In the process of designing and building a residential building, the question of the configuration and structure of the roof necessarily arises. Not only the set of materials for its installation depends on the design of the roof, but also the design of the load-bearing walls on which the roof rests. Therefore, the calculation of the roof structure is one of the most important when designing a house. Rafter structures that support roofs together with sheathing serve as the main subject of calculation.
It can be noted that historically the structure of roof rafters was wooden; all the terminology of modern structures was borrowed from that time. Currently, in addition to wooden ones, metal and reinforced concrete rafters are used, which are used to a greater extent in the construction of industrial buildings. In housing low-rise construction Lumber remains the main material.
But they also have the disadvantage of weakening structural elements as a result of their drilling. IN Lately The American technology of connecting elements of rafter structures using shaped fasteners and self-tapping screws has become famous, the choice of which in stores offering building materials has expanded significantly.
Typically, when constructing a residential building, rafter systems are assembled on site. In this case, despite the apparent ease of working with wood, carrying out this work is fraught with many difficulties. Therefore, it is advisable to involve a team of experienced roofers with extensive experience in this work in the assembly and installation of rafter structures.
Reinforced concrete structures in residential construction were not widely used due to their large weight, complexity of installation due to the need to use lifting equipment and the inability to use individual construction solutions.
The emergence of new construction technologies has also led to changes in the approach to the manufacture of rafter structures. Recently, the technology of installing rafters from light steel thin-walled structures (LSTC) has become widespread, thanks to which costs and installation time are significantly reduced. This technology is applicable for almost all types of construction of buildings for any purpose.
Advantages of rafter systems
The load-bearing elements in this case are structures made of Z and C-shaped galvanized steel beams with perforated slots, which make it possible to reduce the thermal conductivity of the element by almost half. The rafter structure is manufactured according to the developed project in the factory and delivered to the consumer. The advantages of such structures include the following qualities:
- light weight of the structure, which allows the use of load-bearing walls in the building structure with a lower design load and less material consumption;
- reduced construction time;
- manufacturing accuracy and, accordingly, geometric dimensions truss structure;
- Possibility of installation in winter conditions;
- absence of waste and the need for its disposal;
- reliability and durability of structures made from light steel frames;
- environmental friendliness of the material;
- low operating costs for maintaining rafter structures;
- effective heat saving due to the use of modern thermal and waterproofing materials in the rafter structure.
The roof, and especially its frame, is largely determined by how appearance the house itself, as well as its lifespan, and the state of the atmosphere interior spaces. No one will be satisfied with looking at the roof of a house that has sagged as a result of incorrect calculation of loads or the walls covered with fungus due to constant leaks.
Therefore, regardless of the material of the truss structure, wooden or metal, the design of load-bearing structures requires a careful approach in their design and no less careful in installation.
The roof is the most important part of the house. It determines both its external (architectural) appearance and performance qualities. Various types of rafter systems make it possible to implement almost any roof design option that most fully satisfies the developer’s requirements.
Requirements for the rafter system
During its service life, the roof is affected by various factors, the most significant of which are:
- snowfall;
- wind;
- seasonal temperature fluctuations.
The most common material for the manufacture of parts and assemblies of rafter structures is wood. When designing, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of damage to the building material by insects and microorganisms during operation. Impregnation of wooden parts with antiseptic solutions and the use of constructive measures to create favorable conditions operation.
Constructive measures include:
- use of vapor barrier from the attic space;
- inadmissibility of direct contact of wooden parts with masonry or massive metal elements;
- providing high-quality waterproofing roofing carpet.
The effect of snow load is compensated at the design stage by selecting the required sections of structural elements. In climatic regions with significant snow cover, it is recommended to reduce the distance between rafter beams and increase the angle of the roof.
An increase in the angle of inclination, in turn, can lead to an increase in roof windage. In areas characterized by strong and prolonged winds, this factor can lead to both local destruction of the roofing carpet and more widespread damage.
Due to seasonal temperature fluctuations, the building materials used for the roof and supporting structure will expand or contract. The degree of thermal deformation is characterized by the coefficient of thermal expansion. Accordingly, different materials will deform to varying degrees under the influence of seasonal temperature fluctuations.
