this, it is inserted into the wall and laid there so that the inner edge of the roofing material protrudes outward by 2-3 cm.
- Immediately after installing the beam in the groove intended for it, it is secured in place using a special anchor bolt.
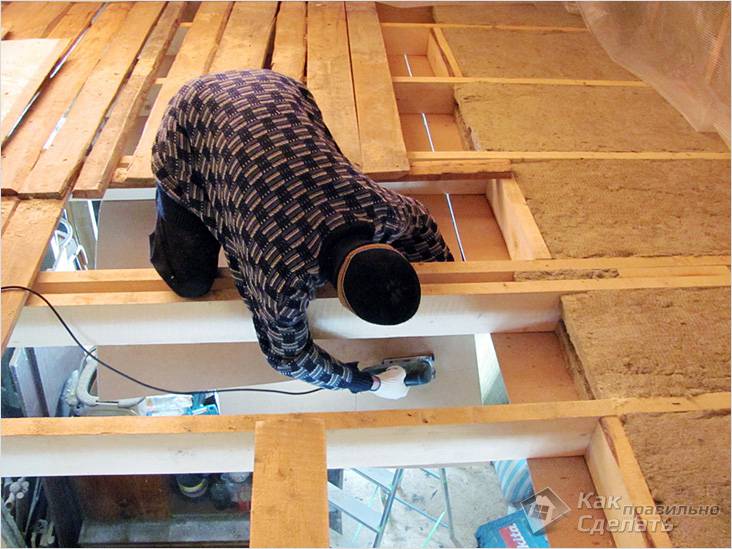

- Next, we move on to the thermal insulation of the floor, for which you can choose ordinary mineral wool or a similar natural material (sawdust, seaweed, etc.). It is not recommended to use polystyrene foam for these purposes, since this material does not allow air to pass through well. Ordinary expanded clay can also be used for insulation, but it is necessary to take into account the fact that the latter puts an increased load on all elements of the structure being built.
- The insulation is laid (backfilled) immediately after you have covered the beams from the bottom finishing material the type you have chosen. On top there is usually a flooring made of planed tongue-and-groove boards, which also serves as the floor for the upper floor.
- After you have filled the voids with insulation, you will need to worry about waterproofing the floor itself. To do this, you will need a waterproofing film, which will need to be laid and secured over the insulation.
![]()
- After covering this entire structure with a finished floor, your floor will be completely ready.
Video
From the following video you will learn how professionals lay floors and calculate the number and sizes of beams for interfloor floors:
Comments:
- Types of floor beams
- Advantages of wooden floor beams
- Selection of timber section
- Installation of floor beams
- Manufacturing of prefabricated beams
IN low-rise construction where the spans between load-bearing walls are small, installing floor beams is a rational solution. There is no point in installing a heavy reinforced concrete prefabricated or monolithic ceiling. Reconstruction or repair of a building often involves replacing floors. Here you also cannot do without beams. But what kind of structures should be installed in order to build a safe ceiling and not spend extra money? Let's look at everything in order.
Scheme of embedding the ceiling into the outer wall: 1 – wall, 2 – lining, 3 – end of the beam to be embedded, 4 – floor slab.
Types of floor beams
- Reinforced concrete.
- Metal.
- Wooden.
Reinforced concrete beams span large spans, but they are installed only with the use of heavy lifting equipment. Metal structures have virtually no restrictions on the span width, but their disadvantage is susceptibility to corrosion and high thermal and sound conductivity. Wooden beams ceilings are free of these disadvantages, which is why they are widely used.
Return to contents
Advantages of wooden floor beams
- Light weight structures. It can easily be supported by walls and foundations, and during installation you can do without lifting mechanisms.
- Easy to install. The work is feasible for people without high construction qualifications.
- High thermal insulation properties.
- Good reliability, strength and durability.
- Lower cost compared to structures made from other materials.
To make beams, you can use both coniferous and deciduous wood. But special attention should be paid to the quality of the wood:
Return to contents
Selection of timber section
Beams are used with rectangular or square cross-section. For a rectangular beam, the wide side should be vertical. This increases the rigidity of the structure and reduces the deflection of the floor. The most common sections: 100x100 mm, 100x250 mm, 150x150 mm, 150x250 mm.
