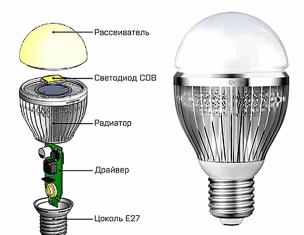
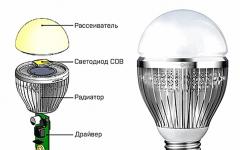
Panel housing technology appeared in our country about half a century ago. Five-story panels - "Khrushchev" or later typical nine-story houses are probably familiar to every Russian. However, such housing over time ceased to meet the needs of buyers.
Old vs new panel
The main disadvantages of the old panel houses- featureless facades, very large apartments, poor sound and heat insulation, monotonous layouts. According to Svetlana Shmakova, Vice President of the SAPSAN Group of Companies, the old ill-conceived layouts with "Khrushchev" kitchens of 6-8 have long become irrelevant square meters, as well as long and narrow corridors, due to which a lot of usable area is lost.
The modern panel allows more flexibility in solving construction issues. It is easier for her to "adjust" to the new urban planning, space-planning, architectural requirements. The main advantage of the new technology is the ability to finalize the layouts "for the customer." Reinforced concrete structures allow you to build objects of any complexity with various types facades and types of facing materials.
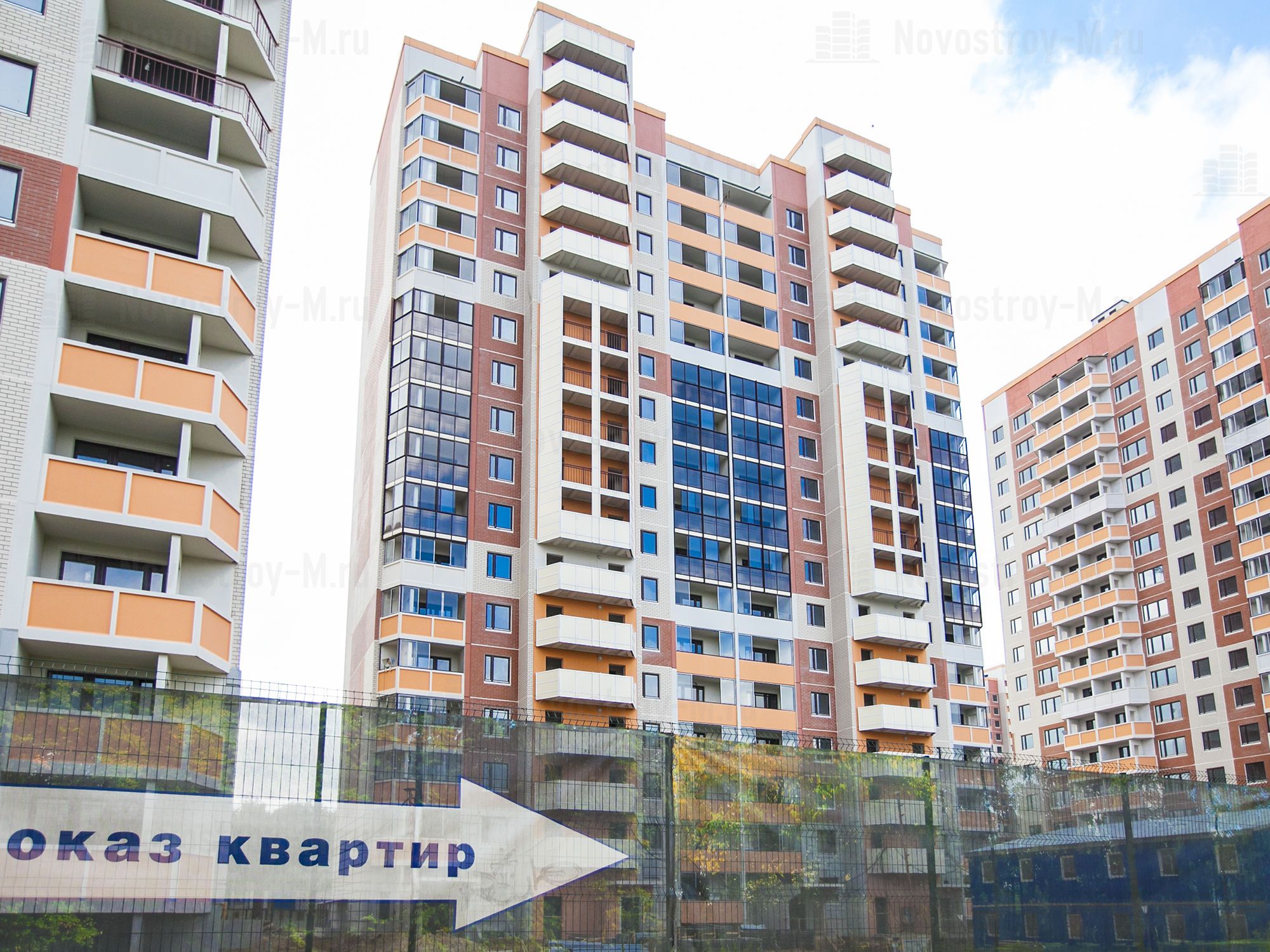
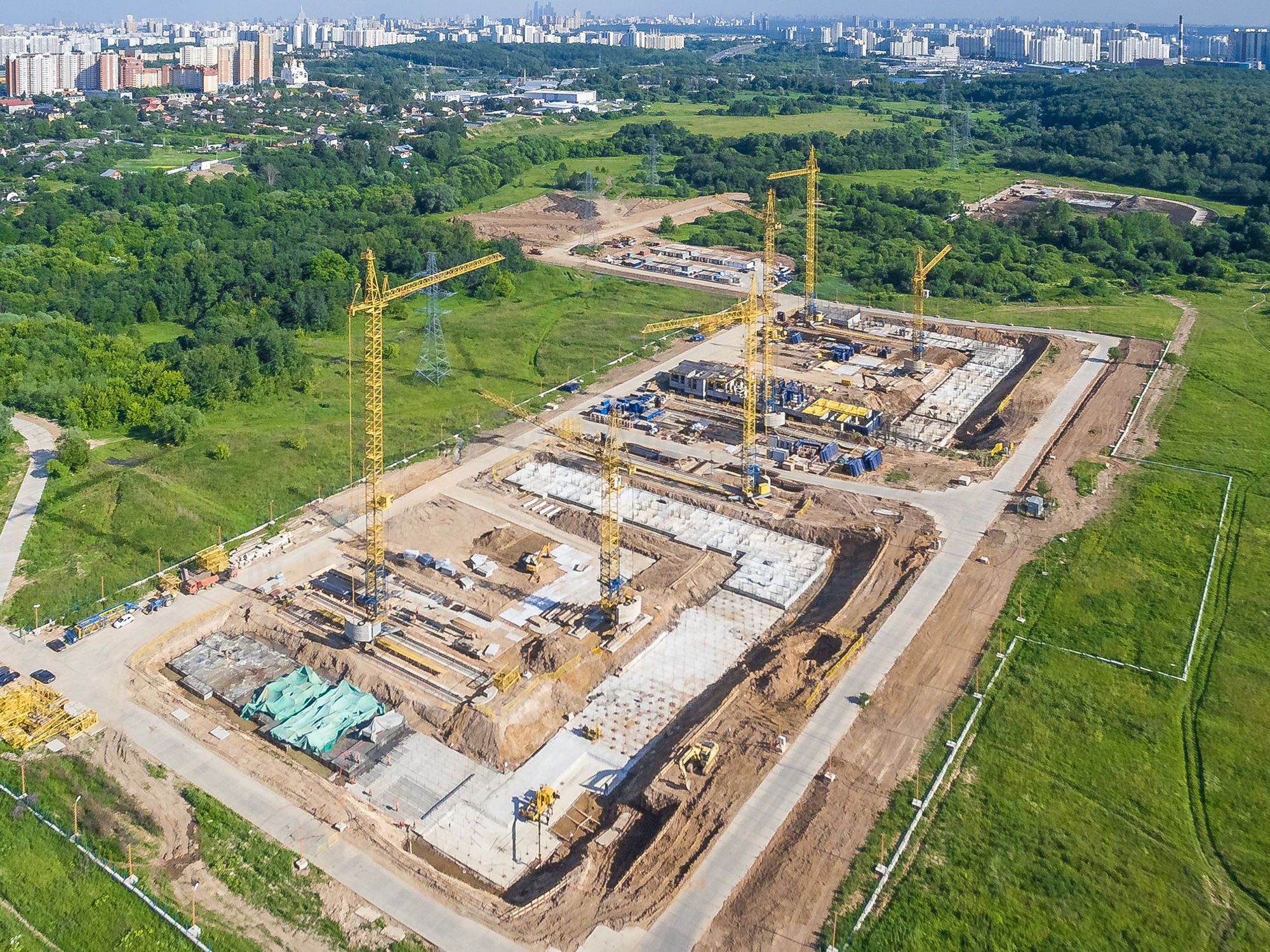
So, especially for the first stage of construction of the residential complex "River Park", the company "LSR" designed a non-standard model of buildings of the "Europa" series. In this series, the project developer can choose to develop various layouts from 25 apartment options, among which there are compact studios with an area of 25-28 sq. m. At the same time, the height of the ceilings is 2.8 meters.
Residential complex "River Park"
Of course, not all new series involve optimal configurations of rooms, kitchens and balconies. But a panel house with a free layout is now quite a common option.
“Over 10-15 years of market development, the old series have already been partially finalized, the quality characteristics of panel houses have improved”
Alexander Zubets, "New Vatutinki"
Of the innovations, it is also worth noting special designs for air conditioners and public areas on the first floors. It became possible to build multi-storey houses, block-sections with apartments of various room sizes appeared. The modern panel, unlike the old one, is insulated and thickened, and a new seam technology is used during installation. Therefore, all past shortcomings (poor thermal insulation and strong audibility) are no longer relevant. Remained in the past and small kitchens. modern kitchen panel house on average has an area of 10-14 square meters.
