The main material for the device overlap in modern construction is reinforced concrete.
Reinforced concrete floors are divided into prefabricated, assembled from prefabricated prefabricated elements, monolithic, concreted in the formwork at the site of the structure being erected, and prefabricated-monolithic.
Before development and implementation in the practice of building prefabricated structures reinforced concrete floors were made monolithic.
1.3.1.Monolithic floors - non-industrial, labor-intensive, require the consumption of timber for formwork and a large number become. In modern construction, monolithic ceilings are used when they are the main element that ensures the spatial rigidity of the building, in buildings complex shape(V plan), as well as with significant dynamic loads on the floors.
Depending on the load, spans up to 3m can be covered with a smooth slab 60-100mm thick. For spans of more than 3 m, ribbed ceilings are arranged (Fig. 9.5), consisting of a slab (3); main beams (purlins) (1); and secondary beams (ribs) (2). The distance between the main beams is from 4 to 6 m, and between the ribs with a plate thickness of 70-100 mm - from 1.5 to 3 m. multi-span beams are a continuous structure. The supports of the main beams are columns (or load-bearing walls), the supports of the ribs (secondary beams) are the main beams (girders).
To obtain a smooth ceiling with a ribbed ceiling, plaster is laid on a steel mesh attached to the ribs from below, or sheets of dry plaster are attached to special hangers, the so-called suspended ceiling. On the upper floor, a smooth ceiling can be obtained by installing a monolithic reinforced concrete floor with the ribs up. Ribbed ceilings have a rectangular grid of columns.
Rice. 9.5. Monolithic reinforced concrete floors. 1 - main beam; 2 - secondary beam; 3 - plate.
In the case when the distances between the columns in both directions of the overlapped room are the same, the ceilings can be coffered type, i.e. the main and secondary beams have the same section height.
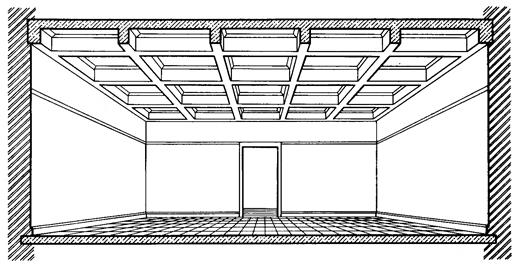
Rice. 9.6. General view of the reinforced concrete monolithic coffered ceiling.
In this case, rectangular or square recesses are formed on the ceiling, in French - caissons. Economically, coffered floors are less profitable than conventional ribbed ones, and their use is justified mainly by architectural considerations.
The advantage of monolithic reinforced concrete slabs lies in the effect of increasing rigidity due to the formation of a solid disk. The minimum height of a solid slab should be 1/35 of the span. Reinforced concrete single-span slabs of solid section are economical only with spans up to 4.5 m; they are also beneficial in acoustic terms due to the large mass.
monolithic iron concrete plates reinforced in one or two directions with steel mesh. The upper reinforcement of the edges of the slab serves to protect its supporting parts from crushing the overlying load or for embedding into the wall. The upper reinforcement above the supports in continuous slabs serves to absorb tensile forces from negative bending moments.
Currently, the supply of fully prefabricated concrete to the construction site is carried out in cars, which leads to the absence of expensive concrete mixing equipment at the construction site, guarantees the quality of the concrete mixture, and eliminates noise sources from the construction site. The erection of slabs made of concrete delivered to the job site has become significantly more economical due to the development of efficient formwork systems.
Monolithic ceilings include ceilings on steel beams with monolithic filling (Fig. 3).
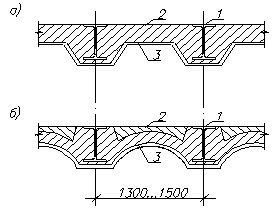
Rice. 9.7. Monolithic ceilings on steel beams: a - ribbed; b - arched; 1 - steel beam; 2 - monolithic reinforced concrete; 3 - grouting the surface.
