In this article, we will look at how a gable roof is made at an angle with our own hands. We will learn about the features of the construction of the construction of such a roof, get acquainted with the advice of builders on this issue.
So, this is one of the simple structures that can be used to create a roof for a house. A do-it-yourself gable roof with an angle will be the final stage in the self-construction of a house.
Design gable roof considered one of the most reliable. It is not as difficult to build as broken roofs, or roofs complex shapes resistant to wind and snow loads.
Gable roof structure
Let us analyze in detail the design of such a roof:
- The base of the gable roof is the Mauerlat. In the case of a wooden truss system, the construction of which we will consider, the mauerlat is a bar, or a log that is laid on top of the bearing wall of the building. Mauerlat serves as an extreme lower support for truss system future roof. During construction timber houses, the bar of the upper crown of the wall of the house serves as the Mauerlat.
- The rafter system, or rafters, are struts that are located from the Mauerlat to the roof ridge. The ridge is a beam that connects the rafters of both roof slopes at the highest point. The rafters at their lowest point do not end on the Mauerlat. In most cases, they are built up with additional length (i.e. "filly") to ensure that rainwater falling from the roof is drained away from the walls of the house structure.
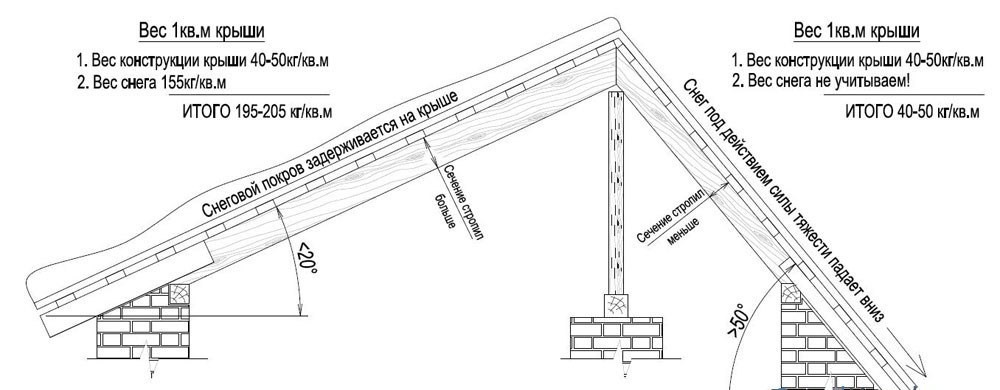
- The optimal angle of inclination for a gable roof should be close to 30 degrees. A greater than 30 degree angle of inclination will increase the horizontal wind loads on the roof and the building itself and will require that it be provided with excess strength to prevent damage from increased winds. A smaller 30 degree angle will help snow accumulate on the roof in winter period, which increase the vertical loads on the structure of the roof itself, the walls of the building and its foundation. Subject to right angle, the roof structure is optimally balanced, and its construction requires the lowest material costs.
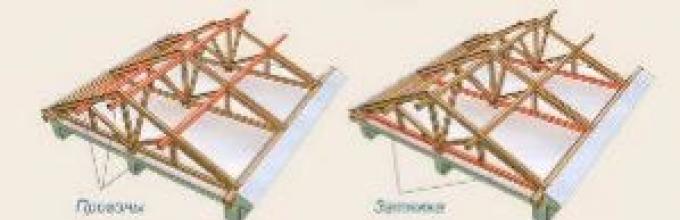
When constructing a gable roof of considerable size (as a rule, with a slope length of more than 3 m), additional elements reinforcing the roof structure are used:
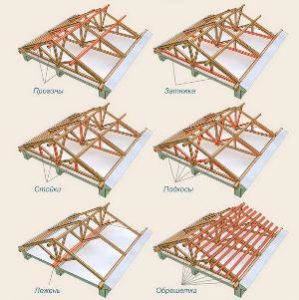
- Lying - a beam, or a log, connecting the opposite walls of the building parallel to the Mauerlat, but shifted relative to it closer to the center of the house. In the construction of a gable roof, the bed is used as a support for a rack on it, which serves to maintain the tightening.
- Rack - a vertical bar resting on a bed and supporting puffs at their junctions with the rafters.