Under unfavorable circumstances, integrity may be compromised roofing or even the appearance of cracks in the load-bearing elements of the rafter structure. The best option is the selection of materials that have approximately the same temperature deformation values.
Elements of the truss structure
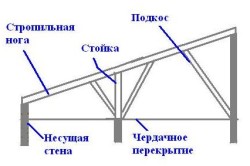
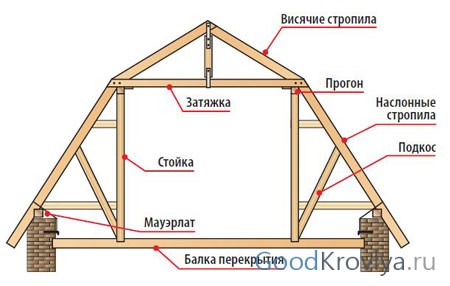
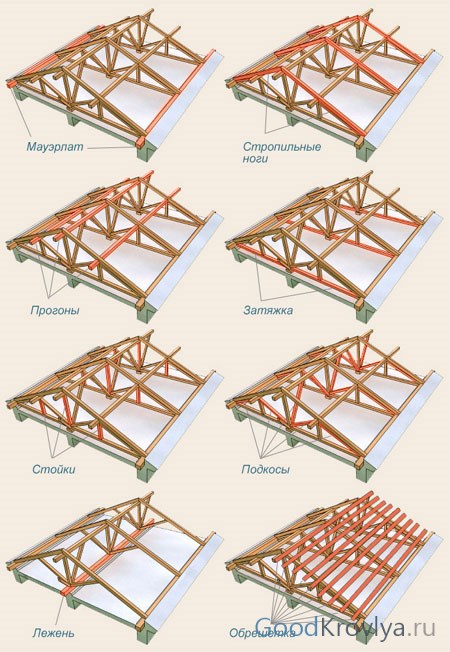
The rafter system supporting the roof consists of several elements:
- rafter beam;
- Mauerlat;
- puff;
- crossbar;
- ridge beam;
- strut;
- rack;
- lie down.
The rafter beam is the main element of the system. The sheathing for the roofing is attached to it. Most often, wooden beams or thick boards are used as rafters.
The Mauerlat is a beam fixed along the upper edge of the wall and serves to secure the lower edge of the rafters and transfer the load to the walls. During construction frame house or a log house, the role of the mauerlat will be played by the upper trim or the upper crown, respectively.
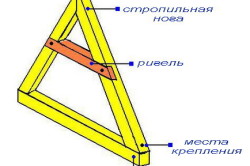
Additionally, to compensate for the thrust load transmitted to the walls, tension beams are used. They can be top-positioned (crossbar) and bottom-positioned (tightening). Very often, the ties simultaneously perform the function of an interfloor ceiling.
When there are significant loads on the roof, to give it additional bearing capacity the upper ends of the rafter legs are additionally reinforced with ridge beams.
The significant size of the span to be covered leads to the need to use additional supports.
Vertical posts are installed under the ridge beam. To strengthen the rafter legs, struts can be used, which are cut into a post or tie at one end, and into the rafter at the other. The strut can be cut at any angle, but the most commonly used angle is 90°.
Beams can be installed perpendicular to the tie rods - beams that serve as support for the vertical posts. In some cases, beds can be used as a base for struts. In practice, when designing and constructing buildings, two main types are used rafter systems
: hanging and layered.
Hanging rafters: features
A roof structure using , is used to cover spans up to 6 m long. With this design, the lower part of the rafters rests only on the external walls, while the upper parts rest on each other.
In the simplest case, such a system consists of two beams connected at the upper ends. In their lower part, the beams rest on the Mauerlat. For such simplicity of design, you have to pay for the large amounts of bursting loads that the rafters will exert on the walls. Loads can be compensated by installing crossbars and tie rods.
To cover spans longer than 6 m, it is necessary to install additional vertical posts and struts supported on the beams. The length of the rafter section between the mauerlat and the strut notch in this case should not exceed 4-4.5 m.