Based on the design calculations, other sections can be used. To select the correct beam cross-section, you need to calculate the load per linear meter of it. It will consist of the weight of the beam itself, structural elements of the floor, furniture and items on the upper floor, as well as the weight of people. Loads must be rounded up, creating a certain margin of structural strength.
| Loads, kg/linear m | Section of beams with span length, m | ||||||
| 3,0 | 3,5 | 4,0 | 4,5 | 5,0 | 5,5 | 6,0 | |
| 150 | 5x14 | 5×16 | 6×18 | 8×18 | 8×20 | 10×20 | 10×22 |
| 200 | 5×16 | 5x18 | 7×18 | 7×20 | 10×20 | 12×22 | 14×22 |
| 250 | 6×16 | 6×18 | 7×20 | 10×20 | 12×20 | 14×22 | 16×22 |
| 350 | 7×16 | 7×18 | 8×20 | 10×22 | 12×22 | 16×22 | 20×00 |
Return to contents
Installation of floor beams
Wooden products are used for spans of up to 5 m for interfloor slabs and up to 6 m for attic slabs. The ends should rest only on load-bearing walls. The pitch of the beams is taken within the range of 0.6 - 1 m. In a rectangular room, the structures are laid parallel to the short wall, if the long walls are load-bearing.
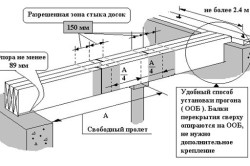
The installation of the floor begins by installing 2 beams at opposite walls. They are placed at a distance of more than 5 cm from the edge of the wall. The placement of products in the same horizontal plane is checked using a water level. The lighthouse cord is pulled between the outer beams and, guided by it, the remaining products are laid at an even distance from each other, but not more than the calculated one.
To adjust the height of the beams, you can trim its end if you need to lower it down, or put a solid piece of wood if you need to lift it up. You cannot place wood chips, because when the wood dries, they can move and fall out. To prevent the structures from moving, they can be temporarily fixed before installing the flooring. The space between the ends on the wall is filled with bricks or blocks.
The end of the interfloor beam should not reach the outer edge of the wall 20-30 cm.
This will allow you to place the product in a dry area without passing the “dew point”, where condensation forms, which has a detrimental effect on the wood. For protection, the ends of the beams are covered with roofing felt or treated with a special protective solution. But in case of installing beams attic floor their ends can extend beyond the outer walls and serve as the base of the roof eaves.
During construction wooden house made of beams, floor beams can be attached to walls using special thrust brackets without violating the integrity of the wall. If a stove or fireplace heating pipe passes through the ceiling, then for fire safety purposes the distance from the pipe to the beam must be at least 40 cm.
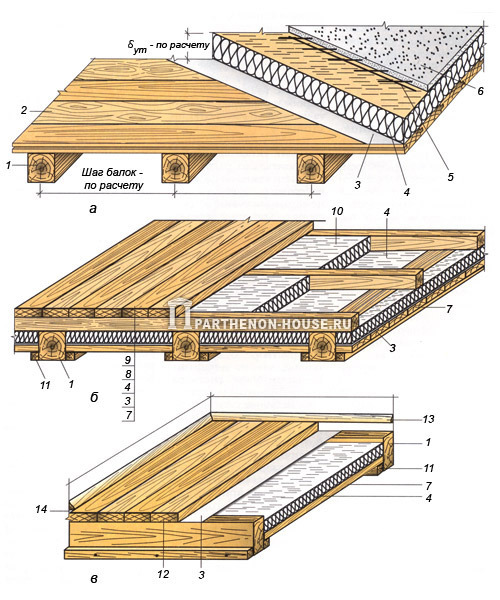
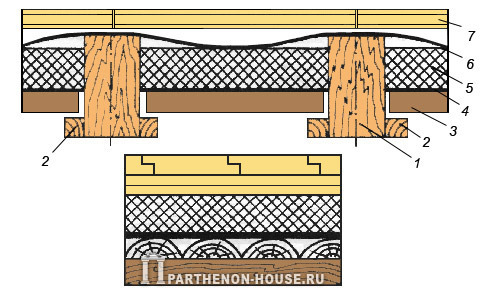
Rice. 1. Types of wooden floors: A - attic floor with insulation along the top skin; b - cross attic insulation; V - above-basement ceiling with inter-beam insulation; 1 - floor beams; 2 - plank cladding; 3 - vapor barrier; 4 - first layer of insulation; 5 - reinforcing mesh; 6 - vapor-permeable screed; 7 - wooden (plank) ramp; 8 - cross frame; 9 - plank cladding (as an option - vapor-permeable reinforced screed); 10 - second layer of insulation; eleven - cranial block; 12 - wooden floor; 13 - plinth; 14 - air exchange slot.