- Puff - a horizontal beam connecting the rafters of opposite roof slopes. Puffs are needed to give roof structure additional strength and strengthening of the roof slope from sagging under significant vertical loads.
IMPORTANT! In order to exclude possible diagonal deformations of the roof, bars are used coming from racks with adjacent puffs. The optimal angle of inclination for such bars is 45 degrees.
The roof structure constructed according to such rules will be reliably protected from deformations in all planes and will serve as a reliable support for the battens and roofing material. Of course, not all designs are suitable for such a universal approach.
The bed, for example, can be located above the level of the Mauerlat and rest on the side walls of the building, located at the level of the puffs. In this option, there is no need to use racks at all, because. the puffs actually rest in their middle part directly on the bed. There are other options for the construction of a gable roof, but in principle all of them will still be similar to each other.
Roofing material and lathing
The roof sheathing is the basis for the roofing material.  The crate can be thick boards laid horizontally on the rafters, or bars. The wider the step between the roof rafters, the greater the thickness should be at the boards of the crate and vice versa.
The crate can be thick boards laid horizontally on the rafters, or bars. The wider the step between the roof rafters, the greater the thickness should be at the boards of the crate and vice versa.
As a rule, a vapor-permeable moisture-proof material is placed under the crate, so that it is located between the crate and the roof rafters. This must be done so that, in the future, the roof could be insulated from the inside with any available heat-insulating material placed between the rafters of the structure.
Depending on the type of roofing material, not only boards, but also moisture-resistant plywood sheets, or similar materials based on wood shavings, can serve as a crate. They are used for mounting the so-called. soft roofing, when a solid solid surface should be located under the roofing material.

Roofing material is what directly protects your house from precipitation. Between the crate and the roofing material must be laid. This must be done in order to protect the crate and structural elements of the roof from moisture, which, under certain conditions, can condense on the inside of the metal sheets of the roof.
For a soft roof, of course, this is not mandatory. Methods for attaching roofing material depend on what exactly you are using. Metal tiles and corrugated board are fastened with special roofing screws, soft roof glued on a solid base, classic tiles, or plastic elements made under it, are fixed with special fasteners.
The end surfaces of the roof are closed by the so-called. a wind board, or a metal profile of the same color as the roofing material. For reliable fastening of structural elements of a gable roof, it is necessary to use corners, perforated plates, tightening bolts. Of course, it is possible to assemble the roof simply on self-tapping screws, but such a design will not stand for long. Responsible places of diagonal structures are fastened with a groove connection.
Construction technologies in modern world are developing by leaps and bounds. This is especially true for private houses. Very milestone in the course of erecting one's own housing is the creation of a roof. It would seem that everything is quite simple, but it is not. In order for the structure to be strong, it is necessary to make an accurate calculation and understand whether the future roof should be steep or flat. How to calculate the minimum and optimal slope gable and four-pitched roof? How does the strength of the building depend on it? How is the angle of inclination calculated?
For a roofing device, the slope is one of the most important parameters included in the calculations.
The roof is the most important component of any architectural creation. It protects the inhabitants of the house from precipitation, wind, low and high temperature and gives it a nice look. Whatever it is, it is important for any owner to know the optimal and minimum angle of its inclination. Sometimes the integrity of the building depends on this, because if it is not properly planned, it can simply collapse. Let's take a closer look at what should be optimal angle slope of a gable roof, how wind affects it, precipitation, how the roof system should be selected, slope, work plan.