Design characteristics
Ceilings consist of a bearing part, which transfers the load to individual supports or walls, and an enclosing part, which includes ceilings and floors. According to the material of the bearing part, it is possible to distinguish reinforced concrete (reinforced concrete) floors, for steel and wooden beams, ceramic and armosilicate. The cost of floors and ceilings will reach 20% of the total cost of the house. The consumption of reinforced concrete for the ceiling will be up to 60% of the total consumption.
It should be understood that the cost of overlapping should be minimal.
In modern construction, the main material for the construction of floors is reinforced concrete. from reinforced concrete (reinforced concrete) can be divided into monolithic and prefabricated, concreted in the formwork. IN Lately for the first floor, only monolithic reinforced concrete floors and prefabricated ones are used. The prefabricated ones allow you to block the span up to 12 m. Speaking of which one is needed, you should know that the consumption of this mortar per 1 m² will be 0.223 m³, and steel - 6.5 kg. This expense is approximate and may vary slightly.
It is worth knowing that floors must necessarily meet the requirements of rigidity, strength, fire resistance, durability, sound and heat insulation, if they separate heated rooms from the outside environment or from unheated rooms. Ceilings in the premises where wet processes, must be waterproof, and in rooms in which gases are released, gas-tight.

IN country houses with brick walls, most often people prefer precast concrete floors with round voids. Their length is from 4800 to 6980 mm, width - from 1000 to 2400 mm, and height - 220 mm. Structures with flat voids 2700-4200 mm long with a gradation of 300 mm, 1200-1500 mm wide, 120 and 160 mm thick are also used.
Panels for the ground floor should be laid on a layer of freshly laid masonry mortar 10 mm thick, embedded on the support at least 120 mm. With a step of 2400-3000 mm, they are connected through one panel with anchors with a diameter of 8-10 mm. The anchors are attached to the hinges and driven into the masonry 250 mm from the end of the panel. It is necessary to finish with a bend at an angle of 90 degrees horizontally by 380 mm.
The seams between the panels are filled with cement mortar. Speaking about what composition should be, it is worth knowing that it is 1: 4 by volume. Installation of panels is carried out with the help of truck cranes.
Reinforced concrete floor installation
Similar designs for the first floor have some valuable qualities. The main ones are durability, high strength and fire resistance. In order to reduce the number of butt joints and assembly operations, when designing the structures of elements of prefabricated reinforced concrete floors (reinforced concrete), it will be necessary to strive to enlarge them.
Next, we will talk about precast concrete floors. It is divided into 3 main groups: beam, large-panel and in the form of flooring (slabs). The structures in the form of decks will consist of flat or ribbed elements of the same type, which are stacked closely. Speaking about which connection method to use here, it is worth knowing that you need to fill the gaps with cement mortar.
Similar structures for the ground floor consist of a reinforced concrete bearing part, a thermal and sound insulation layer and a floor structure. The walls and girders will serve as supports for the decks. The most common are hollow decks, having a height of 160 mm if there is a span of up to 4 m, and 220 mm if there is a span of more than 4 m.
In the process of manufacturing floorings with vertical voids, the consumption of concrete will be 15% less than with round-hollow floorings. Round vertical voids are formed using pipe liners (the liners are welded to the channels). Floorings that can cover entire rooms are called large panels. In this case, the cost will be less. The absence of joints in the panels within the rooms will increase their sound insulation and provide a higher quality ceiling finish.
In order to provide standard soundproofing properties from airborne noise, single-layer structures of panel ceilings on the first floor, which are made of heavy concrete, must necessarily have a mass that exceeds 300 kgf per 1 m².
During the installation of separate type ceilings, in which the soundproofing capacity of the air gap between the lower and upper panels of the precast concrete floor is used, and when installing layered ceilings, it will be possible to ensure the soundproofing normative ability with a floor weight of less than 300 kgf per 1 m².
Interfloor large-panel reinforced concrete (reinforced concrete) ceilings by design can be with a layered floor, with a layered floor and a separate ceiling, of a separate type (from two separate load-bearing panels, with a separate ceiling or with a separate floor). All of the above floor structures have a relatively small mass (less than 300 kgf per 1 m²). Normative sound insulation can be provided by a layered floor structure or by the presence of a continuous air layer in the thickness.