Additional rafter structures will inevitably lead to an increase in the weight of the entire rafter system. With a significant increase in weight, problems may arise related to the load-bearing capacity of the foundation or the structural strength of individual building elements. As a result, it will be necessary to use lighter roofing materials than previously assumed. This can be quite difficult.
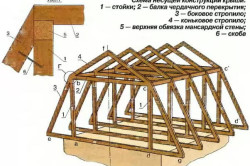
Layered rafters: characteristics
Layered rafter systems differ from hanging ones by the presence of intermediate support points, which can be used as internal main walls or columns. Thus, there are at least three points of support - two external walls and one internal wall or column.
An important point that must be taken into account when designing a layered system is the inverse relationship between the angle of the roof slope and the pitch of the rafter legs. In other words, the steeper the roof, the more often it is necessary to install rafter beams.
Combined rafter system
Covering spans of significant length requires the use of trusses.

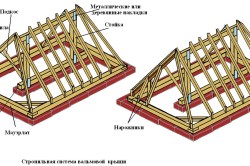
Installation diagram of the rafter system: A – attachment point for the rafters to the mauerlat; fastening fillies; B – general view of correctly executed rafters; B – stretching and bracing; G – correct fastening of the skate; D – fastening to the strut; E – assembled rafters.
Such trusses use characteristic elements of both systems in their design and are a combined rafter system.
Most often, this system is used for the manufacture of so-called mansard-type roofs. The walls of the room on the second floor will be formed by vertical posts, which will also serve as intermediate support points for the rafter beams.
Horizontal beams running along the top of the racks (purlins) will simultaneously serve as a ridge beam for the side slopes of the roof and a mauerlat for the upper slopes.
The part of the truss connecting the upper ends of the racks acts as a crossbar for the side slopes and at the same time serves as a tie for the upper part of the truss.
Additionally, to enhance the strength of the structure, struts can be installed to fasten the vertical posts and rafters of the side slopes of the roof.
A combined truss truss is somewhat more difficult to manufacture than traditional types of truss systems. However, the labor intensity and complexity of manufacturing are more than compensated by the lack of need for additional supports when covering large spans and increasing the load-bearing capacity of the roof.
Although every stage of its creation is important for a good roof, the rafter system can be called the basis of the entire roofing structure, since the type of roof depends precisely on the configuration of the rafter system. Exist different kinds rafter systems, the correct choice of which can significantly affect the quality and functionality of the entire roof.
When choosing the type of roof, the owners of the future home actually choose its rafter system. For example, the design of a gable roof and a hip roof is noticeably different. The principles of installation of such elements as:
- Mauerlat (the base of the roof to which the rafters are attached is made of wooden beam or reinforced concrete);
- sheathing (thin plank flooring on top of which roofing material is laid);
- waterproofing layer (a special film that prevents moisture from precipitation from penetrating under the roof);
- vapor barrier layer (membrane film that absorbs steam condensate generated inside the house and then evaporates it outside);
- thermal insulation layer (insulation that is installed in the space between the rafters).
The type and type of rafters are chosen depending on what kind of roof you plan to build. An improperly designed or manufactured rafter system can lead to damage to the roof soon after its use.
Advice: Before starting roofing work, a project must be drawn up, which takes into account not only the features of the truss structure, but also the type roofing material, strapping, sheathing, insulation, etc. It is best to invite an experienced engineer for this, who can calculate the design weight of the future roof and compare it with the permissible load for the walls and foundation of the building. During the construction process, you cannot change the design without agreeing with a specialist. Increasing the load, for example, replacing roofing material with a heavier one, can lead not only to damage to the roof itself, but also to the collapse of the walls of the house.
The roof configuration and its quality depend on the rafter system
What types of roofs are there: types of structures
An impressive number of roofing structures have been invented over the years of human history. Some are more suitable for industrial buildings, others - for elegant works of architectural art. In private construction, a number of roofing structures are used, which combine qualities such as:
- practicality;
- relatively low costs;
- aesthetic appearance;
- ease of manufacture;
- functional features, suitable for a specific climate zone, etc.
