Page 1
The pivotally movable support (support B in Fig. 118) makes it possible, in addition to rotations, to move the end of the beam parallel to the reference plane. In accordance with this, the reaction of such a support passes through the center of the hinge and.
The first type is a cylindrical movable or pivotally movable support. It consists of an upper balancer attached to the system, a lower balancer, a cylindrical hinge placed between the balancers, and rollers that can move along the reference plane. Such support allows rotation of the system around the hinge and translational movement along the support plane.
Although this ray represents five constraints, it is actually statically defined. A statically indeterminate structure is one where there are more unknown than static equilibrium equations. This is different from the global zero bending moment equation, which considers all forces on either side of the hinge.
However, there is a much easier way to do this, which is completely practical, without helpers computer science. So let's replace this beam with the following parts. Other parts are also isostatic and can be solved trivially. The result is internal strength.
The cross section of the beam passing through the pivotally movable support can be displaced parallel to the reference plane / - / and rotated, but it cannot be displaced perpendicular to the reference plane. Only one reaction occurs in the support - in the form of a force R perpendicular to the support plane. Fixing a beam with such a support imposes one connection on it.
Compiling these diagrams, they are identical to those obtained by the original beam. They are beams that rest on other beams and which can therefore be "taken off" from the rest of the structure, resolved, and then distributed to the rest of the structure. There is no need to worry about the influence of external forces or neighboring beams transmitting shear forces, due to the fact that the bending moment must be zero at each end of the Gerber beam.
This means that the shear integral along the Gerber beam must be zero, which can only happen if only loads inside the beam and reactions at its ends are taken into account. The support in the structure is the element that helps other members to resist stress. Discussed Various types carriers, their reactions and applications for structures and their details.
The cross section of the beam passing through the pivotally movable support can be displaced parallel to the reference plane / - / and rotated, but it cannot be displaced perpendicular to the reference plane. Only one arises in the support reaction-in the form force R perpendicular to the reference plane. Fixing a beam with such a support imposes one connection on it.
Types of support and reactions in structures and their applications
The supports in the structure transfer the load to the ground and provide stability to the structure supported on it. Support types can be basically divided into two types.
External supports and reactions and applications in structure
External supports. . Supports that are usually provided from the outside without disturbing structural elements are external supports. There are various types of external media.Fixed support and reactions and applications in the framework
Fixed supports are also called rigid supports. Fixed props are limited in both rotation and translation so they can resist any type of force or moment. In structural analysis, there are three fixed support unknowns that can satisfy all three equilibrium equations.
When calculating beams, there are three main types of supports (three types of fixing the ends of the beams): hinged movable support; pivotally fixed support; rigid termination of the end of the beam.
The fact that the main parametric resonance occurs at 0 2Q is easy to explain - in the time it takes for any point of the beam axis to complete one cycle of oscillation, the center of the section coinciding with the pivotally movable support performs two cycles of oscillation along the axis of the rod.
Attached support and reactions in structure
To ensure good structural stability, at least one rigid substrate must be provided. A beam fixed in a wall is a good example of a fixed support. Fixed support - Fixed beams in the wall. An attached support or hinged support can resist both vertical and horizontal forces, but they cannot resist momentum. This means that hinge support is limited to translation.
Using the equilibrium equations, the components of the horizontal and vertical forces can be found. The best example for a hinged support is a door leaf that rotates around its vertical axis without any horizontal or vertical movement. Rotation of the fixed support or articulated support is only allowed in one direction and resistance in the other direction.
The right free end of the real beam in this section of the fictitious beam corresponds to the termination. In the section above the pivotally movable support, the deflection of the real beam is equal to zero, and the angle of inclination is different from zero. Therefore, a hinge should be introduced into this section of the fictitious beam, in which the fictitious bending moment M is always equal to zero, and the fictitious transverse force Q is different from zero.
Support for cutscenes and reactions and applications in the structure
Articulated supports are also used in three hinged arch bridges with two supports at the ends, and a third hinge is provided at the center of the arch, which is called the internal hinge. The figure below shows the pivot bearing of the Sydney Bridge. Rollers only resist perpendicular forces, and they cannot resist parallel or horizontal forces and moment. This means that the support leg will move freely along the surface without being resisted by a horizontal force.
The pivotally movable support (Fig. 7.6) allows the beam to move in the horizontal direction and the beam to rotate relative to the support at a certain angle cf. In accordance with this, only a vertical reaction occurs in a pivotally movable support, which will be denoted by R. Fastening a beam with such a support imposes one connection on it.
This type of support is provided at one end of bridge spans. The reason for supporting the rollers at one end is to allow the bridge deck to contract or expand in relation to the temperature difference in the atmosphere. If roller support is not provided, this will cause serious damage to the banks of the bridge. But this horizontal force must be resisted by at least one support to ensure stability, so the support post must be installed at one end just not at both ends.