The guaranteed service life of the new "panels", due to the design and technological features, has doubled and is about 100 years. Therefore, such houses will not be demolished in the coming decades. The only thing is that in some cases they will require serious reconstruction, as, for example, in the case of wet facades (plaster). This option, in comparison with hinged and brick facades, is extremely short-lived. No matter how well the developer plasters the walls, best case they will lose color, and in the worst case, they will also crack.
However, the speed of construction panel houses The old and new series are practically the same. As Georgy Novikov, head of the department of analytics and consulting at MIEL-Novostroyki, said, the duration of the installation phase may have been reduced, but only slightly (a typical residential building panel series installed in 10 months). But if we consider the general construction cycle from a legal point of view (from excavation to commissioning), then it has not changed and is about 1.5 years.
Leader in the panel housing market- P-44T/K series
According to experts, the most popular panel series today is P-44T/K. Such houses are distinguished by more interesting planning solutions and a small number of apartments per floor. The series "Europa", "GRAD" ("Grad-1M", "Grad-2M", "Grad-4M") are popular.
Another example is the PIK-1 panel series developed by PIK Group from scratch. Its innovation is in the lower cost of production.
Another example is the DOMMOS series, an in-house development by the developer GVSU Center. It is distinguished by the variability of facades, including the presence of design solutions for houses with stained glass and cladding with ventilated facades.
At the moment, using a modern panel, quite a lot of new buildings are being built. Thus, LSR Group is building several facilities in the capital at once using new technology, including the Luchi comfort-class residential complex in the Solntsevo district, a residential complex in the Beskudnikovsky district and residential buildings on Dmitrovskoye Highway. As Konstantin Kuznetsov, managing director of LSR. Construction - Moscow", in the residential complex "Luchi" (series "Europa") will build 9 multi-storey residential buildings from 6 to 25 floors with apartments of various sizes and layouts.
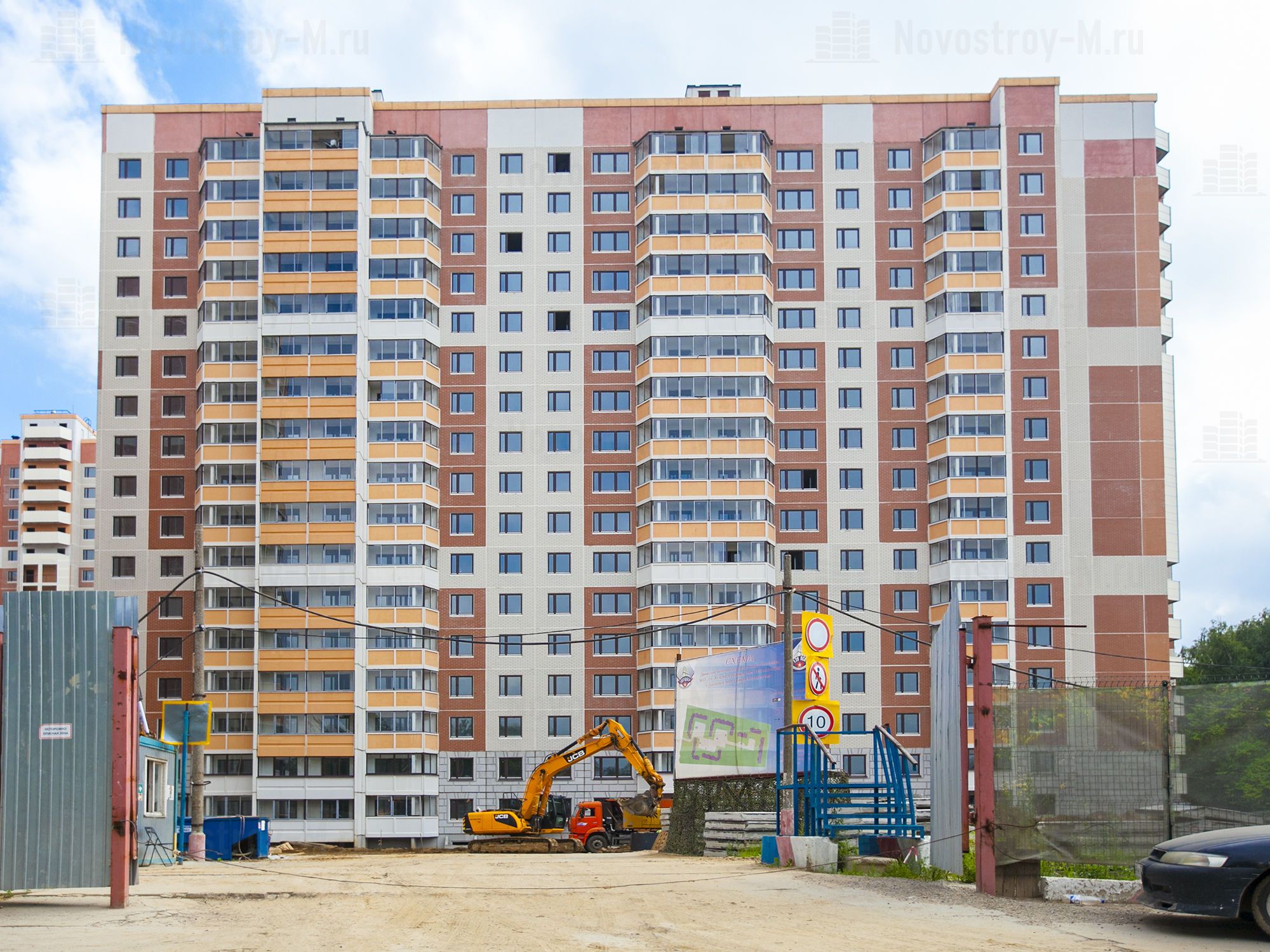
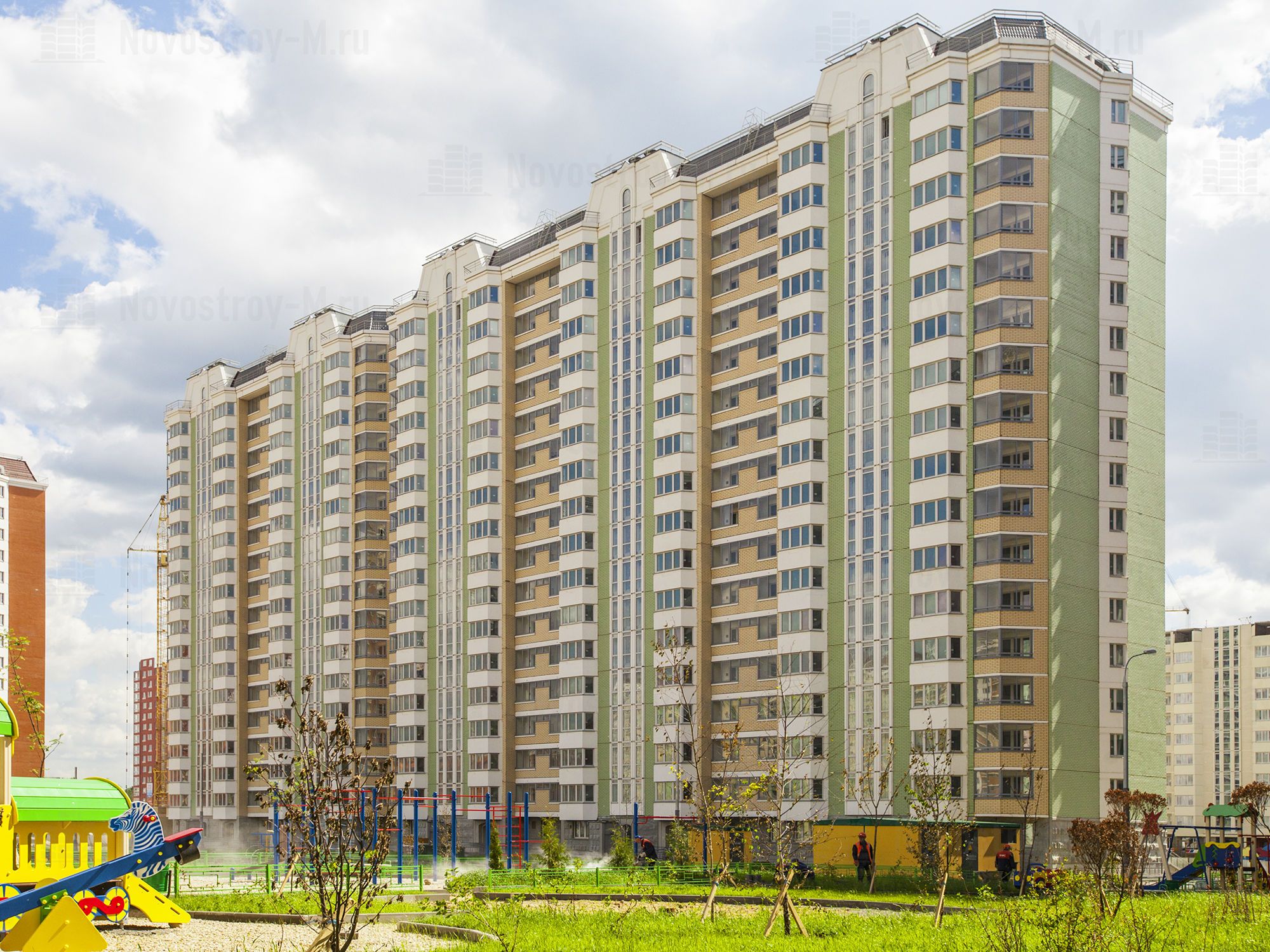