Tip: Since wood is most often used for the manufacture of rafter structures, attention should be paid the right choice, processing, and storage of this material. The humidity of timber and boards should be within 20-25%. Wood is stored in stacks placed on pallets. It is best to store materials indoors, reliably protected from the weather and well ventilated. Before starting work, the wood is treated with antiseptics and fire retardants to increase its resistance to fire, mold, bugs, etc.
![]()
Most common roof types
The most widespread types of roofing structures in private construction are:

In addition, there are no-loft, attic and mansard roofs.

The Sudeikin roof has an unusual configuration and excellent functional characteristics
Hanging and layered rafters - what's the difference
This is what professional roofers call the main types of rafter structures. The hanging rafter system of a house is most often used in the construction of single-span buildings with walls made of brick, stone, etc. At the top point, the hanging rafters rest on each other, and at the bottom - on the upper frame (mauerlat). To prevent the rafter legs from moving apart, their lower ends on opposite slopes are additionally connected with a horizontal tie. Ties can be used as floor beams, however reinforced concrete floor, rigidly connected to the walls, can also act as a tightening. Above the base of the rafters there is sometimes an additional tightening - a crossbar. This is how hanging rafter systems are installed in buildings with a span of less than six meters.
Tip: If the roof slope is steep enough, for example, 40-60 degrees, it is advisable to install an attic. In this case, the project should correlate the installation location of the crossbars and the height of the attic space.
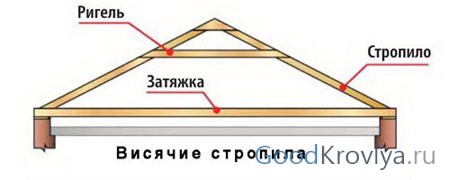
Hanging rafters have a very simple design and rest only on the outer walls
For buildings with a span of more than six meters, hanging rafters are supported with special racks and struts. Install these additional elements for special runs, the basis for which is the ceiling. In this case, the length of the lower part of the rafter legs should not exceed four and a half meters.
Hanging rafter systems are ideal for spanning large spans without installing intermediate supports. However, elements that compensate for the load that falls on the rafters significantly increase the weight of the rafter system itself, which can limit the choice of roofing materials.
Suspended rafters are suitable for almost all types of roofing structures; they are used for span lengths in the range of 10-16 meters, for roofs with a slope of 20-60 degrees, regardless of the wall material. For large spans, intermediate supports (internal load-bearing walls, columns, etc.) are required.
The upper part of the layered rafters rests on a ridge beam, which is supported by special supports. The lower parts of the rafter legs rest against the upper frame. As a result, the main load is transferred vertically, which lightens the weight on the walls and eliminates the need to install horizontal tie-downs.
Tip: For buildings with a significant span, instead of a ridge beam, it is sometimes advisable to use two side purlins, additionally reinforced with struts and crossbars, to reduce possible bending of the rafter legs.
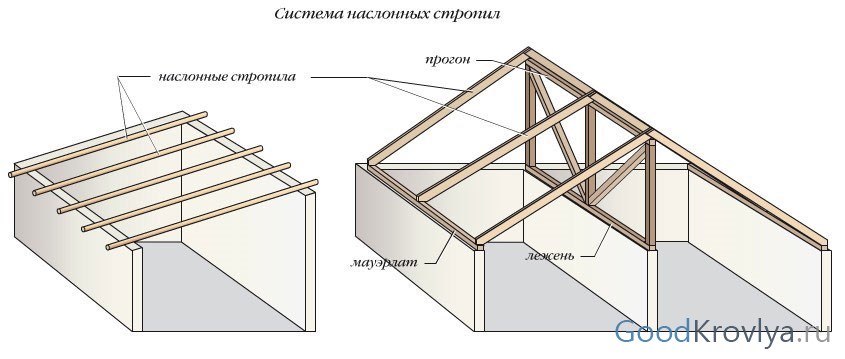
Layered rafters are mounted with support on intermediate elements
Layered rafters are widely used to create attic roofs various types. The optimal height of the attic wall should be approximately a meter and a half. To construct a roof with a broken slope, layered rafters are also used. This type of rafters is considered universal, they are easy to manufacture and do not require high labor costs, however, a prerequisite for their installation is the presence of additional supports.