Beams
most often represent wooden beams rectangular section. For roll-ups it is advisable to use wooden boards. To save wood boardwalks can be replaced coasting from ribbed or hollow gypsum or lightweight concrete blocks. Such elements are somewhat heavier wooden rolls, but they are non-flammable and do not rot.
To ensure better sound insulation from airborne sound transfer along the roll, a clay-sand lubricant 20-30 mm thick is made, on top of which slag or dry calcined sand 6-8 cm thick is poured. A backfill made of porous material absorbs part of the sound waves.
IN wooden floor structure includes flooring made of planed tongue-and-groove boards, nailed to the joists, plates or boards, which are laid across the beams at intervals of 500-700 mm.
Wooden floor beams
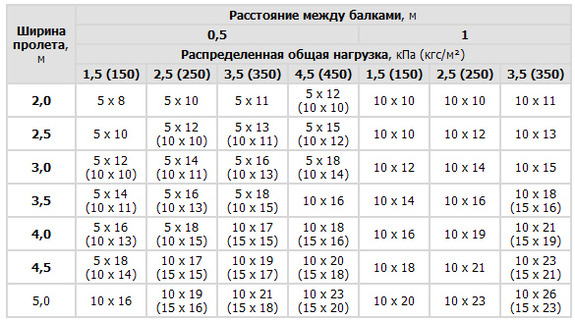
Load-bearing elements beam floors are wooden beams rectangular section with a height of 140-240 mm and a thickness of 50-160 mm, laid at intervals of 0.6; 0.8; 1m. Section of wooden floor beams depends on the load, filing ( roll forward) with backfill, and a plank floor laid over the joists as directly over the joists (Table 1.).
Table 1. Minimum cross-section of rectangular wooden floor beams
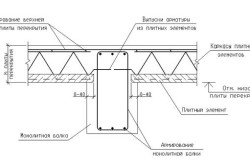
Using hardwood as floor beams not permissible, since they do not bend well. Therefore, as a material for manufacturing wooden floor beams They use coniferous wood, cleared of bark and antiseptic without fail. Most often, the ends of the beams are inserted into nests specially left for this purpose in brick walls directly during the masonry process (Fig. 2 a. or Fig. 2 b.), or are cut into the upper crown of log, block and frame-panel walls.
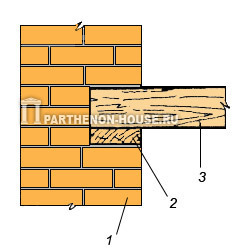
Rice. 2. a. Sealing wooden floor beams into the outer wall: 1 - wall, 2 - lining, 3 - end of the beam to be sealed.
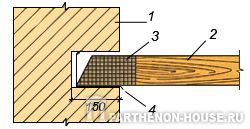
Rice. 2. b. Sealing wooden floor beam into a brick wall: 1 - brick wall, 2 - wooden beam, 3 - end of the beam treated with antiseptic paste or wrapped in roofing felt, 4 - waterproofing from two layers of roofing felt.
The length of the supporting ends of the beam must be at least 15 cm. Laying beams leads in a “beacon” way - first the outer beams are installed, and then the intermediate ones. The correct position of the outer beams is checked with a level or spirit level, and the intermediate beams with a lath and a template. The beams are leveled by placing tarred scraps of boards of different thicknesses under their ends. It is not recommended to place wood chips or trim the ends of beams.