According to experts, about half of the volume in the houses of panel series falls on the panel of the new generation. In particular, among the projects in the "old" Moscow, the implementation of which began over the past two years, buildings are being built in seven residential complexes according to the most modern technologies: "River Park" (series "EuroP"), "Warsaw highway, 141", "Meshchersky Forest", "Elninskaya, 14B" (all three - series "PIK-1"), "Mitino World", "Olgino Park" in the city of Zheleznodorozhny (series "DOMMOS") and "Nekrasovka" ("DOMRIK"). A new microdistrict in the South-Eastern Administrative District of Moscow - P-44T / K is being built up.
“In the new series of residential buildings, the focus is on attractive architectural appearance, energy efficiency, functionality and convenience. planning solutions»
Igor Sibrenkov, Morton-Invest LLC
New panel housing construction technologies are used in (Andreevka) and Domodedovo Park (Domodedovo). The construction of houses in Zelenogradskoye is carried out using sandwich panels with an additional 25 cm insulation. Distinctive feature houses is a mirror glazing. In the residential complex "Domodedovo Park" in a number of buildings there are houses of the panel series "Europa", which are distinguished by a seamless "warm" facade.
Panel vs monolith
Modern prefabricated houses often look so much like monolithic housings that many buyers do not immediately distinguish between a panel and a monolith. Thus, the boundaries between different types housing constructions are gradually being erased. Soviet stereotypes that a panel house is an economical option with all the ensuing consequences are becoming a thing of the past. Therefore, if in the same project there are both panel and monolithic houses, then the former often buy even more because of the lower cost.