Video manual on splicing and strengthening rafters
If the span is more than 16 meters, it may be advisable to use roof trusses. Each truss is an independent flat structure, which includes rafter legs, crossbars, tie rods, braces, racks, etc. The rafter truss is carefully calculated in advance. As a result, all elements of the rafter system are located within the upper and lower chords of the truss. This design does not require additional support on columns or internal load-bearing walls. Pressure on the outer walls of the farm is exerted only vertically.
With the help of roof trusses, you can create a roof of any suitable configuration and with any permissible slope. Rafter trusses can be manufactured directly on the construction site or ordered ready-made structures at the factory. They are lifted onto the roof and then installed at a given distance.
The design of a roof truss intended for mansard roof, will be somewhat more difficult than for the attic option. If the span is very large, it is advisable to assemble roof trusses from several components.
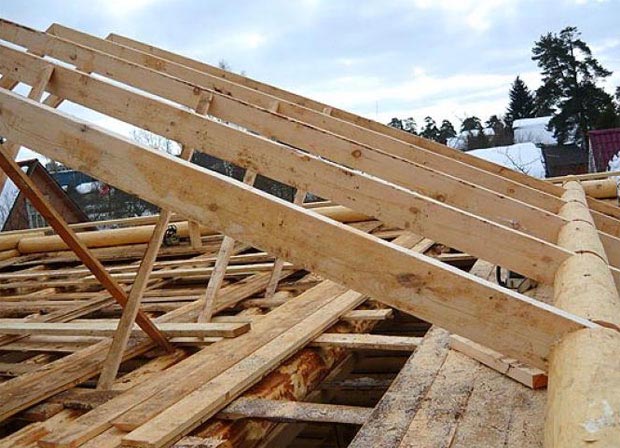
Despite the complexity of the design, roof trusses allow you to speed up roof installation
In addition to amazing versatility and no requirement for additional supports, the use of roof trusses significantly increases installation time and has a positive effect on its quality. At the same time, accurate design calculations make it possible to reduce wood costs by almost a third compared to handicraft manufacturing of rafters. Another advantage of using prefabricated trusses is that they provide greater freedom in the layout of large spaces. However, it should be noted that accurate calculations and design of these elements will require some additional costs.

The reliability and proper functioning of the entire roof, and ultimately the comfort of all residents of the house, depend on the correct manufacturing of the truss structure. You cannot do without professional help in this difficult matter.
For roof construction today the most different variants rafter systems. But, despite all the variety of their types, each is based on the same requirements that must be met in order for the roof to be durable. When creating a roof yourself, it doesn’t hurt to know the design features of the most popular systems.
General information about rafter systems
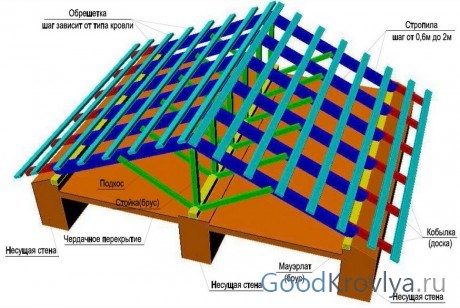
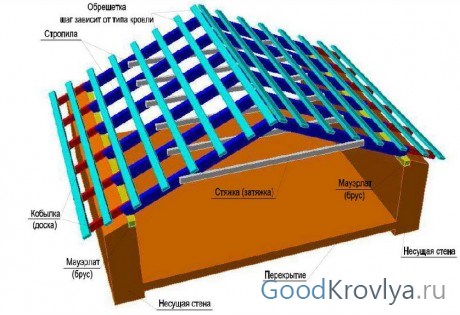
The rafter system is a roof frame that rests on the supporting structures of the building and serves as the basis for insulation, waterproofing and roofing materials.
The type of construction and dimensions of rafter systems depend on:
- building size;
- roof truss material;
- roofing material (mainly from its specific gravity);
- roof loads in the form of snow and wind, characteristic of the region;
- preferences regarding the shape of the roof.
Each of these factors is important in deciding which types of rafter system are best suited for a particular situation.