Wooden floor beams are laid as a rule, along a short section of the span, parallel to each other as much as possible and with the same distance between them. The ends of the beams resting on the outer walls are cut obliquely at an angle of 60 degrees, antiseptic, burned or wrapped in two layers of roofing felt or roofing felt. At sealing wooden beams In the nests of brick walls, we recommend treating the ends of the beams with bitumen and drying them to reduce the likelihood of rotting from moisture. The ends of the beams must be left open. Spatial niches at sealing wooden floor beams fill around the beam with effective insulation (mineral wool, polystyrene foam). When the thickness of brick walls is up to 2 bricks, the gaps between the ends of the beams and the brick wall are filled cement mortar. You can also, as an option, insulate the ends of the beams with wooden boxes, having previously tarred them. In thick walls (2.5 bricks or more), the ends of the beams are not covered, leaving ventilation holes. This protects the ends of the beams from moisture condensation. Moisture diffusion in a wooden beam shown in Fig. 3.
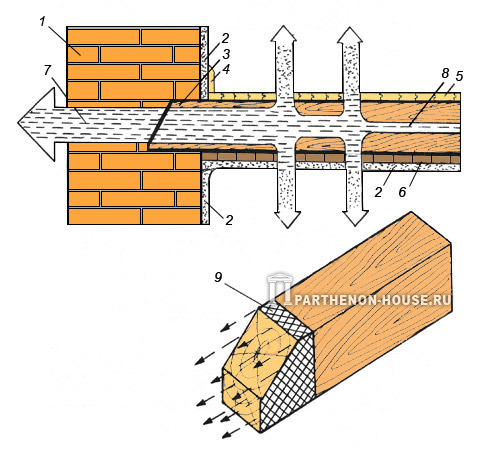
Rice. 3. Diffusion of water vapor in a wooden beam: 1 - brick wall; 2 - layer of plaster; 3 - air gap between the end wooden beam and brick; 4 - plinth; 5 - floor made of tongue and groove boards; 6 - wooden boards; 7 - water vapor; 8 - liquid moisture; 9 - roofing felt or roofing felt
When supporting beams on internal walls, two layers of roofing felt or roofing felt are placed under their ends.
Every third beam embedded in the outer wall is secured with an anchor. Anchors are attached to the beams from the sides or bottom and embedded in brickwork.
If there is no timber of a suitable cross-section, you can use boards knocked together and placed on edge, and the total cross-section, compared to the whole beam, should not decrease.
Moreover, instead of paving beams you can use logs of the appropriate diameter, hewn on three sides, which is more economical (round timber is much cheaper than lumber), but in this case the logs must be kept in a dry room for at least one year, like log house.
To enhance load-bearing capacity of the floor can be used cross diagram of installation of power beams. When using this scheme, the ceiling rests on all the walls of the building along the contour. The intersection nodes of the beams are tightened with clamps or twisted wires. Cross floor scheme used extremely rarely, since it is much easier to reduce the pitch load-bearing beams and make an ordinary overlap, but on making cross slabs is spent smaller quantity lumber than traditional, with the same load-bearing capacity of floors.
Structural differences in floors are observed when they are insulated (Fig. 1.). Interfloor overlap are not insulated, the attic (with a cold attic) is insulated with the installation of a lower vapor barrier layer, and the basement is insulated with the installation of an upper vapor barrier layer.
Roll up
The next step in the construction of floors is reel flooring. To attach it to the beams, nail cranial bars with a cross section of 5 x 5 cm, directly on which they are laid reel boards. (Figure 4.)
Rice. 4. Rolling on cranial bars with insulation: 1 - beams; 2 - cranial bars; 3 - subfloor; 4 - glassine; 5 - insulation; 6 - glassine; 7 - floor boards
Plates roll forward fit tightly to each other, removing all the gaps between the individual boards. Strive to bottom surface roll forward was in the same plane as floor beams. For this it is necessary to boards select a quarter (rebate). For run-on structures It is not necessary to use full-fledged boards; they can be replaced with a slab. A lining of boards 20-25 mm thick is secured with nails driven in at an angle. As we have already noted instead boards for rolling You can use fiberboard, gypsum slag and other lightweight concrete slabs, which increases the fire resistance of the floors. Stacked roll forward cover with a layer of roofing felt or roofing felt and fill or lay insulation: as in the walls, here you can use mineral wool, sawdust, slag. When insulating floors, loose insulation materials are not compacted, but are backfilled on? beam heights. The type of insulation and its thickness are determined from the calculated outside air temperature, using the data in Table 2.