Some buyers are confused by the fact that, compared to a monolithic house, there are more load-bearing walls in a panel house, so the options for “reworking” an apartment are somewhat limited. But residents can still, for example, expand the bathroom at the expense of the area of the corridor or move the doorway. On the other hand, in a monolithic house, during repairs, you have to spend additional funds on building walls. However, it is worth noting that fewer and fewer buyers are asking the question of redevelopment and want to buy ready-made housing on a turnkey basis. And this means that panel housing construction today offers customers the most best options suitable for the average family.
According to Andrey Kolochinsky, managing partner of VectorStroyFinance Group of Companies, panel houses are popular with developers primarily due to the speed of their construction. Such a building is being built 1.5-2 times faster than a monolithic house of the same size. Monolith is usually individual project, therefore, during construction, unforeseen problems may arise that require new architectural and technical solutions. Because of this, the speed of construction is slowed down. In addition, agreement project documentation for an individual monolithic project, it lasts much longer than for a panel one, because such projects require a separate examination, since they are not familiar to the authorities, unlike a typical panel.
"Modern panel houses look no worse than those that were built according to an individual design project"
Maria Litinetskaya, Metrium Group
Developers prefer panels for purely economic reasons. In the early 2000s, up to 60-70% of buildings in Moscow accounted for standard construction - panel houses. For the first time, the share of monolithic housing construction exceeded the panel one in 2004, and already in 2006 it almost reached 80%. The crisis of 2008-2009 served as a new impetus for the emergence of typical new buildings. So, in 2009, half of the objects that came out were panel houses. In 2010, the share of such buildings increased by 1.5-2 times compared to the pre-crisis period.
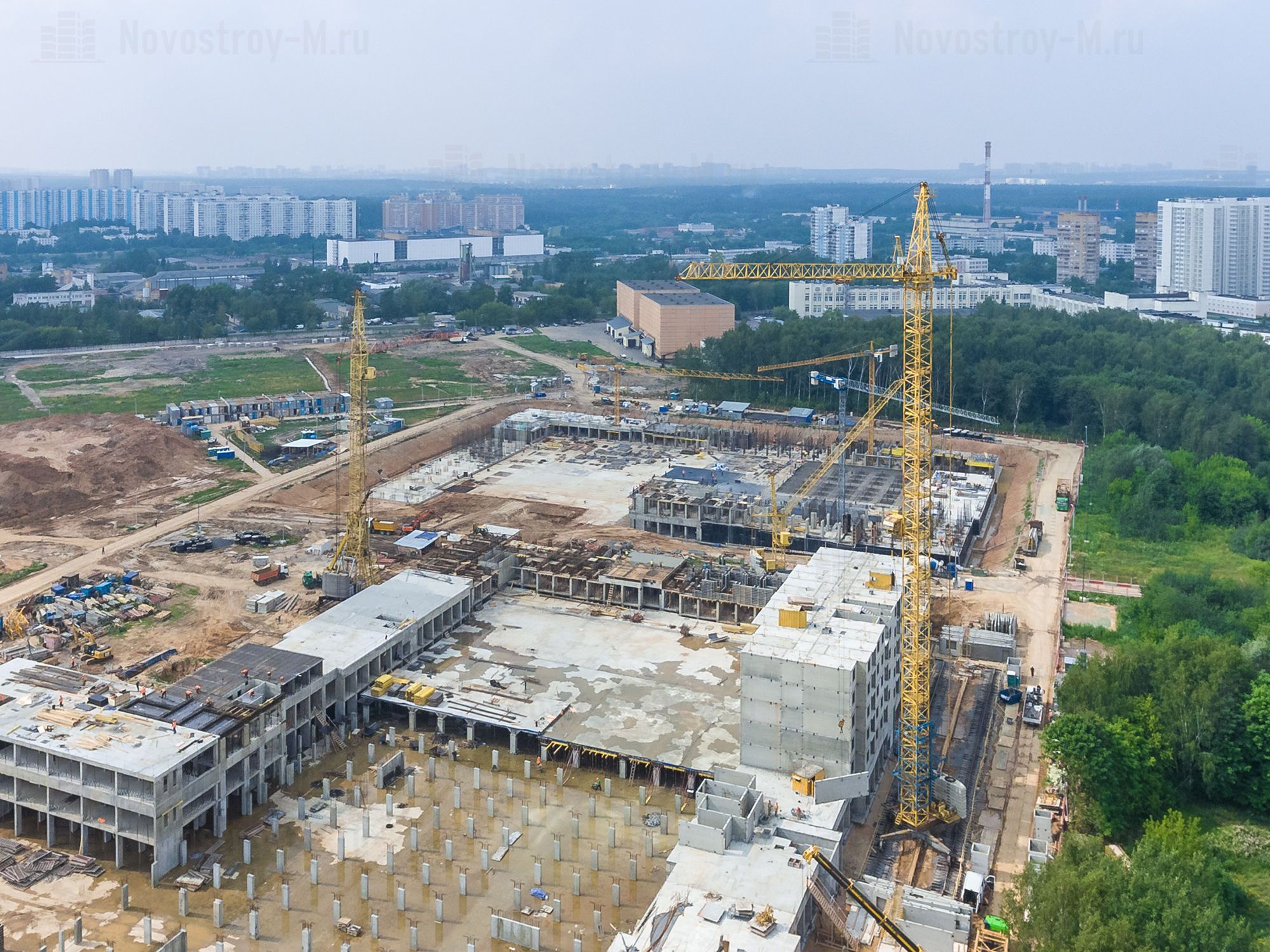
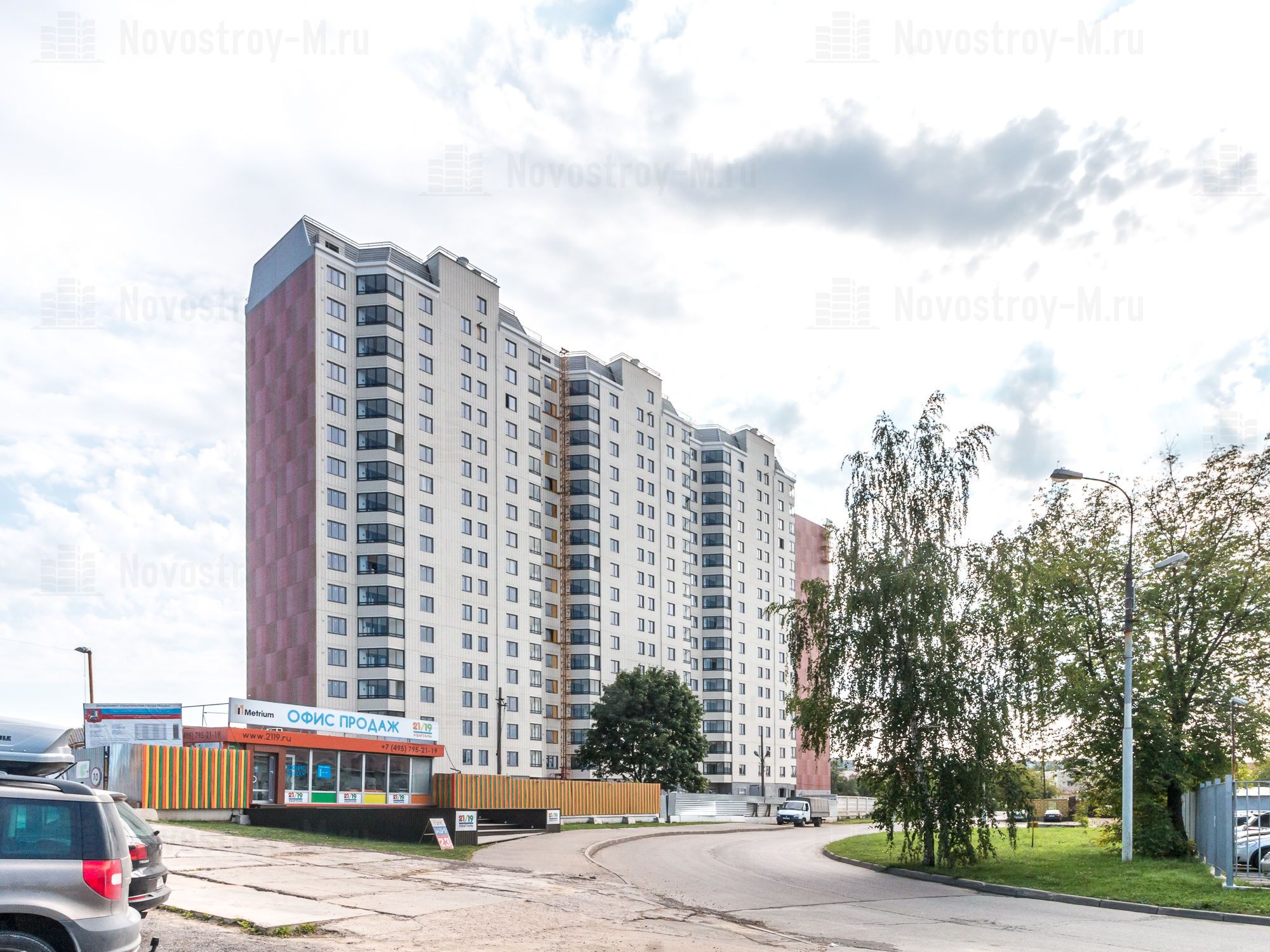
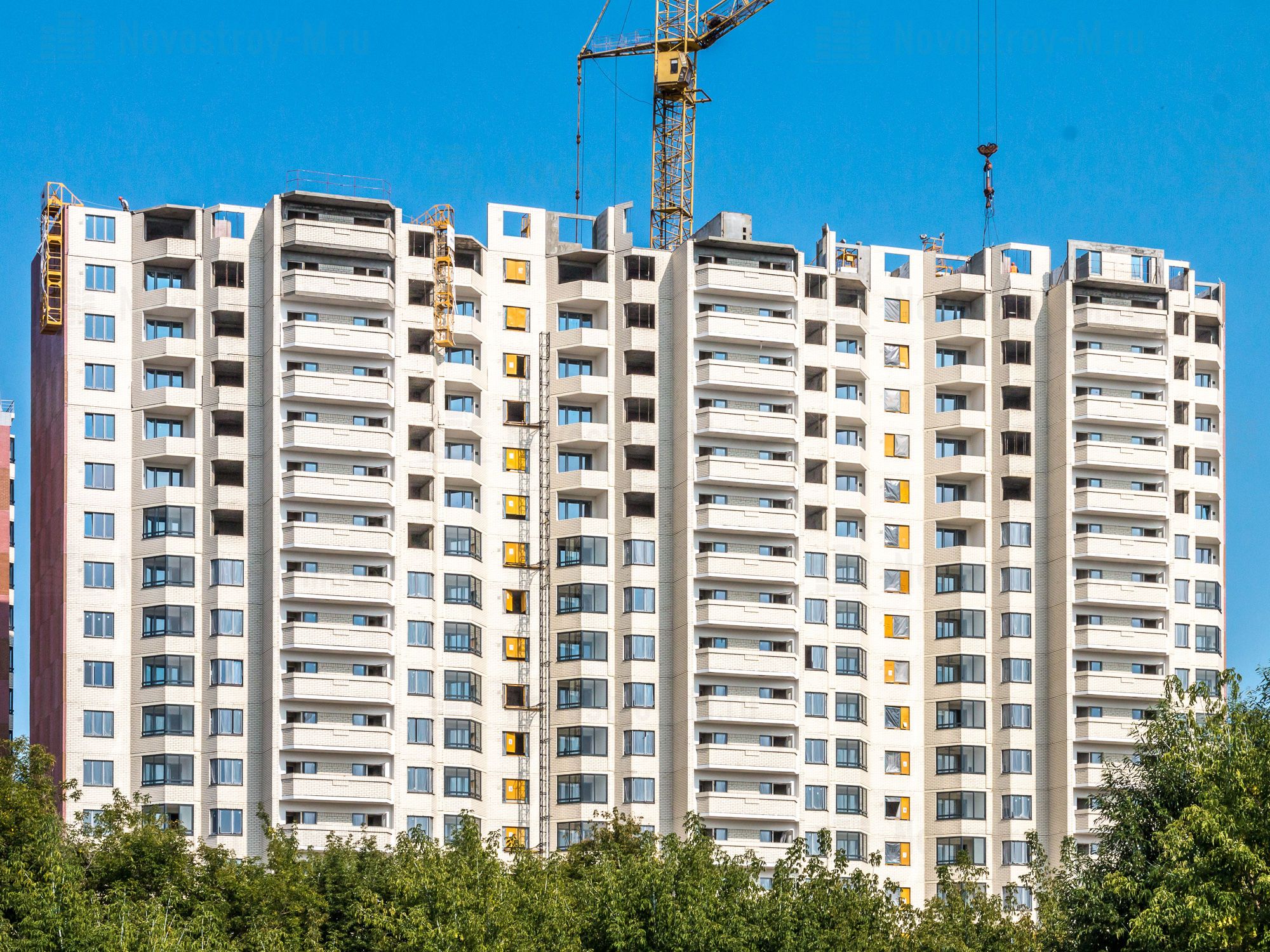