Floor panels for the first floor are made solid, hollow (having round voids) and tented. A single-layer load-bearing panel is a reinforced concrete slab with bottom surface constant section, which is ready for painting, and the top is flat.
Single-layer solid reinforced concrete (reinforced concrete) panels, which have a thickness of 140 mm, can cover a span of up to 3.6 m. 16 cm, or expanded clay-reinforced concrete, which have a thickness of 18 cm.
The hipped panel has the form of a slab, which is framed along the contour with ribs facing in the form of a cornice. they are also arranged from flat reinforced concrete panels having a thickness of 14-16 cm. The type of overlap will depend on which span should be blocked. The maximum span is 12 m.
Installation of a beam structure
Interfloor prefabricated reinforced concrete structures beam type consist of T-beams and filling between the beams. The filler in this case will be a roll of lightweight concrete and gypsum concrete slabs, having a thickness of 80 mm and a length of 395 mm, reinforced with slatted wooden or bar frames. In the attic floors - lightweight concrete slabs, which have a thickness of 90 mm and a length of 95 mm, reinforced with welded steel mesh.
Seams in slabs and beams are filled with cement mortar and rubbed. Ground and attic floors it is imperative to insulate, and interfloor - soundproof. To do this, sand or expanded clay bedding, a layered coating with an elastic gasket should be used in the slabs.
It is recommended that sound and heat insulation in slabs be carried out not by means of weight gain. building structures. Due to the fact that the elements of beam structures have a relatively small weight, they are often used in buildings that are equipped with low-capacity cranes (about 1 ton).
In the process of installing reinforced concrete beam floors in sanitary facilities, a waterproofing layer should be included in the slabs. For this, 1-2 layers of roofing material on bituminous mastic are most often glued over the flooring or panels for this. Beam ceilings are used if it is necessary to cover a span of 3-7.5 m.
Installation of monolithic buildings
Monolithic structures are made according to pre-installed formwork. Such ceilings on slabs will serve as an additional rigid frame of the building in the process of transferring the load to the load-bearing walls from the floor. Their device requires a certain professional skill. It must be carried out according to the project under the guidance of a specialist builder.
Manufacturing such structures in situ has some advantages. To do this, you do not need to have special transport or any lifting equipment. To move and raise concrete, it is enough to have small-scale mechanization.
The basis monolithic structures embedded in the Monier plates. In it, the reinforcement is placed in places of tension, meaning the lower part of the slab. This is due to the fact that steel has a tensile strength 15 times greater than concrete. The reinforcing frame of the slab should be located at a distance from the formwork walls at a minimum distance of 3-5 cm. This is necessary so that the concrete can fill this space.
The span, which is covered with a monolithic slab, should have a maximum length of 3 m. For plumbing pipelines, care should be taken to install metal or vinyl sleeves that have an inner diameter larger than the pipeline being laid. The gap of the pipeline and metal sleeves must be minted with tarred tow.
The disadvantage of such monolithic structures is the installation of wooden formwork over almost the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe house. However, this does not mean at all that it is necessary to expose the formwork all at once. Overlapping can be performed in separate spans, while transferring the formwork as the concrete sets.
Formwork installation
For the installation of a monolithic reinforced concrete floor, it will be necessary to install a horizontal removable formwork.
Such formwork can be made of wooden panels (from cut boards that have a thickness of 25-35 mm) or waterproof plywood that has a thickness of at least 20 mm. If the formwork panels, which are made of boards, have gaps, a layer of waterproofing film is needed over the formwork. It will be needed so that the liquid solution cannot flow out.
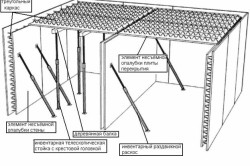
Removable formwork should be laid on transom beams, which will be supported by supporting vertical posts. Racks can be telescopic, made independently from round timber with a diameter of 8-15 mm and beams, or factory-made.
The formwork must be installed without gaps, strictly horizontally. Steel reinforcement in the form of a mesh with cells measuring 200x200 mm is laid and tied using a soft knitting wire along a horizontal structure.