Table 2. The thickness of the attic floor filling depending on the outside temperature
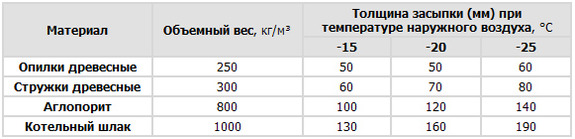
Lastly, the upper edge of the beams is covered with roofing felt or roofing felt, and a lags. notice, that lags are not mandatory floor element. Laying lags economically justified if the beams have a rare location.
We also draw your attention to what floor elements will turn out to be superfluous during construction basement And attic floors:
- V basement floor no filing
- V attic floor no logs and clean floor
Basement ceiling can be designed in such a way that the beading and insulation will be superfluous (of course, without compromising performance), however, in this case, roofing felt padding will be required over the entire floor area, and the backfill will be gravel or compacted crushed stone (Fig. 5.)
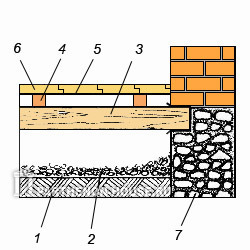
Fig 5. Option basement floor devices: 1 - compacted soil; 2 - gravel; 3 - beam; 4 - lag; 5 - roofing felt; 6 - clean floor; 7 - foundation-base
It is impossible to build a house without connecting elements - floors. They are the ones supporting base each floor of the building. Even if the building is one-story, the ceilings serve as the ceiling and floor. The entire weight load falls on the floors.
Things that are in the premises, people - all this load must be successfully carried. It should also be taken into account that with each additional floor the weight load on the underlying areas increases. This is why the correct calculation of floor beams is so important.
What are floor beams
Traditionally, wooden and reinforced concrete floors. They represent a dividing plane between the floors of the building. Each of them is installed along the main load-bearing elements - floor beams. Their strength is very important. In addition to the load that the floor itself can withstand, the beams also take on the weight of the structure separating the floors itself.
Rules for laying floor beams
If a brick building is being erected, then to install it interfloor ceilings Special holes are left in the walls, which are prudently left during the laying of the walls. If the house is built of wood, then the holes into which the beams will subsequently be laid are simply cut down in the right places. The beams must be laid in such a way that the supporting length of the ends extends into the openings by at least 15 cm.
The horizontal positioning is checked with a level or spirit level. To maintain the exact distance between the beams being arranged, you can use a piece of lath required length. It will serve as an indicator of the distance through which the next beam should be installed. These supporting elements should be fastened every two beams. They are made using anchors.
To align the beams horizontally in the openings in which they are laid, you can place wooden dies under their ends. We should not forget about insulation when carrying out this work. All free space, which remains in the openings after the beam is installed in it. should be filled with insulation. Typically glass wool is used for these purposes.
It is also important to do waterproofing. Therefore, pieces of roofing felt in two layers or dense polyethylene are laid in each opening. Beams can be positioned in both parallel and cross directions. But the latter is quite difficult to install and is rarely used in practice.

Calculation of floor beams
The basis for calculating the cross-section of the beam, which will serve support beam, the following rule is laid down: the cross-section of the support must be at least 1/25 of its length. For example, if the length of the beam is 6 meters, then its thickness should be at least 25 cm. The shape of the room over which the ceiling is erected is often rectangular.
It is more expedient to lay the beams in such a way that their length is as short as possible. That is, the support for their ends should be the openings in the most long walls this room. For example, if its dimensions are 3/6 meters, then the beams should be installed three meters long. But this is a conditional figure, since it only indicates the width of the span.
The beam itself should be 50-60 cm larger for the reason that it should rest on the walls at both ends by at least 25 cm. Next, in order to correctly calculate the floor beams, the weight load should be taken into account. For residential buildings its average value is 400 kg/m2
For an attic floor this value can be half as much. Next, the distance between the beams is included in the calculation. It can be 1 meter, 75 cm or something else. The optimal span width for wooden beams is 2.5-4 meters. The best beam shape is rectangular, with a beam height to width ratio of 1.4:1.