Nevertheless, since the mid-2000s, monolithic housing construction has been confidently holding the lead in Moscow, and from 2012 to 2014, it accounted for almost 90% of new buildings in the capital. In 2016, the situation has changed. Supply share in panel houses in the mass segment of the primary market of "old" Moscow amounted to 23%. For comparison: at the end of 2015, apartments in panel houses occupied only 12% of the Moscow market.
The distribution of the volume of supply, expressed in the total area of apartments by construction technology relative to the total volume of supply, according to the company, looks like this (as of July 2016).
Cottages made of reinforced concrete panels have a number of advantages over similar buildings made from other building materials. But also this type of construction has its own characteristics, which you need to familiarize yourself with.
Finished project houses assembled from reinforced concrete panels
Material device
To understand the difference between and (concrete goods), you must first understand what kind of material it is. It has one difference from ordinary building concrete - steel "insides". During the casting process, steel reinforcement is added to the product. It improves such qualities of reinforced concrete as resistance to loads and increases its ability to bend.
Thanks to improved physical qualities, it became possible to produce ready-made blocks from a new material, from which, according to standard projects, private cottages were also made.
Advantages and disadvantages of panel houses
"Typicality" has become the main argument of opponents of the construction of residential buildings from reinforced concrete panels.![]() The process of building a panel house
The process of building a panel house
In their opinion, such a house will not be original. However, practice has shown that reinforced concrete products can be successfully used to build the most original cottage in the world.
Other disadvantages of reinforced concrete houses include the following:
- poor thermal insulation;
- low sound insulation;
- large plate weight.
But all these arguments were relevant 20 years ago. At present, instead of steel, so-called composite materials have begun to be used for the manufacture of reinforcement. These are polymers that improve the physical properties of reinforced concrete panels while reducing the standard weight of the slab.
To protect the surface of the concrete itself, manufacturers use special coatings that protect the material from water, the so-called, as well as reduce heat loss and sound permeability. But this is not the main advantages that reinforced concrete buildings have.  An example of installing reinforced concrete panels in the frame of a house The main advantage is the speed with which a cottage can be built from such material. In addition, in terms of durability and strength of a house made of reinforced concrete structures have no equal. As the builders joke, such a house is able to withstand a hurricane wind and withstand the force of a small explosion.
An example of installing reinforced concrete panels in the frame of a house The main advantage is the speed with which a cottage can be built from such material. In addition, in terms of durability and strength of a house made of reinforced concrete structures have no equal. As the builders joke, such a house is able to withstand a hurricane wind and withstand the force of a small explosion.
The advantages of the concrete goods also include:
- the ability to build at any time of the year;
- a variety of planning options;
- the possibility of exterior decoration of houses with any material;
- fire protection;
- cheapness of materials.
And now we will consider all the stages that the construction of reinforced concrete cottages goes through.
Stage one: design
The first step is the most important. Because in the process of compiling the estimate documentation and calculating the dimensions of the future house, the calculation of the number of parts that will be required for its construction is also carried out.  Layout of all floors of a private two-story house from reinforced concrete panels This takes into account everything, including external walls, window and door openings, horizontal ceilings and internal walls. This method is good because it protects the owner of the future home from unscrupulous builders. When building a brick house, there is always the opportunity to write off Construction Materials to "overrun". With reinforced concrete products, such a number will not work for clever foremen. Most builders offer customers standard house designs.
Layout of all floors of a private two-story house from reinforced concrete panels This takes into account everything, including external walls, window and door openings, horizontal ceilings and internal walls. This method is good because it protects the owner of the future home from unscrupulous builders. When building a brick house, there is always the opportunity to write off Construction Materials to "overrun". With reinforced concrete products, such a number will not work for clever foremen. Most builders offer customers standard house designs.
But the variety of parts produced by manufacturers allows you to create a unique, one-of-a-kind structure.
Thanks to this, many modern cottages made of reinforced concrete components have a unique look.
The presence standard projects frees developers from worries, who see their future home as simple and practical.
Read also
Projects of one-story private houses
Stage two: foundation
As noted above, the reinforced concrete components of houses are characterized by significant weight.  The process of laying the foundation for a cottage made of reinforced concrete panels Therefore, the foundation for them must be made capital, capable of withstanding heavy loads. Under the construction of objects of this type with a significant deepening. Steel reinforcement is introduced into concrete for greater resistance.
The process of laying the foundation for a cottage made of reinforced concrete panels Therefore, the foundation for them must be made capital, capable of withstanding heavy loads. Under the construction of objects of this type with a significant deepening. Steel reinforcement is introduced into concrete for greater resistance.
The height of such a foundation is on average 180 cm, of which 140 cm are located below ground level. The width of the base is at least 40 cm. Before pouring concrete, a sand cushion is laid at the bottom of the trench, which acts as a drainage and shock absorber. Its thickness is 20 cm. Coarse river sand is taken for a pillow. 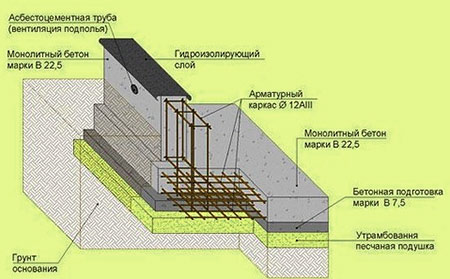 Scheme for mounting the foundation for a house from reinforced concrete panels The foundation itself is cast from concrete grade M250 and higher, into which steel reinforcement is introduced. For ventilation, in the process of making the foundation, holes are made above the ground for air vents.
Scheme for mounting the foundation for a house from reinforced concrete panels The foundation itself is cast from concrete grade M250 and higher, into which steel reinforcement is introduced. For ventilation, in the process of making the foundation, holes are made above the ground for air vents.
Experienced builders note that the time of year does not affect the quality of work on. However, in rainy weather, the foundation of the house is better not to do. And if work is carried out in the summer, in the heat, then as the concrete hardens, it is recommended to moisten it with water. This will protect it from cracking due to high temperatures.
RESIDENTIAL HOUSE SERVICE
(introductory lecture)
The history of serviced housing, in my opinion, has more than one millennium. The relationship of many functions (place of residence, work, rest, sleep, etc.) has always been observed in the dwelling. Since ancient times, trade, being one of the most important city-forming elements, has almost always been associated with housing. For many centuries, a person's dwelling was a single-family house, which combined a dwelling and a place of work.
The growth of industrial production (industrial revolution), and the new social ties and new institutions of organizational structures that appeared against this background, launched the process of separating housing from production.
However, since the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th century, due to the rapid growth of cities, megacities, it becomes obvious the need to create multifunctional, multi-storey complexes that would reflect the need of a modern person in the most effective form of interconnection: work-housing-leisure.
In design residential complexes in Russia, the following stages can be distinguished:
In the 20s of the last century, the ideas of communal houses with collective service (separation of the food function from the apartment) spread in the architectural community;
In the post-war period, residential buildings were quarters with a semi-enclosed courtyard space, where children's institutions were located, and shops and consumer services were located around the perimeter on the 1st floors. The future concept is being laid - a sleeping area.
In the 60s, the idea of multi-storey residential complexes was born, which reflect the requirements for increasing the building density, consolidation and diversification of business centers. The city is divided into residential and business zones. This leads to the emergence of enterprises of approximate service to the population (the first stage of service) - household, sports and health, trade, medical, recreational, etc.
This stage can be characterized as a turning point. In Russia and abroad, the fundamental concepts of the IFJC are being formed.
The next two decades are characterized by the ongoing process of urbanization, the concept of “complex development of residential areas” appears, on the basis of which the population is served, landscaping, engineering equipment, transport support (servicing institutions were taken at the rate of 0.5 - 0.75 m2 per person ).
Since the end of the 20th century, residential complexes have been created that, due to optimal functional saturation, increase the efficiency of urban land use. Among the functional areas of the complex are: residential area; office area (offices, bank branches, legal offices, bureaus, etc.); service area (trade, restaurants, concert and sports halls); transport; technical.
Thus, the MFLC is a single, integral and at the same time complex urban planning object that combines such functions as: residential, public, transport, etc.
The MFLC is characterized by high efficiency in the use of the urban area; engineering infrastructure; improvement.
MAIN STAGES FOR THE FORMATION OF THE IFJC
Table 1
TYPES OF MFLC
table 2