Influence of climatic conditions
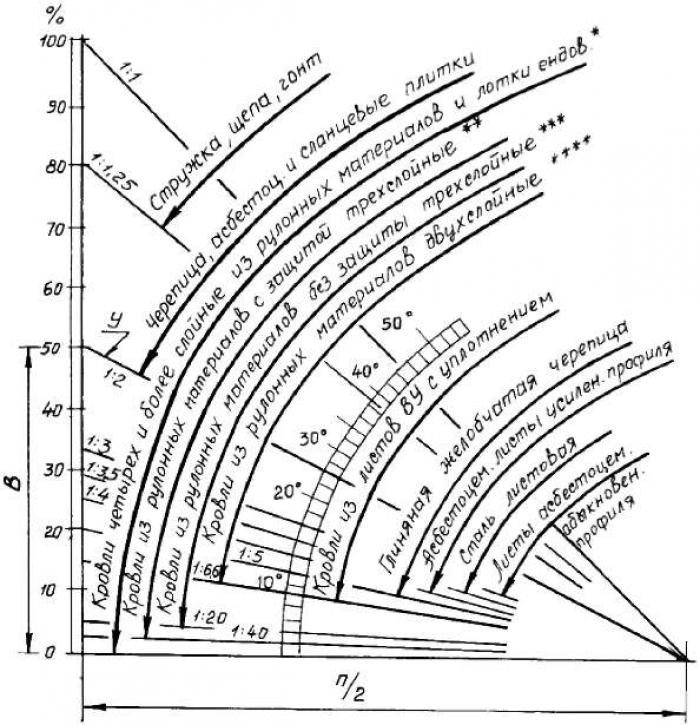
Most private houses have pitched roofs. Most often you can find two-slope or four-slope. Their slope may be different. How can you calculate the optimal and minimum slope angle, what does it depend on? The score is influenced by many factors. The main ones are the climatic conditions and the properties of the roofing material. So, let's focus on the most important of them first. The simplest of the indicators is the wind. The wind load is directly proportional to the angle of the roof slope. If it is too small, for example 5-10 degrees, then the wind is able to penetrate under the roofing material, since in this case it is located almost parallel to the surface, which can damage the coating or completely tear it off. With too large an angle, the same as in the previous case. Here the wind can simply knock down the flooring.
Therefore, for areas with frequent strong winds for a gable and four-slope roof, the most optimal slope angle is 15-20 degrees. For regions that are calmer in this regard - 35-40 degrees. The slope also affects the tightness of the house. If the angle is large, then the water will run away from it without accumulating on the surface. The same goes for snow and mud. Therefore, for rainy areas, the best slope is 45 degrees, and for dry areas - 30.
Roofing materials
The angle of the slope of a gable roof or a four-slope roof is also determined by the type of roof.

Rolled materials are used for arranging roofs with an inclination angle of not more than 60 degrees.
Roll materials - such as roofing material - are used even on those buildings where the slope of the roof slope is 0 degrees. That is, it all depends on the roof. They do not have high protection, and the number of layers of roofing material will depend on the slope of the roof. With a slope of up to 15 degrees, 4 layers will be needed in the calculation, at 40 - 3, with more than 45 - 2 layers. The optimal material for a gable structure with a slope of 30 degrees is asbestos-cement sheets. For tiles, a slope of 22-40 degrees is suitable. If there is a minimum slope angle of about 12 degrees, then overlapped metal sheets can be used.
An interesting fact is that the high values \u200b\u200bcharacteristic of a gable or four-slope design are more susceptible to heat loss than others. Therefore, it is impossible to do without taking into account the height of the building, otherwise create in living rooms in the future, the optimal parameters of the microclimate will not work. The minimum slope should be chosen for areas prone to strong winds and hurricanes.
Tilt Angle Measurement System
The roof system needs careful measurement. To do this, it is necessary to determine the optimal minimum slope two-slope or four-slope design. All this is included in the work plan. Here the angle itself or its value as a percentage is measured. To determine the degree, you need to make a calculation or make a model on paper. The percentage is calculated as follows: the height of the ridge is taken and divided by half the width of the building. The resulting value is multiplied by 100%. The calculation is as follows: as a percentage, 1 degree is equal to 1.7%, and 45 degrees is 45%.
It is important to note that slate, which is the most common roofing material, has a very large minimum angle. At its lower location, the wind is able to drive moisture under it and it becomes damp. This can cause increased humidity in the house itself, which will negatively affect the occupants and conditions.
It is important to remember that for gable roof both large and small can be fatal. Because of this, its accurate calculation is important. At a large angle, the wind can tear off the coating and make the dwelling uninhabitable, and too small contributes to the penetration of wind between the seams of the roof, the penetration of precipitation into it and the destruction of the roofing material. Often, gable roofs are characterized by their failure. It's connected with constant load on the roof of precipitation, in particular snow, which can accumulate on it in tons in winter time. Of great importance is the slope for the diversion of water, in otherwise it can accumulate under the roof and degrade the air quality in the attic room, promote the appearance of fungi and bacteria.