Rebar frame
The reinforcement on the formwork is laid in such a way that a gap of at least 25 mm remains between it and the formwork. To do this, use standard special plastic coasters or make them yourself from wood, plywood or other material. What material to choose is up to everyone. Any of the above will be needed.
The diameter of the steel reinforcement that is used to arrange a monolithic reinforced concrete structure will depend on the size of the floor and the load it will carry. It can be in the range of 12-20 mm.
Depending on the strength of the monolithic reinforced concrete floor, there may be 1 or 2 rows of reinforcement. The second row of steel reinforcement is laid on supports made of reinforcement, which are pre-installed on the bottom row and secured with soft tie wire. The height of the supports will depend on the thickness of the reinforced concrete structure being made.
The maximum consumption of reinforcement per ceiling will be 15-20 kg. It is worth knowing that the consumption may be less.
Comments:
- Reinforced concrete floors - the main panels in the construction business
- What are monolithic panels?
Floor panels are the main part of any building. They include load-bearing elements that load the walls, or individual supporting elements. According to the material of the bearing element, reinforced concrete structures are distinguished. The price of floors is 20% of the total cost of the building.
The composition of the floor panels contains load-bearing elements that exert a load on the walls.
Reinforced concrete floors - the main panels in the construction business
Currently, potential developers prefer to take panels made of reinforced concrete material. In turn, they are divided into:
- Prefabricated.
- Monolithic.
Panels must have characteristics such as strength, rigidity, fire resistance, reliability, and quick installation properties. If a building is being built where high humidity is implied during operation, then the floor panels must be resistant to moisture. In country houses, you can often find the use of these structures made of reinforced concrete panels with the presence of round voids. Basically, their length can reach up to 6800 mm, and their width - up to 2400 mm.

Reinforced concrete structures have a huge number of advantages. They have high strength, long service life, and most importantly, they are fire resistant. When creating a project for the construction of a house or any other building, potential developers try to enlarge them in order to reduce the number of installation actions and butt contacts. Prefabricated type reinforced concrete floors are divided into 3 main classes:
- In the form of flooring (tiled form).
- Large-panel.
- Beam.
Deck-shaped structures have flat or ribbed components of the same type in their composition, which must be mounted tightly. Their connection is carried out by means of a special cement mortar. Consequently, they include load-bearing reinforced concrete parts, which have high rates of thermal insulation and sound insulation.
Back to index
Interfloor large-panel reinforced concrete structures
According to the design features, interfloor large-panel structures made of reinforced concrete may have a layered floor. They are lightweight, soundproofing abilities are carried out using a special layered floor structure or the presence of a continuous air gap in the thickness of the ceiling. The floor panels themselves can be solid, hollow and hipped. The hipped panel is a special type of slab, which is framed along the contour with ribs. The ribs are always directed downward.
Ceilings are horizontal elements of a building that divide its internal space into floors and perceive permanent and temporary loads. Overlappings are classified according to the following criteria: by location in the building - basement, interfloor, attic; By beam structures and beamless; according to the material - reinforced concrete (prefabricated and monolithic) and wooden.
Overlappings must meet the requirements of strength, rigidity, soundproofing, industrialism and economy. Depending on destination individual rooms ceilings must meet the requirements of water tightness, thermal insulation, fire resistance, etc.
Floor panels can be solid (single-layer and layered), hollow, ribbed.
Solid flat reinforced concrete slabs are made 3.6 - 6.3 m long, 2.4 - 7.2 m wide, 120 and 160 mm thick. They are used in the ceilings of large-panel prefabricated buildings and are supported along the contour (on three or four sides).
The most common are multi-hollow panels with round voids (Fig. 7a).
They are most often made from concrete of class B15 and B25 with a length of 2.4 to 7.2 m and a width of 1-1.8 m with a thickness of 220 mm.
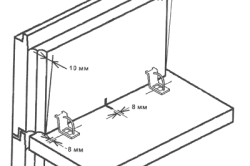
Floor panels are laid on walls and girders on a layer of cement mortar. The ends of the panels must rest on the walls at least 100 mm (more often 120 mm.). The voids at the ends of the panels are sealed with lightweight concrete. This is necessary to protect the panel from crushing, as well as to improve heat and sound insulation. On the outer walls, the ends of the panels are anchored into the masonry, and when laid on the inner walls or girders, they are attached to each other with anchors. Such fastening provides a rigid connection between floors and walls, which largely determines the stability of the building.