Internal infrastructure of the complex club type - specific. It has, for example, a reception hall, a billiard room, a sauna, a gym, a wine cellar, here it is free, since everything is included in the cost of operation. At the same time, it is assumed that residents have their own hairdressers, masseurs, doctors, tailors, etc., who come on call. The block of service establishments is available only to residents and guests of the complex.
INelite complex there are practically no places for joint stay of residents, but at the same time a service block is significantly developed, which is available exclusively for residents of this complex.
INcommercial complex service is available not only to residents of this complex. As a rule, the business component of service is significantly developed in the structure of this type of MFLC. In our project, it is this type of MFLC that will be accepted for design under the name "Residential building with service."
Table 3

Below is a detailed functional diagram of the MFLC. For our project, it is important to understand the need to include three main components in the planning structure of a residential building. The specification of the composition of these components should occur at the pre-design stage of design.
Table 4

It can be noted that at this stage, the domestic and foreign practice of designing the MFLC are similar. When forming large complexes, it is necessary to take into account various factors (social, economic, urban planning, etc.)
PRE-DESIGN ANALYSIS
The design of a serviced residential building (MFHC) is based on a multifactorial analysis of the urban development situation:
Determination of the belonging of the territory to the urban functional zone;
Determination of the place of the territory in the transport and planning structure of the city, (with
in order to identify the belonging of this territory to the main transport and planning axes of the city). Considered power and proximity transport hub, the prospect of its development or its exhaustion;
The actual functional load of the territory adjacent to the design area is investigated;
Study of the building support fund with fixation of monuments of architecture, history and culture;
Based on this analysis, a decision is made on the formation of the composition of the groups of the complex: typology of residential, public and transport (garages, parking lots).
Compiled together with the teacher design assignment (or terms of reference).
TYPOLOGY OF IFJC
As mentioned above, according to the internal infrastructure of the complex, three types of complexes can be identified: club type; elite type and commercial type.
In our projectcommercial type will be accepted for design.
MARCHI offers the following classification:
IFJK 1 rank- belongs to a powerful transport hub with underground and several ground transport routes, located on the main planning axes of the city center development. In a complex of the 1st rank, a public group may have an expanded composition and include objects of citywide significance. Depending on the capacity of the transport hub, the capacity of public and business institutions of the MFJK of the 1st rank can be accepted by 10 - 20 thousand employees. In the general balance of the areas of such a complex, a residential group can be up to 30%. If the complex is located above the transport hub, then the residential group can be represented by specific types that are not designed for permanent residence (studio apartments, offices with apartments, hotels, private boarding houses)
IFJK 2 ranks occupy less important town-planning situations. Such complexes are formed on the axes of planning areas, where passenger traffic is provided by underground and surface modes of transport. Estimated number of employees
social and business institutions accept up to 12 thousand people.
The public part does not include unique objects and is focused on trade, food, libraries, leisure and educational centers. The residential group of the complex is 50% total area. It is possible to use all types of housing.
IFJK3 ranks occupy the territory near transport highways - axes residential areas. These complexes may have public and business institutions with up to 5,000 employees, but may be formed on the basis of public and commercial functions. The residential group is 60-80% here. It is possible to use all types of housing.
It is these factors that we will use in our design.
The above typology is not strictly regulatory. It is designed at the stage of pre-project analysis to determine the type and rank of the MFLC, to help in determining the approximate space-planning parameters for drawing up a design assignment.
URBAN PLANNING ANALYSIS
The town-planning significance of the territory has a decisive influence on the location of a multi-storey residential building with a whole range of service premises. It is such a house that we have to design, and it is characterized by high efficiency in the use of urban territory; engineering infrastructure; improvement.
Residential buildings of this type are preferable to be located near highways of urban or regional significance in such a way that they create significant urban dominants.
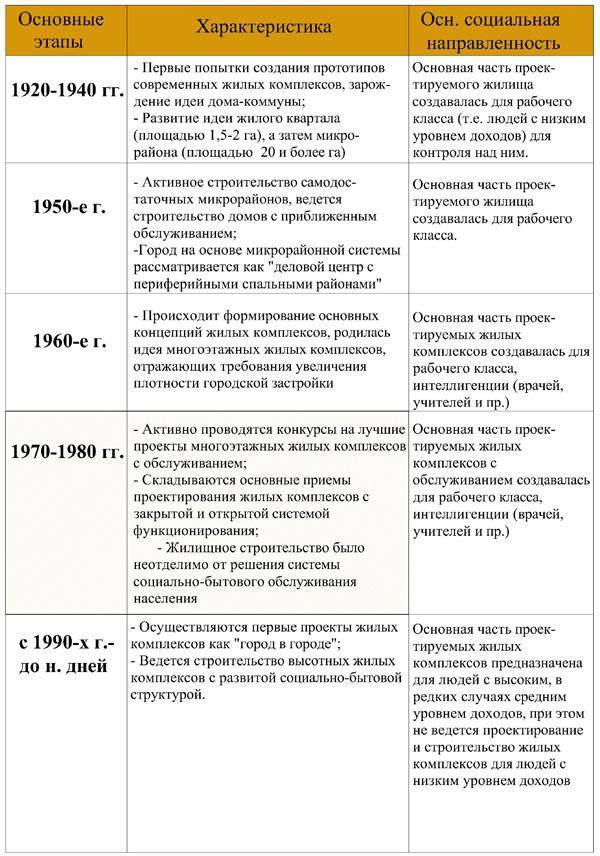
1973 France. Lyon agglomeration. The city of Ile - d * Abo, the population in 30 communes - 250 thousand people. Epida-Skanida building. Arch. F. Dubois.
But at the same time, it must be borne in mind that the economic feasibility of high-rise residential buildings, as a mass product, ends at 25-30 floors. In our project, a residential building should have no more than 25 floors.
The area of the land plot of this category of a residential building can be from 1 ha to 5 ha
Basic requirements for land plot given in SP 42.13330-2011 (updated version of SNiP 2.07.01-89*)
Some of them:
Distances between buildings should be taken on the basis of insolation and natural light calculations, see SNiP 11-4-79, as well as on the basis of fire safety standards (the minimum distance between buildings of 1 and 2 degrees of fire resistance is 6m). Insulating gaps between buildings with windows along the long side must be at least two building heights. Between the ends with windows - at least 1.5 of the height of the building.
The rate of provision of urban population with private vehicles is 300 cars / 1000 inhabitants (ie 1 - 1.5 cars per family or apartment). For public buildings business zone- up to 20 cars per 100 employees. For the service area - from 7 to 25 cars per 100 m2 of total area.
Distances from open parking lots to residential and public buildings, see table 10
(10 cars - 10m; 11-50 cars - 10-15m).
Drives to the building should be designed with 2 lanes: freight - 2x4 = 8m.; the rest - 2x3 \u003d 6m.
Passage of fire engines (width 5.5 - 6.0 m) from two longitudinal sides for buildings over 9 floors high and from four - for single-section tower-type buildings,
The distance from the edge of the passage to the wall of a building up to 10 floors high is at least 6–8 m, over 10 floors - 8–10 m. (In this “fire zone”, the erection of fences and tree planting is not allowed).
Through passages in buildings should be provided with dimensions - at least 3.5x4.25 (H) m., at a distance of no more than 100 m from each other.
Sizes of the playgrounds of the residential area: for children - 0.7 m2 / person; for adults 0.1m2/person; sports - 2m2 / person; household - 0.8 m2 / person.
The normalized area of landscaping for 1 person is 6 m2.
The above rules are for informational purposes only. With appropriate justification for inclusion in design assignment they are subject to change.
ACCOMMODATION GROUP
Designing a dwelling near transport arteries requires special attention in solving problems such as noise, vibration, gas pollution, etc. In practice, such techniques are used as two-layer enclosing structures (glazed loggias); planning (location of bedrooms from the side of the courtyard, placement of a public and business zone up to the 4th floor), etc.
For the design of a residential group, it is possible to use all types of housing.
In this lecture, we will skip the analysis of the typology of residential buildings, since you have already designed a mid-rise residential building (without elevators), and you should have mastered all the design standards. THOSE. we will not talk about sectional, blocked, gallery, corridor, individual, attic buildings.
We will not talk about the types and composition of apartments, about insolation and natural light. You already know about it and know how to use it.
However, we will consider some aspects related to the design of high-rise buildings according to SNiP 31-01-2003.
First of all, the staircase and elevator assembly requires our attention.
With a building height of up to 9 floors, an ordinary (not “smoke-free”) staircase is used, one elevator 630 (or 1000) kg garbage chute (the largest total area of apartments on the floor is 600m2)
With a building height of 10 to 12 floors, it is necessary to provide an evacuation staircase of the Ist (through the outer air zone) or II (with air overpressure) types, an elevator hall designed for two elevators (passenger and cargo-passenger) of 400 and 630 kg (or 1000 kg), as well as a garbage chute on the intermediate platform of the stairs or in the elevator hall. The largest total area of apartments per floor -600m2
With a building height of 13 to 19 floors, regardless of the type of "smoke-free" evacuation stairs, two elevators (passenger and cargo-passenger) of 400 and 630 kg (or 1000 kg) are required, but with the largest total area of apartments 450 m2
With a height of a residential building from 20 to 25 floors and with a floor-by-floor total area of apartments up to 350 m2, three elevators are required: one - 400 kg. Two of 630 (or 1000) kg.
With a height of a residential building from 20 to 25 floors and with a floor-by-floor total area of apartments up to 450 m2, four elevators are required: two of 400 kg each. Two of 630 (or 1000) kg. Table 5

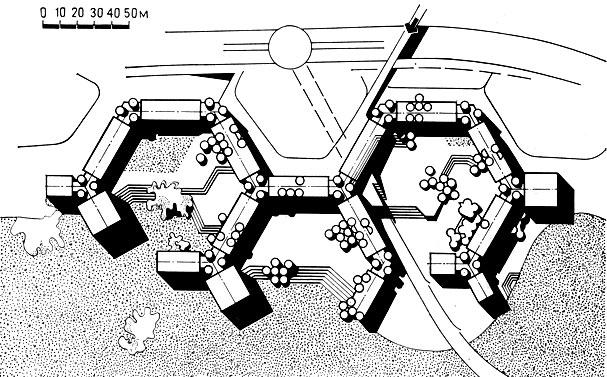
Elevators with a carrying capacity of 630 or 1000 kg should have cabin dimensions of 2100x1100 mm for access by a disabled person or transportation of a person on a stretcher. Elevator shaft dimensions 2900x1750mm Width of the platform in front of the elevators, not less than: for an elevator 630kg. with a cabin 2100 wide and 1100mm deep ("lying") -1.6m .; with a cabin 1100 wide and 2100 mm deep - 2.1 m. With a two-row arrangement of elevators, the width of the elevator hall is assumed to be at least 2.5 m. Elevator shafts are not located adjacent to living rooms.
An example of a two-row arrangement of elevators in buildings up to 25 floors high

If the total area of apartments on the floor exceeds the specified standards, two evacuation stairs should be designed (usual for 9 floors of buildings and smoke-free for all others).
As the 2nd evacuation entrance, it is possible to provide for a staircase of the 3rd type (external), or a blind wall on the balcony 1.6m. Evacuation stairs must have an exit directly to the outside or a vestibule separated from adjacent corridors by type 1 partitions (with a fire resistance limit of 45 min.)
Ladder 3 types.