Materials for rafter systems
The most common material for creating rafter systems is wood. Typically, timber 150 by 150 millimeters or boards 50 by 150 millimeters are used. But if it is necessary to strengthen the structure, thicker timber is used, and the boards are connected to each other. Of course, all this applies only to private houses; other technologies are used in the construction of high-rise buildings and industrial buildings.
Rafters 150x150 are made of timber, usually pine. It is best to use aged timber, which does not change its shape after the roof is created, and then the structure will be more stable.
Rafters 50x150 are also used - they are made from boards. are used only for creating roofs of private buildings, in the case of multi-storey buildings And industrial buildings use metal elements.
Rafters 50-150 have to be stitched to give them the required strength.
Before installation, wooden rafters must be treated with antibacterial and fire-fighting agents. Antibacterial impregnation prevents rotting if the elements are in a humid environment (for example, under the influence of roof condensation inside). Fire-prevention treatment reduces the flammability of wood.

There are currently no difficulties with processing rafters. There is a large selection of antipyretics and antiseptics on the market. You can also use preparations for comprehensive wood protection. It is better to treat wood with a brush - spraying the product does not allow achieving a good degree of impregnation. Regardless of what types of rafters will be used, they can be reinforced with additional metal elements.
Racks made of metal profiles are most often installed under ridge girders to create support - they are the ones most subject to loads. However, steel rafters require more serious roof insulation, since metal conducts cold well.
Regardless of the material from which the rafters are made, the system is assembled in such a way that its structure is sufficiently rigid. For this reason, most species have a triangular shape - this is exactly what geometric figure allows you to create the greatest rigidity.
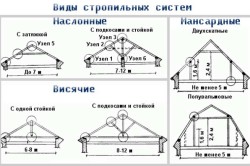
Rafter systems can be layered (sloping) or hanging.
Hanging rafter system
Extension rafters (hanging) have only two points of support for each pair of rafter legs. Such support points are usually the load-bearing walls of the house. In this case, the rafter legs work both for bending and compression. They should not rest directly on the walls, but on the mauerlat - this is a thick supporting beam made of wood or a structure made of boards fastened together, firmly attached to the end of the load-bearing walls.

The rafter legs are attached to the mauerlat using a notch. The rafter is also fixed additionally - with a bracket or bracket. The design of the system provides a bursting force that is transmitted to the wall fence. The most common way to compensate for expansion is to create a tie connecting each pair of rafters at the bottom. Usually the tie is placed at the very bottom, in this case it also serves as a ceiling. If the tightening is located higher, it must be more powerful, since the load on it increases significantly. In addition to the fact that this element compensates for the bursting force, it also does not allow the rafter legs to move apart.
The process of attaching rafters on a pitched roof:
Layered rafter system
Sloping rafters (sloping) require the presence of a middle load-bearing wall in the building.
Layered rafters have the following characteristic features:
- The walls of buildings serve as support for layered rafters, and their middle part is supported by internal columnar supports or a middle load-bearing wall.
- The elements of the layered system can work exclusively in bending; they are not subjected to compressive loads. Thanks to this, thinner parts can be used for rafters of this type, and the system is lightweight. Thus, the layered system allows you to save a lot on lumber.
- If the building has a complex structure, you can alternate types of rafter systems when creating the roof. Where there is no support, they install, and where there is a support or a middle load-bearing wall, inclined ones are installed.
Hip rafter system
A hipped hip roof requires the creation of a special rafter system. Due to the complex geometry of such a roof, the rafters must serve different purposes, so they come in the following types.
Diagonal rafters (sloping) form the ribs of the roof, connecting the corners of the building with the ends of the ridge beam. Sloping rafters are the longest and must have great strength, since they are subject to the main load.

The central (ordinary) rafters connect the mauerlat with the ridge beam on the sides of the slopes. Such rafters are installed in parallel.
Low-rise construction is very often started by people who previously had nothing to do with the construction of houses. To make a building high-quality and durable, you have to pay attention to every detail. When the foundation and walls are finished, it’s time for the roof, which cannot exist without a special supporting structure- rafter system. Here it is important to understand which elements should be applied, how to choose construction material– wooden or metal rafters, and how to correctly install them. However, to understand this issue, it is worth starting with the basics.