Next, the maximum bending moment is calculated using a special formula. If the distance between the beams is 1 meter, then it will be 80000 kg/cm. There are special tables that show average indicators for certain types of wood, take into account the percentage of wood moisture content, its service life coefficient and many other indicators.
All this can be found on specialized websites or in the literature on house construction. In the event that the joists will first rest on the floor beams, and then the boards, then the cross-section of the joists should also be calculated.
Installation of wooden floor beams is used in the construction of low-rise structures made of wood or brick. This is due to the fact that they are highly durable, easy to process and install, and are also environmentally friendly.
Types of wooden floors
There are several types of wooden floors according to their main purpose:
- Basement. Designed for laying floors on the ground floor and dividing a non-residential basement from living rooms. Therefore, the main requirement that is placed on them is to ensure high-quality heat and sound insulation.
- Interfloor. Used to separate living spaces between floors in cottages and townhouses. Therefore, the requirements for thermal insulation are minimal, but for sound insulation, on the contrary, they are increased, since sound waves inside the building can propagate not only through the air, but also through solid material.
- Attics. They perform almost the same functions as the basement ones. However, due to the location of a cold room above a warm one, additional attention must be paid to installing a vapor barrier to avoid the formation of condensation in the ceilings.
Beam selection
The selection of floor beams is based on their main purpose and maximum expected loads. The most common are beams made of wooden beam rectangular section with a height from 120 to 240 mm and a thickness from 50 to 160 mm. The distance between them when laying is usually from half a meter to a meter. When insulating the space between beams, the contact of materials is ensured most tightly without additional actions, unlike logs.
Figure 1. Installation of attic-type plank flooring.
Log floors are most advantageous in terms of withstanding perpendicular loads and lateral shifts. If you have the opportunity to harvest wood yourself, then processing it will require a minimum of effort. The main issue is the natural drying process to prevent cracking or warping within one year. Suitable for installation are beams that have ideal geometry and are free of knots and areas of pest damage.
IN frame houses It is allowed to make floors from boards with a thickness of at least 25 mm. This is due to the fact that more massive beams can cause increased loads on the base and walls. Also, boards are used to minimize the cost of construction, but not at the expense of reducing the strength of the building below the permissible level.
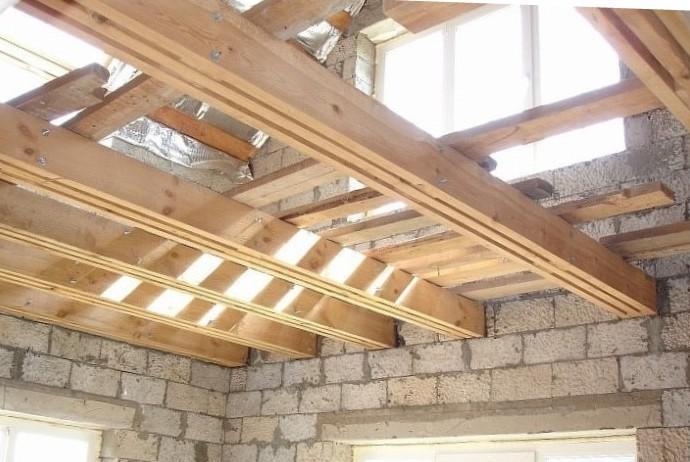 Figure 2. Splicing floor boards.
Figure 2. Splicing floor boards. The choice of hardwood beams is highly discouraged, as they are not always able to withstand bending loads. Experts recommend conifers that are well cleaned and treated with antiseptics.
Calculation of wooden floors
Installation of wooden floors is carried out with beams with an aspect ratio of 7:5. Dimensions are selected depending on their length and expected loads. Minimum permissible deflection should be up to 1/300 over the entire length. Sometimes, in order to reduce deflection, it is allowed to use a construction lift when installing a curved beam or merging two beams at a certain angle. The thickness is selected so that it is more than 1/24 of the length. In this case, it is possible to splice boards of the same type of wood to the calculated cross-sectional dimensions with fastening with self-tapping screws every 20 cm and their arrangement in a checkerboard pattern.