An example of a staircase-elevator assembly with a smoke-free staircase of type 1 in a building up to 19 floors high.

The greatest distance from the door of the apartment to the evacuation stairs is 25m. and 40m when located between stairwells.
The norm of the total area of an apartment per person is: in club-type houses (business class) - 40m2; elite housing - 30 m2; commercial (social) housing - 20 m2. In Krasnoyarsk, the average indicator of the norm of the total area per 1 person is 24 m2.
For reliable operation of engineering systems that provide favorable conditions for the functioning of all groups of the building, it is necessary to provide technical floors - upper and lower. The lower technical floor, which separates the residential from the public area, will also make it possible to move from a small step of the supporting structures of the housing to a large module of the public group (for example, the use of a coffered floor, etc.). Roofs should be designed with an internal drain.
PUBLIC AND BUSINESS GROUP
The palette of the public and business group of the building is extremely wide (see the right side of Table 4).
For a list of public institutions prohibited for placement in residential buildings, see SNiP 2.08.01-89 * a. namely: catering establishments with more than 50 seats; stores with a trading floor area of more than 1000 m2; specialized stores (construction, moscow-chemical, sale of explosives, specialized fish and vegetable), baths; saunas; laundries, dry cleaners: public toilets, funeral homes.
The composition of service establishments is regulated only design task to be compiled by each of you .
When designing objects of a public and business group, one should be guided by SP 118.13330.2012 (updated version of SNiP 31-06-2009).
A serviced residential building, as an important town-planning object, should form a single whole with all its functional groups. And at the same time, each group should be as isolated as possible, have independent entrances.
Entrances should be located in a pedestrian area at ground level or a pedestrian platform.
The public and business group is usually located in the stylobate part, which may have several floors, but may be built into the residential part.
Slope of evacuation ladders - no more than 1/2; slope of ramps inside the building - no more than 1/6; slope of ramps outside the building - no more than 1/8; the slope of the ramp for wheelchair users inside and outside the building is 1/12. Minimum Width march - 1.35m. The number of rises (risers) in the march is not less than 3 and not more than 16.
Each floor of the building must have 2 emergency exits. As the 2nd exit, it is allowed to use a type 3 staircase (external) with a slope not steeper than 1/1, or a non-combustible roof.
The distance between evacuation exits (stairs) is standardized similarly to housing, elevators are also standardized.
Conference halls should be provided at the rate of 1.1 m2 per person, the area of the lobby - 0.4-0.6 m2 per person. The number of continuously installed seats in a row should not exceed 26 for one-way exit from the row and 50 for two-way exit.
The area of the lobby is 0.3 m2, wardrobe - 0.15 m2 per person.
Bathrooms are designed on the basis of: men - 1 toilet for 20-30 people and 1 urinal for 15-18 people; women - 1 toilet for 15-30 people; washbasin - 1 appliance for 2 toilet bowls.
The multi-storey part of the public and business group is often designed with the use of atriums and passages. This allows you to illuminate with natural light the premises located in the depths of the building, as well as create a light communication block.
Atrium- this is a part of the building in the form of a multi-light space of 3 or more floors developed vertically. An atrium developed horizontally in the form of a multi-light passage (with a length greater than the height) is called passage.
The height of the atrium is limited to 10 floors (approximately 30m), whereas in foreign practice there are no such restrictions. For example, in the building of a commercial bank in Frankfurt am Main, the height of the atrium is equal to the height of the building - 260m.
The location of unloading sites from the side of the residential yard is prohibited.
AUTO S T O Y N K I
In this lecture, we will skip a detailed analysis of space-planning solutions for car parks, since you have already designed a parking lot, and you should have mastered all the design standards. However, we will consider some aspects according to SNiP 21-02-99.
As a rule, parking lots are located in the underground part of the stylobate, but they can be located in the ground or above-ground part. In the underground there can be no more than 5 floors, in the overground no more than 9 floors. Parking lots cannot be located under the residential part, under children's and medical institutions.
Parking can be carried out with the participation of drivers and without the participation of a mechanized way (provided that no more than 30 cars are placed on the floor).
Entry and exit from the parking lot is carried out by ramps: one single-track ramp 3.5 m wide for 100 cars; one double-track ramp 6.0 m wide - up to 1000 cars on all floors (or two single-track ramps).
Ramp slope: open - no more than 10% (per 1 meter of rise - 10 meters of length); closed no more than 18% (per 1 meter of lift - 6 meters of length); curvilinear - by more than 13% (for 1 meter of rise 8 meters of length), with an inner radius of 4.5-6m.
The floor height is assumed to be 2.5 m, but not less than 2.1 m to the bottom of the protruding structure.
The size of the parking space is 2.5x5m. The width of the passage between parking spaces is at least 7.5 m (this circumstance should be taken into account when assigning a constructive step).
Underground parking lots are divided into fire compartments with an area of 3000 m2; elevated multi-storey - 5200 m2, single-storey - 10400 m2
At least 2 evacuation exits are provided from each compartment
The distance to the emergency exit should be: at a dead end 20m and 40m between the exits in the underground parking; to a dead end 25m and 60m between the exits in the elevated parking.
Entrances to the underground parking and ventilation shafts should be no closer than 15m. from residential and public buildings.
The use of the same stair-lift units for the underground and above-ground parts is not allowed.
If the exit from the parking is to the lobby, then it is necessary to provide a tambour-lock with air overpressure.
VOLUME OF M N O - P L A N I R O V O C N E INDICATORS.
The project must specify the following indicators:
Land area.
Building area (determined by the circumference of the outer edge of the basement)
Floors of the building (includes all above-ground floors and all technical)
Number of floors (all floors are taken into account - above ground and underground)
Construction volume of the residential group (aboveground + underground).
Construction volume of a public and business group (aboveground + underground).
The total area of the public and business group (determined by the inner contour of the outer walls).
Number and composition of apartments.
The total area of apartments (defined as the sum of all the premises of the apartment, including loggias with a coefficient of 0.5; balconies and terraces with a coefficient of 0.3)
S O S T A V P R O E C T A
situational diagram.
General plan of the site M 1:500.
Facades of the building M 1:100 and (or) 1:200
At least 2 cuts M at least 1:200
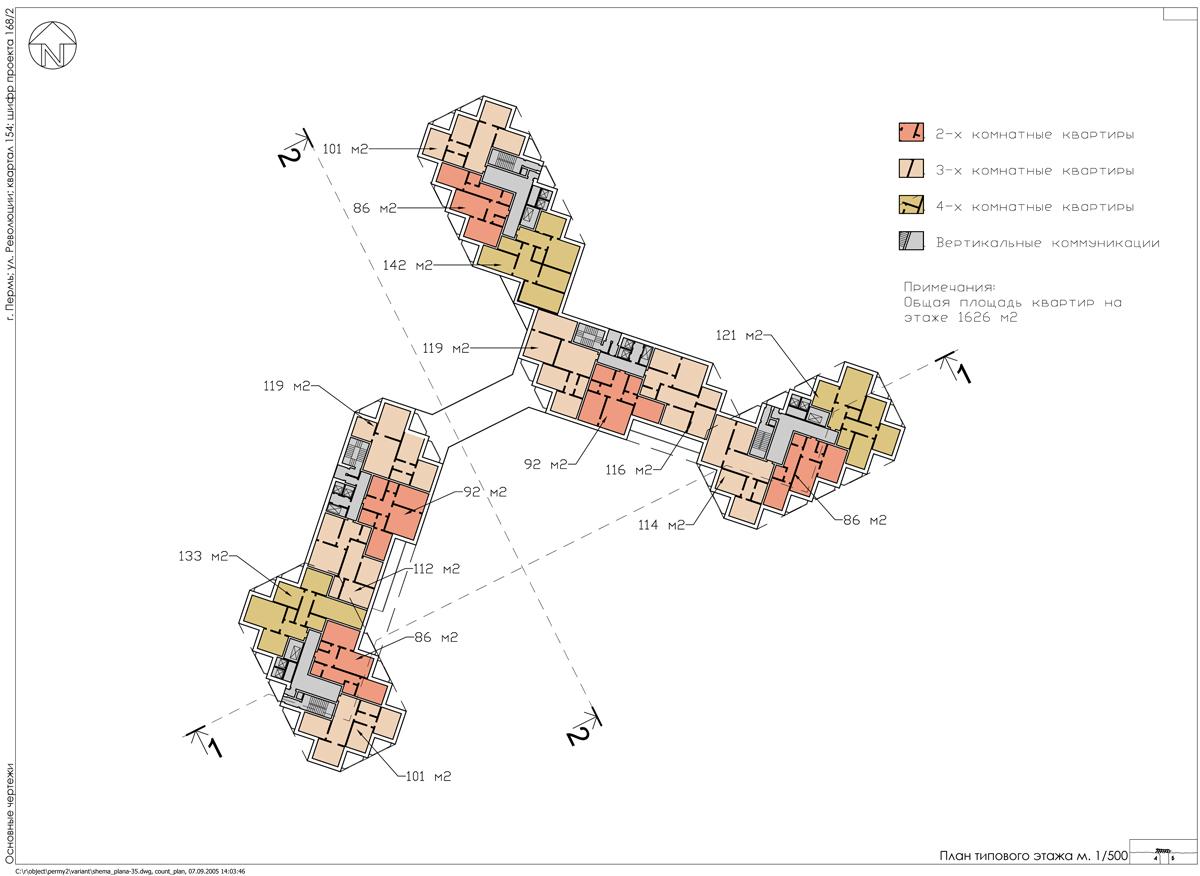
Floor plans: residential group - typical floor M 1:100 and (or) 1:200,
stylobate - all floors including underground M not less than 1:200
Apartment plan M 1:50
3D visualization
Volumetric planning indicators.
Multiple explanatory note
Working layout.
The volume of demonstration material is 1.5 (?) - 2.0 m2.
APPENDIX A DRAFT COMPOSITION IS VOLUME