The rafter system is load-bearing structure, on which the roof is being installed. The task of the rafters is to withstand and redistribute the weight of all loads to which the roof is exposed: snow cover, strong winds, rain and other natural anomalies.
Each element of the rafter system has its own function, and this factor should be taken into account when creating the structure:
- Rafter legs - must have a high margin of strength to withstand the load of the entire roof.
- Mauerlat is a beam laid on top of the erected walls, which evenly redistributes the weight from the rafters.
- Racks – wooden beams, having a vertical location.
- Screeds - they bear the entire load from the tensile forces of the roof.
- The sheathing is the base on which the roof is subsequently laid. The beams of the structure are mounted perpendicular to the location of the rafter legs.
The rafter system is the basis on which the roof of the entire house is based.
The classic solution for the rafter system is wood, but this is not the only possible option. You can find proposals for the manufacture of rafters from the following materials:
- Wood, as already mentioned, is the most popular material.
- Reinforced concrete. Three configurations are possible: rafter systems, trusses or panels.
- Metal.
The choice of material is usually carried out using three factors:
- its cost;
- complexity of installation;
- compliance with the design of the building being constructed.
In addition, roof parameters also play an important role. Without knowing them, it is impossible to make a final decision. What the rafters will be made of depends on:
- fire resistance;
- service life;
- required span size;
- tilt angle;
- thermal performance indicators.
Structural elements of the rafter system gable roof
And yet, the leader in the construction of this element of the building is wooden rafter structures, which, thanks to the variety of technologies, can meet almost any design requirements.
Video presentation of the program for calculating rafters and trusses
Typically, coniferous wood is used to make rafters. There are very serious requirements for it in terms of grade, the presence of defects and a number of other indicators, the main of which is humidity (no more than 18%). In addition, according to SNiP, roofing structures are required to withstand a total load of about 200 kg per square meter. This means that the thickness and strength properties of the timber must be high.
Important!
The optimal cross-section of the rafters is 50×150 mm, while the cross-sectional area should be at least 50 square meters. cm.
Sometimes it happens that the boards for the rafter system do not meet the stated requirements. In this case, they are connected together, increasing the required length or width.
The main disadvantages of wood material include:
- flammability;
- susceptibility to pests;
- insufficient choice of beams in length during the construction of large buildings.

For the production of rafters, timber with a section of 50x150 mm is used
The first two factors are neutralized with the help of special products, regular application of which and impregnation of wood before installation work help cope with natural features tree. As for the third point, there are two possible solutions: increasing the length using a connection necessary elements or choosing a different material.
Usually they choose the first option, despite the complexity of this process. The reason is the advantages of wooden rafters over other systems:
- Environmental friendliness of the material;
- Light weight;
- Possibility of installation without the participation of construction machines;
- Low cost;
- Possibility of adjusting the size at the work site;
- A variety of ways to attach system elements to each other and to the walls of the house.
Thus, it turns out that wood is not only a tribute to tradition, but also a truly convenient solution when developing and installing a rafter system.

Wood is the material most often used for rafters
Types of rafter systems
Wooden rafter systems come in three types:
- Layered;
- Hanging;
- Roof trusses.
Each design has its own characteristics and recommendations for installation.
Layered rafters and their characteristics
They are considered the most inexpensive and most common solution in the construction of houses. Their main design feature is that the system is supported not only on the perimeter of the external walls, but also on the internal load-bearing wall or a support replacing it. This approach allows you to increase the width of the rafter system.
Important!
Layered rafters experience only one type of load - bending, which increases their strength characteristics and service life.
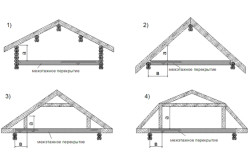
Layered rafters have become widespread in houses with the following parameters:
- For pitched roofs– with a house width of up to 7 meters;
- For gable roofs– building width up to 18 meters with an increase in the number of racks from 1 to 3;
- For four- and two-slope roofs - at an angle of inclination up to 40 degrees.