The joints between the panels are filled with cement-sand mortar grade 100.
floors
Floor Requirements:
strength (resistance to abrasion and crushing), rigidity (quietness when walking), hygiene (easy to clean from dust and dirt), ease of use, decorative, industrial, cost-effective.
Depending on the purpose and nature of the premises, special requirements are imposed on the floors: water resistance, fire resistance, etc.
According to the type of material, the floors can be wooden (plank, parquet, wood fiber), ceramic, cement-mosaic, roll materials.
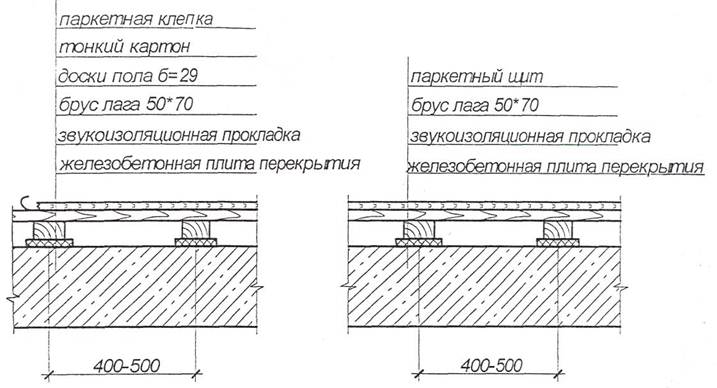
Plank floors are made of tongue-and-groove boards 29 mm thick, nailed to the logs.
If the floors are made on the ground (Fig. 8, a), then the logs are supported on brick or concrete columns 200 - 250 mm high. On the posts for isolating the lag from capillary moisture, under wooden antiseptic pads, two
Rice. 7. Prefabricated reinforced concrete slabs a) multi-hollow; b) solid flat.
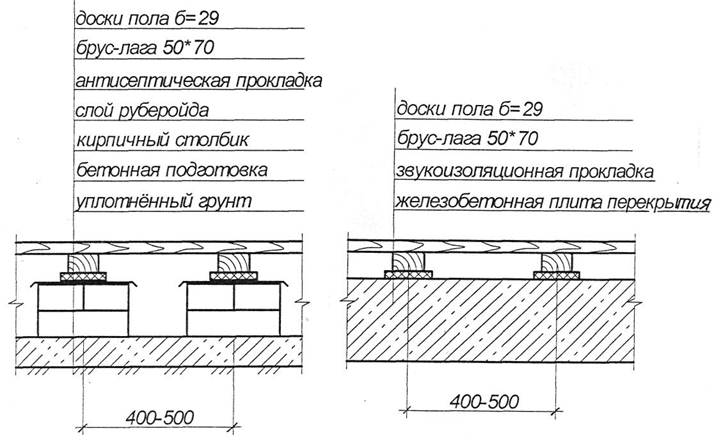
Rice. 8. Plank floors a) on tongue and groove; b) on the floors.
roofing layer or roofing material layer. The distance between the lags (span of the floor structure) is taken equal to 500 - 600 mm.
If plank floors are made along the floors (Fig. 8.6), then the antiseptic pads on which the logs rest are laid directly on the floor slabs.
The floor surface is planed by machines, the seams between the boards are puttied, the floor surface is painted with oil paint 2 times over the drying oil layer.
Parquet floors are assembled from parquet staves (slats) 16 mm thick, made from hardwood: oak, beech, maple, less often from coniferous species (Fig. 9). The edges of the rivets have grooves and ridges. The rivets are connected to each other in a tongue and groove.
If the floors of the type-setting parquet are made along the interfloor ceilings, then the parquet riveting is laid on a solid boardwalk laid on the logs through elastic antiseptic gaskets. When laying a parquet floor on a wooden base, a layer of cardboard or several layers of thin paper is preliminarily laid to prevent creaking when walking. Parquet is fixed to the boards with nails nailed into the grooves of each riveting, such a parquet floor is expensive and laborious.