When building a house, the issue of the slope of the roof and the type of roofing material is one of the fundamental ones. Since these two issues are highly interrelated, let's take them together - the choice of slope and the choice of roofing material.
The slope of the roof depends on how many slopes the roof has - one, two, three or four.
Types of roof construction
1. Wooden
Most common in construction.
Its composition:
- rafters
- Racks
- Struts
- Mauerlat
- crate
- Puffs
Hanging truss systems are used where there is no middle load-bearing wall.
This design has advantages: relative cheapness, strength, environmental friendliness.
Disadvantages: fire hazard, the possibility of rotting and exposure to fungus and woodworms.
Service life 25 years.
2. Metal-wood.
This design is combined and has elements of both wood and metal. Can cover spans of 20 meters. Its upper belts are made from wood, the lower ones - from periodic profiles or reinforcement. That is, metal elements here work in tension, wooden elements work in compression.
They are rarely used because of the high cost - mainly such a roof is made for swimming pools and industrial enterprises.
Service life 45 years.
3. Reinforced concrete
Service life 50 years.
Roof types
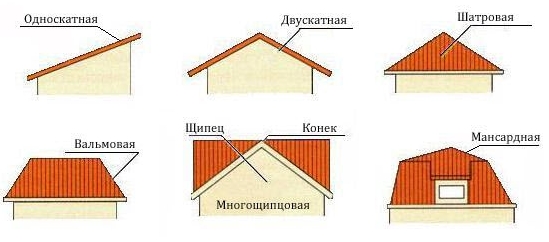
1. Shed have a single roof plane from wall to wall. These roofs are usually built with a slope to the south to rid the roof of snow. Often used for sheds and garages.
2. Gable roof
. This is the most popular type of roof, it is used in 90% of all roofs. Differs in simplicity, durability and convenience in service.
3. Four-pitched roofs
(hip) have, as the name implies, four slopes. They are used when it is not planned to use the attic.
4. Four-pitched tent
have four slopes, with vertices converging at one point. Such roofs are built on square buildings or in buildings with a polygonal plan.
5. Multi-gable roofs
have steep slopes in the form of a quadrilateral, connecting at one vertex.
6. Mansard roofs provide living space - attic with a window.
There are dozens of other types of lids - barrel-shaped, conical, diamond-shaped, folded, cross, flat, etc.
What affects the slope angle
- Purpose of the house
- Roof material
- Climatic conditions
If the roof has more than two slopes, it is important what the attic is used for. If not residential, then there is no need to build a high roof. If a living space is arranged from the attic, you will have to build good roof with a serious twist. To do this, you need to choose the type and design of the roof and the appropriate roofing material.
In regions with a strong wind load, for example, in coastal and steppe regions, it is better to build a roof with less windage. Where the sun shines strongly enough - in southern latitudes, where there is little rainfall, the roof is also built not large.
But in regions with heavy precipitation, the roof angle has to be made significant - up to 60 degrees.
metal roof
The metal tile has a lot of weight, so it is better to make a roof with a minimum angle of inclination. Especially in regions where strong winds blow. For roofs made of metal tiles, the minimum angle of inclination should be 22 degrees - such an angle of inclination of the roof prevents the accumulation of moisture at the joints.
Minimum Angle must be at least 14 degrees. If used soft tiles, then the minimum angle is 11 degrees, but during the construction of the roof, an additional continuous crate is needed.
Roof made of corrugated board
The most popular material is corrugated board. It is lightweight, easy and quick to mount and fasten. The minimum roof pitch is 12 degrees.
Roof made of rolled materials
It could be:
- Ruberoid
- polymer coating
- Ondulin
In any case, it is necessary to take into account the dependence of the strength of the roof on permanent (the weight of its own structure) and temporary loads (snow, wind, etc.). The type of lathing and construction step will depend on the slope of the roof. The lower the slope, the shorter the pitch of the crate should be done. The minimum step of the crate is 35 cm.
Also note that the steeper the angle of the roof, the more roofing materials you need to buy. If the angle of inclination is more than 10 degrees, bitumen waterproofing must be used. For roll material, an additional coating (additional coloring) should be used.