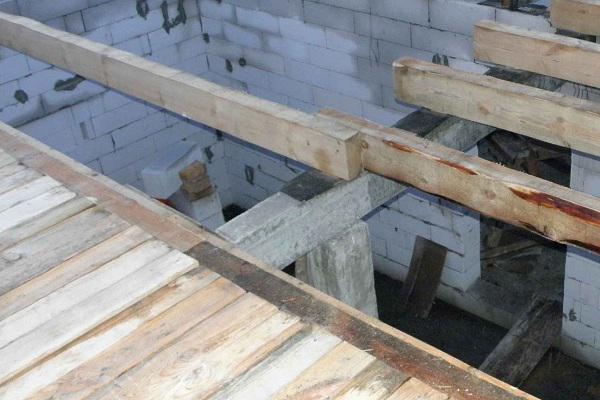 Figure 3. Installation of wooden beams on a concrete partition.
Figure 3. Installation of wooden beams on a concrete partition. The length of the beams should be more distance between the walls by at least 30 cm, so that on each side it enters the wall 15 cm. Data for selecting beam parameters are given in Table 1.
Table 1. Load distribution between beams depending on the distance between them and the width of the spans.
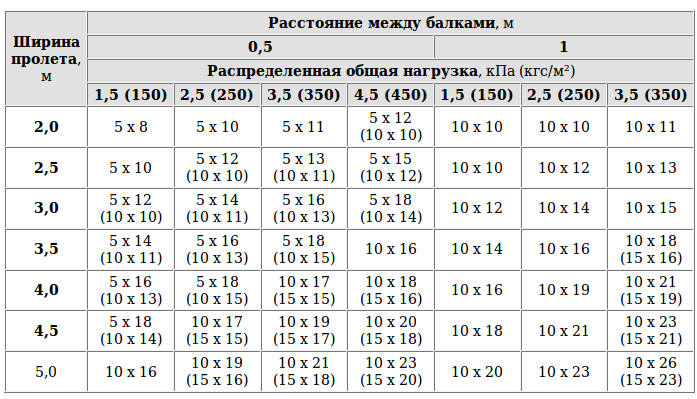
Installation of floors
Installation of floor beams is carried out according to marked beacons to maintain parallelism and spacing. At the initial stage, the installation of the outer beams is carried out. To do this, they are cut to the required length with bevels at the ends at an angle of 60º, thoroughly treated with an antiseptic, and then wrapped in roofing felt with an overlap of 15 cm in length and subjected to thermal heating. This treatment allows you to preserve the integrity of the wood for as long as possible and prevent its damage, especially when in contact with non-natural materials or metal. In some cases, it is allowed to process only the ends that will go into the wall to maintain the aesthetics and decorativeness of the ceilings.
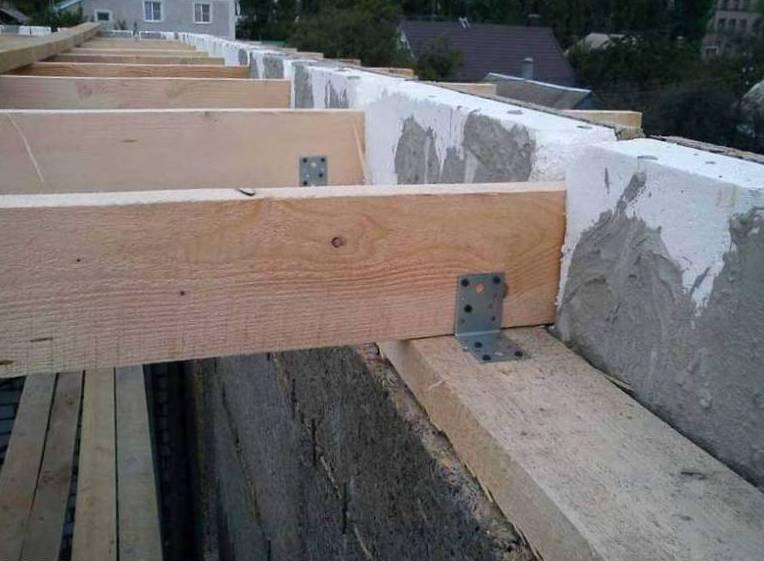 Figure 4. Installation of the attic floor on the trim.