Block parquet is sometimes also laid on a cement-sand screed or on a poured asphalt concrete screed. This floor construction on floors is rarely used, more often - in floors on the ground.
Industrial parquet floors are made from factory-made parquet boards.
The surface of the boards is machine-sharpened, polished and impregnated with parquet lacquer or wax mastic.
Ceramic tiles have high abrasion resistance. The disadvantages of floors include rigidity and a large amount of heat absorption (cold floors), as well as significant construction labor intensity. Ceramic floors in dry rooms (lobbies, stairwells, etc.) are laid along a layer of cement-sand mortar on an underlying layer of lightweight concrete (Fig. 10, a).
In rooms with high humidity, the floor construction provides for a waterproofing device - 2 layers of roofing material on hot bitumen along the underlying layer. Waterproofing is brought to the wall above the plinth.
Cement-mosaic floors are made from a mixture of cement-sand mortar and colored small crumbs of stone up to 25 mm thick on a cement screed 20 mm thick. The covering of the mosaic floors is separated by strips of glass or brass to make an ornament (Fig. 10.6). This prevents the appearance of shrinkage cracks. After grinding the hardened surface, the coating acquires a unique pattern with a variety of color shades. Such floors are decorative, low-fading, waterproof, but cold, so they are laid in lobbies, trading floors, and other premises intended for short stay of people.
Rice. 9. Parquet floors, a) type-setting (piece) parquet; b) panel parquet.
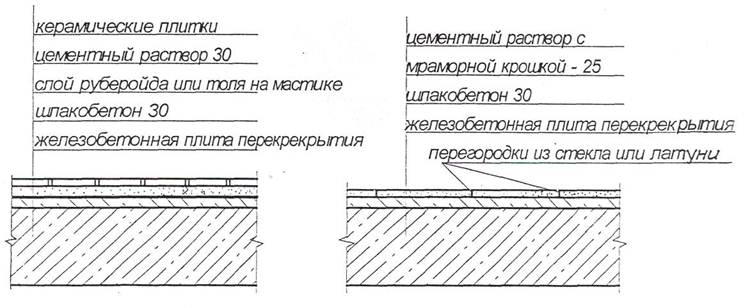
Figure 10. a) ceramic floors; b) cement-mosaic floors.
There are several ways to build floors:
- Use floor slabs.
- Construction of a monolithic reinforced concrete floor.
- The device is a prefabricated-monolithic version.
- Laying of wooden crates, subsequent flooring of drywall or wooden flooring.
Hollow-core floor slabs have a number of significant advantages over other methods: - Hollow-core floor slabs are manufactured industrially, ensuring compliance with all manufacturing standards and the specified design load; - reinforced concrete floor slabs are installed with minimal labor costs and the highest speed of construction, whether it is the installation of a reinforced concrete slab for a private house or a high-rise building; - reasonable price for hollow core floor slabs, relative to other options. In the construction of prefabricated buildings, wall panels are used, using concrete floor slabs in this case it is possible to increase the speed of the process, while the construction resembles a large constructor. Typical dimensions wall panels are ideal for attaching reinforced concrete slabs, creating a solid frame.
In the construction of prefabricated buildings, wall panels are used, using concrete floor slabs in this case it is possible to increase the speed of the process, while the construction resembles a large constructor. Typical dimensions of the wall panel are ideal for attaching a reinforced concrete slab, creating a solid frame.
Production of reinforced concrete floor slabs
According to the types of floor slabs, hollow slabs are made in special metal forms (formworks) with different outlines of voids. A pre-prepared reinforcing cage is lowered into the mold, after pouring the concrete mixture, poissons are introduced - special pipes that will determine the hollow shapes of the slabs. It is important which form is used - the price directly depends on this. The most important criterion for selecting a manufacturer is the quality of products, confirmed by the relevant certificates, it is on this basis that manufacturers of floor slabs are selected - Ryazan Concrete Concrete Plant No. 2, Eco Yaroslavl.