Calculation of the angle of the roof
The formula for calculating the roof angle is: Sin A=a/b, where:
a - half the width of the roof at the level of the box of the house - for example 3 meters
b- roof height at the level of the ridge - usually 180 centimeters
We substitute approximate values: Sin A=a/b= 300/180= 1.67. Further, according to the Bradis table or an online calculator, we translate the sine into degrees - it turns out 58 degrees. This will be the angle of the roof.
The roof of the house should be reliable protection houses from the adverse effects of the external environment, differ in strength, stability, fire resistance. However, developers are no less concerned about its cost-effectiveness. Therefore, “How to build a gable roof” is not an idle question, given that this type of construction is much more profitable and practical than others with a more complex configuration.
Developers often face the question of how to make the roof of the house reliable, and living under it as comfortable as possible. One of the most popular designs is a gable roof.
The design of a gable roof consists of three separate elements:
- The rafter system, which acts as a supporting frame for the entire structure.
- An insulating layer that ensures a long service life of the roofing system.
- A roofing material that has two main functions: protective and decorative.
The reliability of the construction of the house practically depends on the highest quality performance of each of these elements.
picture of a gable roof
Frame: main parameters and characteristics
Before you make a roof, you need to clearly understand what the frame is, individual elements and installation features. The main elements of the frame are:
- roofing
- crate and counter-lattice,
- rafters,
- skating run,
- racks,
- Mauerlat.
- diagonal and slanted connections.
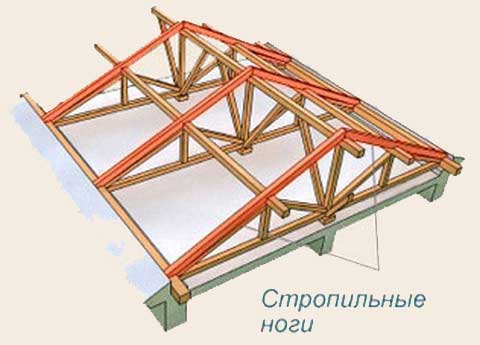
The rafter system is divided into two types:
- hanging - the outer two walls act as a support for the rafters;
- layered - has from three points of support on the outer and inner walls.
Types of rafters can be combined: use layered for parts of the house with intermediate supports and hanging where they are not.
In private construction, wooden rafters and lathing are mainly used, made of timber and boards of certain sections. Wood is more available and cheaper.
The choice of the angle of inclination
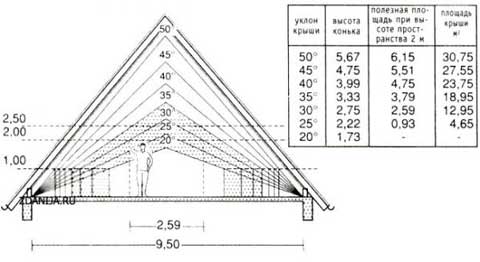
Traditionally, a gable roof has an angle that varies between 11–45°. For more accurate use of data on the following parameters:
- roofing material,
- wind loads in the area where the house is being built,
- snow loads in the same region.
These factors are considered together because they are interrelated. For example, a large roof angle in an area with strong winds:
- requires reinforcement of the truss,
- the roof area is larger and, accordingly, more material will be required.
All this ultimately leads to significant additional costs and may even affect the strength and reliability of the frame. When calculating the optimal angle of inclination, special maps of snow and wind zones are used.
When calculating the angle of inclination of a gable roof, one should not forget about the thermal insulation characteristics of the snow cover. Do not neglect natural thermal insulation, which will help to keep warm at low temperatures, and too large an angle to quickly get rid of snow from the roof surface.
Height
Thus, the slope is necessary so that precipitation does not stagnate on it and, accordingly, do not push through the roof. Knowing its value, you can accurately calculate to what height the roof ridge should be raised.
If the gable roof has a slope of 45 °, then the height of the ridge is half the width of the house. For other angles, the calculation of this indicator comes down to multiplying half the width of the house by the appropriate coefficient.