Figure 4. Installation of the attic floor on the trim. The correct position of the beams is determined using a plumb line and level. In this case, it is highly not recommended to allow distortions, since the load will be distributed unevenly and the estimated service life will be reduced.
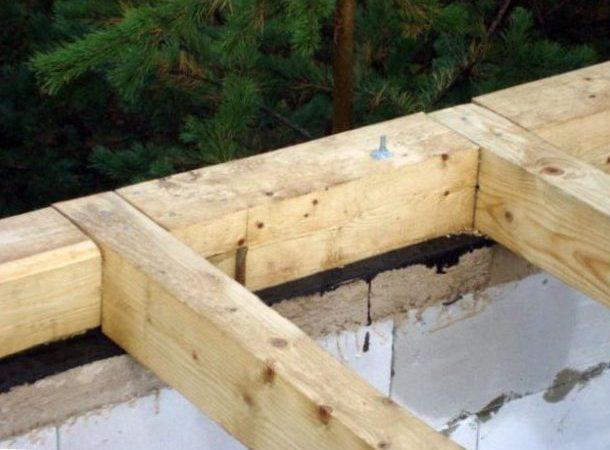 Figure 5. Method of installing floor beams with insufficient wall thickness.
Figure 5. Method of installing floor beams with insufficient wall thickness. The intermediate beams are installed according to a specially made template, and the position is controlled using a long rail. If necessary, cut boards are installed under them to ensure alignment and reliable fixation. It is prohibited to shorten beams to fit the dimensions of the holes in the wall, as well as to cut off the ends or place wood chips. The end parts of the beams are always left open. If the wall thickness is not enough, then the ends of the beams are sealed with cement mortar.
The installation of flooring on wooden beams depends on its type and the need to install insulating layers. To install hydro-, steam- and thermal insulation, it is necessary to cover the beams with chipboard slabs 10-15 mm thick. In this case, they must be positioned relative to the load-bearing parts of the floor so that the joining seams fall on the beams. Then a layer of vapor barrier is laid in the formed niches with an overlap of 15 cm and sizing with tape. Thermal insulation is laid on top of it, which is usually mineral or stone wool. The installation should be as tight as possible without minimal gaps. A waterproofing layer is laid on top and covered with boards with a thickness of at least 25-30 mm.
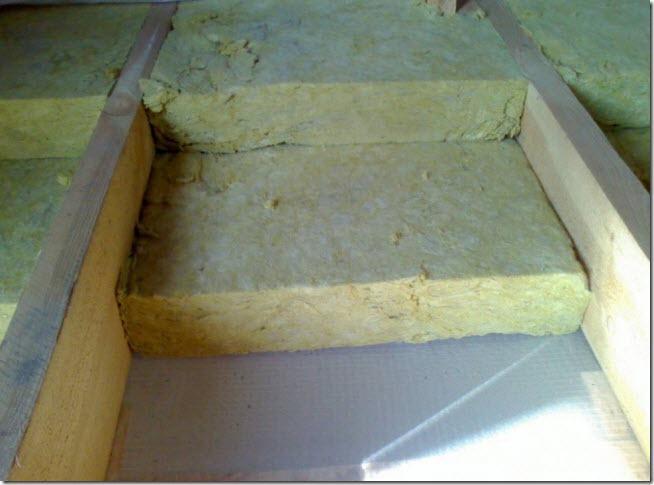 Figure 6. Laying thermal insulation.
Figure 6. Laying thermal insulation. The number of layers is determined by the purpose of the overlap, and in each specific case the installation of one or another layer can be abandoned. But excessive savings in case of non-compliance with operating rules, you need to be prepared for damage to the wood and the need to repair the floors.
 Figure 7. Floor sheathing.
Figure 7. Floor sheathing. Conclusion
Laying wooden floor beams is one of the main stages in the construction of frame and brick low-rise buildings. Therefore, it is necessary to take a responsible approach to the calculations of the required load-bearing capacity and the selection of building materials. The service life of the building largely depends on compliance with installation technology.