course project. Diploma "Golden Capital 2013"

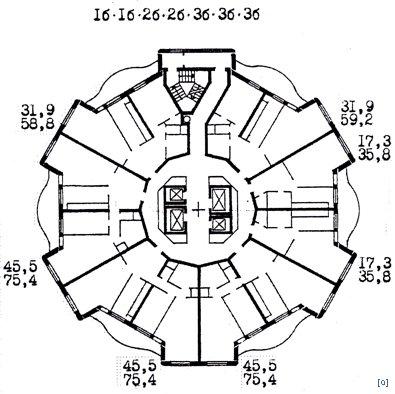
Dormitory "Star of Sauron" - course project, Tomsk.

course project.

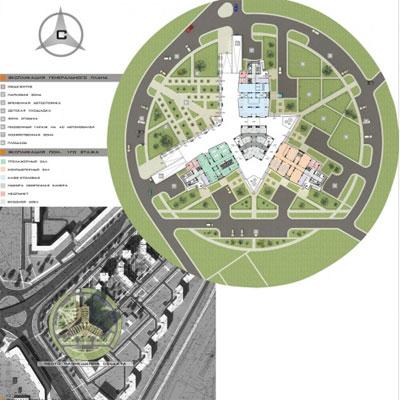
 Multi-storey residential building in St. Petersburg
Multi-storey residential building in St. Petersburg
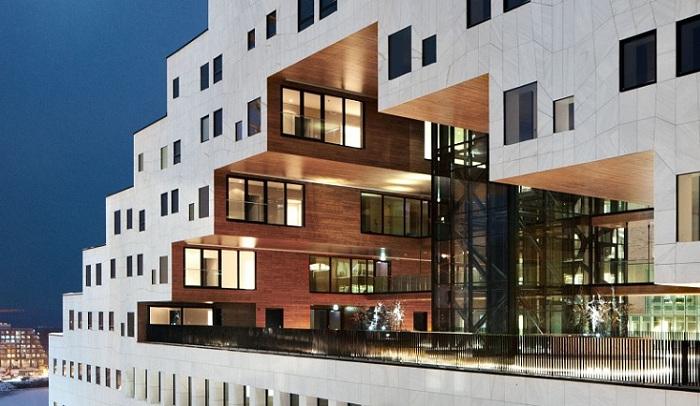



The Carve (Econet.ru)

Multifunctional complex in Minsk: high-rise residential building with service; multifunctional 35-38 floor Building (2-level underground parking, 2-5 floors. Service, including a physical and health zone, food, trade, public services, above - residential apartments and offices); through the elevated passage - the hotel.

Bashkiria, Ufa. "Ufa Kremlin" business class. 9 multi-storey residential buildings with penthouses and built-in-attached facilities of the KBO, an office, retail and hotel complex with banks and underground parking, a kindergarten, a school.
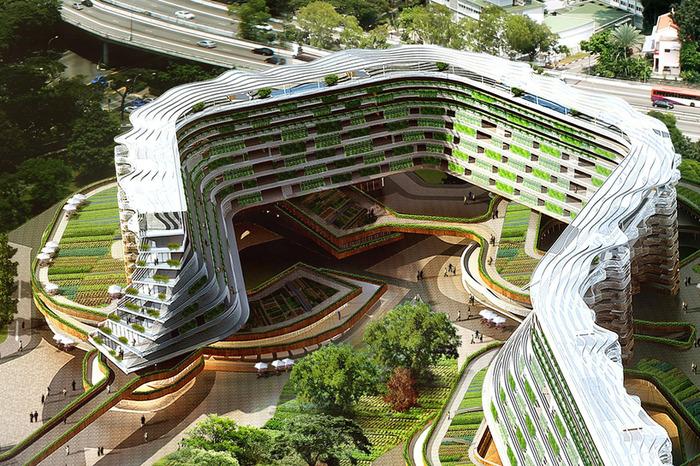

Farm building in Singapore.
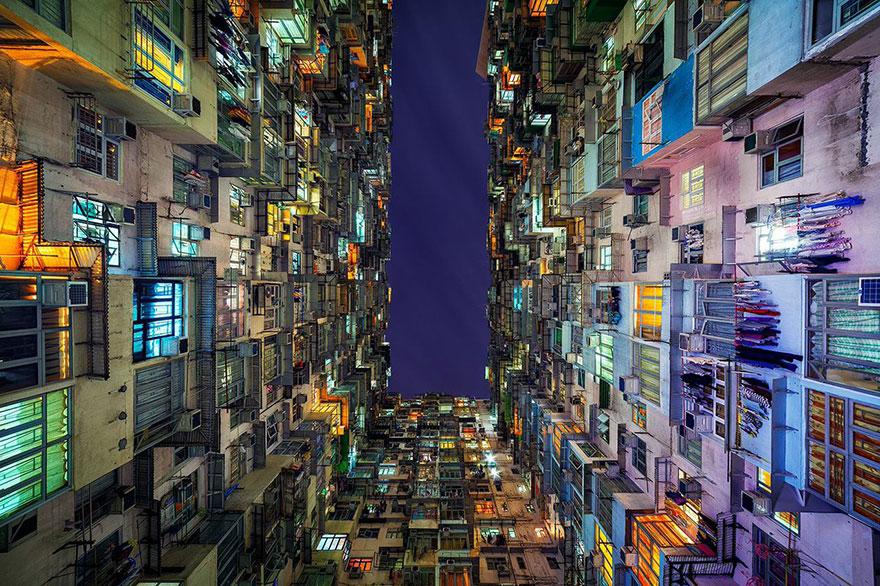

Residential development in Hong Kong.
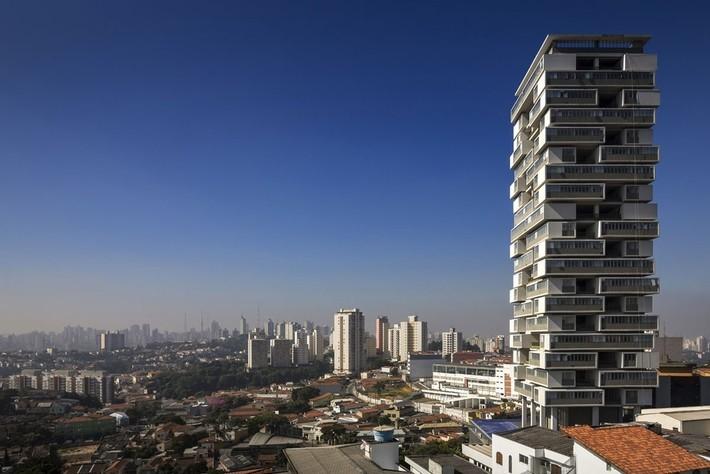

Brazil. Sao Paulo. 20-storey residential building "360*"
Each apartment has its own yard. Entrance vestibule on the 2nd floor, where a bridge over the pond leads from the street. Below is a gym, lounge, party room, concierge apartment. Below - 3 tiers of parking. Even lower are staff apartments, a sauna and an outdoor pool.