Layered rafters are an inexpensive and reliable solution for forming the roof of a building
The convenience of layered rafters is that they can be installed perfectly in almost any building. A convenient layout, simple installation and a classic roof solution - all this serves as a stabilizer of demand for rafter systems of this kind.
The main feature of the installation of this rafter system is that after laying the Mauerlat, a waterproofing layer should be laid on it. And only the next step will be the installation of rafter legs.
Layered rafters help create a lighter roof than with other structures.
But not every configuration of a house under construction allows for the installation of layered rafters. Sometimes it's worth taking advantage alternative option.
Features of hanging rafters
It is worth considering the installation of hanging rafters if the building design does not provide for internal load-bearing walls. The recommended span width in this case can vary from 6 to 12 meters. In rare cases it is still possible longer distance, but the requirements for the design of the rafter system will become more stringent.
The peculiarity of hanging rafters is that they rest with their entire weight on the external load-bearing walls
Hanging rafters press the entire weight of the roof onto the outer walls of the building. To ensure a more rigid structure, the rafter system uses a tie, which ensures optimal structural rigidity.
The rafters are fastened in a spacer, and the attic floor, if there is one, is attached directly to the trusses. Most often, such structures are used in houses with single-, double- or hipped roofs.
For information!
Hanging systems are mounted separately, and a ready-made rafter configuration is installed on the roof
The third solution for installing a wooden truss system is trusses. Unfortunately, they are practically never found in low-rise construction. In the rare cases where they are applicable, one may see a complex lattice system where load distribution occurs in different ways.
Manufacturing and installation of wooden rafter systems
If previously wooden rafter structures were assembled in fact on the territory of the facility under construction, now there is no need for this. Having a house project in hand, it is very easy to order the necessary configuration from enterprises engaged in this type of work.

Rafter systems for roofs of complex configurations must be calculated and installed by specialists
This solution will allow you to obtain rafters with precisely sized dimensions and reliable fastening. Builders will only need to assemble the necessary structure from blanks and lift it for installation on the load-bearing walls of the house.
If you still want to do all the work yourself, then you should adhere to strict consistency and adhere to a number of conditions. The installation instructions contain the following requirements:
- Treatment of all wooden elements with antiseptic and fire-fighting compounds. First of all, this concerns mauerlats and supports of internal load-bearing walls.
- The rafter legs at one end rest against the mauerlat lying on the outer walls of the building. A notch and nails are used as fastening.
- For layered rafters, it is worth considering the width of the building, since if its value is less than 6.5 meters, then there is no need to use support on the internal wall. If the width varies up to 12 meters, then one intermediate support is required, if more than 12 meters - two.
- Installation is carried out from bottom to top.
- There is a special requirement for the height of the Mauerlat - above the height attic floor it must rise at least 400 mm.
- Fastening of vertical posts is carried out using two alternative methods: cutting with a hidden veneer into the frames and additional reinforcement with nails.
- The racks are plumb and equipped with a pair of fasteners. This helps maintain the integrity of the structure in high winds or other bad weather conditions.
- A purlin is laid parallel to the ridge, which can be made by extending the boards to the required cross-section.
- The purlin serves as support for the upper ends of the rafter legs.

Traditionally, rafters are installed immediately at the construction site, but you can order a ready-made structure in production
Important!
Some projects allow the rafters to rest directly on the racks, without the participation of a purlin.
- At the ridge, the rafters are connected by overlays.
If we talk about the sequence of work, then first the two outer pairs are installed according to the project, and then the remaining elements.
Important!
The upper part of the first pairs should be strictly horizontal.
After installing the rafter legs, you can begin work on installing the sheathing, and then continue with the rest of the roofing work.
conclusions
Build a cozy building without a rafter structure wooden house impossible. There will also be no comfort in the new building if the installation was carried out with errors and shortcomings. Therefore, you should choose: order a ready-made rafter system or invite professional craftsmen to assemble the required configuration according to the project.

Accurate calculation of the rafter system for roof loads is important
It is better not to take on such work on your own - there are too many nuances to take into account when working with wooden material. In order for the rafters to please you with quality, like the whole house, it is worth responsibly resolving issues related to their installation.