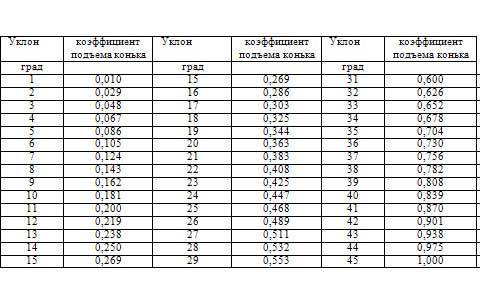
For example, if the width of the house is equal to the width of 8 m, and the roof has a slope of 40 °, the calculation is carried out as follows: 4 x 0.839 \u003d 3.356, where 4 m is half the width of the house, 0.839 is the lifting factor corresponding to 40 °.
How to calculate the area: the main consumption of roofing material
When calculating the area of any roof:
For, whose slopes are parallelograms, the area is:
S total \u003d 2ab \u003d 2a + 2b, where a and b are the height and width of the parallelogram, respectively.
After the calculations are completed, it is desirable to add ten percent to the resulting area - this will block possible errors.
How to make a gable roof and avoid mistakes
Construction can be divided into the following stages:
- erection of the structure of the truss system;
- creation of an insulating carpet consisting of layers of hydro-, steam-thermal insulation, and, if necessary, also sound insulation;
- roof covering installation.
Construction is started by purchasing all the necessary material, the amount of which was calculated on the basis of the previously made drawing.
- Mauerlat installation. Mauerlat bars to the wall of the house can be fixed in one of the following ways.
- Pouring an armo-belt with studs - a layer of concrete is poured onto the walls of the house, into which threaded pins (studs) are immediately imbedded with a step of a meter and a half. The stud should protrude from the concrete by 3 cm so that it can be screwed with a nut during the final fastening. The height of the armored belt is approximately 20-30 cm.
- Installation of studs in the last rows of masonry - they are installed in the 3-4 top row. When laying the wall, the pins easily enter the inter-brick mortar. In this case, it is necessary to calculate that, taking into account the height of the Mauerlat, when laying the pins, a small protrusion for the nut remains.
- Before installing the Mauerlat, one or two layers of waterproofing (roofing material) are placed on the studs.
- Installation of rafters and fastening to the Mauerlat. In order for all rafters to be identical, it is recommended to perform a single reference template for them, according to which there will be corners and boards of truss trusses. To the Mauerlat, using fasteners and an internal cutout in the rafter leg.
If the upper joint of the rafter triangle is carried out without a ridge, it is better to do it end-to-end, fixing it on the sides with fasteners and bolts.
![]()
For spans greater than 4.5 m, auxiliary fasteners for rafters and a ridge beam are required. In this case, supports are installed under the ridge. True, they somewhat complicate the design of the truss truss and increase its weight, but at the same time increase the rigidity of the structure. Racks are fixed to the ridge beam with the help of special fasteners, and with rafters - brackets.
- Installation of battens and roofing pie. Having finished the installation of the rafters, the crate is laid - depending on the future roofing material, either sparse or solid. Laying is carried out with a small, approximately 300 mm, outlet above the gable - for the cornice.
- A heat insulator, a vapor barrier and a waterproofing layer are laid between the installed rafters. on the heat insulator inside rafters, and waterproofing - with outside after the crate. The construction of a gable roof is completed by laying roofing material.
Professional builders are well aware that the angle of inclination of a gable roof should be as suitable as possible for operating conditions. Do not think that this is a problem only of an aesthetic nature. The slope of a gable roof depends on many other factors.
This indicator is measured in degrees from the horizontal line. It is believed that it can vary from 5 to 60 degrees. The spread is quite large, since five degrees will form a practically flat roof, and a roof with a slope of 60 degrees may be too steep. On a low building, a roof with a large slope can look completely out of proportion.
On this topic, among professional roofers, there is a bike that may well turn out to be true. They say that some customers pick up the slope of the slope "by eye". Workers, armed with long boards, go to the roof and put them like rafters, and the future homeowner evaluates the result visually, giving commands “higher”, “lower”, etc.
Of course, real experts act differently. They are well aware that when choosing a gable roof slope, you should consider:
- predicted snow load;
- the amount of rainfall;
- possible wind loads;
- type of roofing material;
- the thickness of the roofing cake, etc.