Support for rockers and reactions and applications in the structure
Rocker support is similar to a support post. It also resists vertical force and allows horizontal translation and rotation. But in this case, the horizontal movement is due to the curved surface at the bottom, as shown in the figure below. Thus, the number of horizontal movements is limited in this case.
The design schemes of the shafts and axles of the gearboxes are presented in the form of stepped or smooth beams on hinged supports. Bearings that simultaneously perceive axial and radial loads are replaced by pivotally fixed bearings, and bearings that perceive only radial forces are replaced by pivotally movable bearings. The position of the hinged support is determined taking into account the contact angle of the rolling bearing axes (c. When a 0 for radial bearings, the position of the support is taken in the middle of the bearing width. The axes of the satellites that do not rotate relative to the load vector can be considered as statically indefinable beams with elastic seal.
Support for links and reactions in the framework
This does not allow translation in the direction of the link. It has a single linear net force component in the direction of the line, which can be resolved into vertical and horizontal components.
Simple supports in the structure and their reactions
A simple support is simply a support on which a structural element rests. They cannot resist lateral movement and moment like roller bearings. They only resist the vertical movement of the support with the help of gravity.| Reduction of stress concentration at the landing site with a guaranteed tightness.| Rational form of splined sections of shafts. |
The design schemes of the shafts and axles of the gearboxes are presented in the form of stepped or smooth beams on hinged supports. Bearings that simultaneously perceive axial and radial loads are replaced by pivotally fixed bearings, and bearings that perceive only radial forces are replaced by pivotally movable bearings. The position of the hinged support is determined taking into account the contact angle of the rolling bearing axes (c. At a 0 for radial bearings, the position of the support is taken in the middle of the bearing width. The axes of the satellites that do not rotate relative to the load vector can be considered as statically indeterminate beams with an elastic seal.
Horizontal or lateral movement is allowed to a limited extent, after which the structure loses its support. It is like a brick resting longitudinally on two bricks. This type of support is not normally used for structural purposes. However, in areas of frequent seismic activity, simple supported structures are visible.
Internal supports and reactions and applications in structure
Internal supports are provided inside the structural element, which means that the internal support divides the complete element into parts. In this way, external reactions can be found for each part, which will be easier to analyze. Below are the types of internal supports provided in the structure.
Consider now a section of a real beam with an intermediate hinge. In this section, the deflection and the angle of inclination are not equal to zero. Moreover, the hinge allows a break in the curved axis of the beam, therefore, the angles of inclination of the tangent to the left and right of the hinge must be different. To satisfy the specified conditions, it is necessary to introduce a pivotally movable support into this section of the fictitious beam. Then the fictitious bending moment M above the support will be different from zero, therefore, the deflection in this section of the real beam will also be different from zero.
Like articulated support, the inner loop also resists translation in both directions and only allows rotation. In the designs for the axial elements, internal hinges are provided and middle hinges of the beams are provided. They can be widely seen in arch type bridges in the center of the arch.
The inner cam rollers are the same as the cam rollers, but they are provided in the middle of the structural member. This type of internal support rollers is used in tower cranes or port cranes, so when moving horizontally, support materials or elements can be moved from one place to another.
Pages: 1
On fig. 1.21 shows a horizontal beam based on hinged and movable and fixed supports at points A and B.
Reaction R A of the pivotally movable support is directed normal to the supporting surface towards the beam. The articulated movable support is placed on rollers, which do not prevent the beam from moving along the supporting surface. If we do not take into account the friction of the rollers, then the line of action of the reaction R A passes through the hinge center perpendicular to the bearing surface.
The hinged-fixed support prevents translational movements of the beam along the coordinate axes, but allows it to rotate about the hinge axis. Reaction action line R B of the hinged support passes through the center of the hinge, but the modulus and the direction of the reaction are not known in advance.
On fig. 1.22 shows the beam AB. According to the axiom of the parallelogram of forces, which allows the reverse interpretation, the reaction R B can be decomposed into components parallel to the coordinate axes.
WITH

More complex types of connections and their reactions are considered later, when the concepts are introduced. pairs of forces And moments of forces about a point and an axis.
Axiom of connections - any non-free body can be considered as free, if we discard the bonds and replace their action with the reactions of these bonds.
On fig. 1.23 shows the beam AB, considered as a non-free mechanical system, on which external constraints are imposed.
The hinged fixed support at point B does not allow the beam to move translationally parallel to the coordinate axes and allows it to rotate in the plane of the figure. Based on this, the reaction R B is decomposed into its components Y IN, Z B, parallel to the coordinate axes.
The hinged-movable support at point A does not allow the beam to move to the supporting surface, therefore its reaction R And directed along the normal.
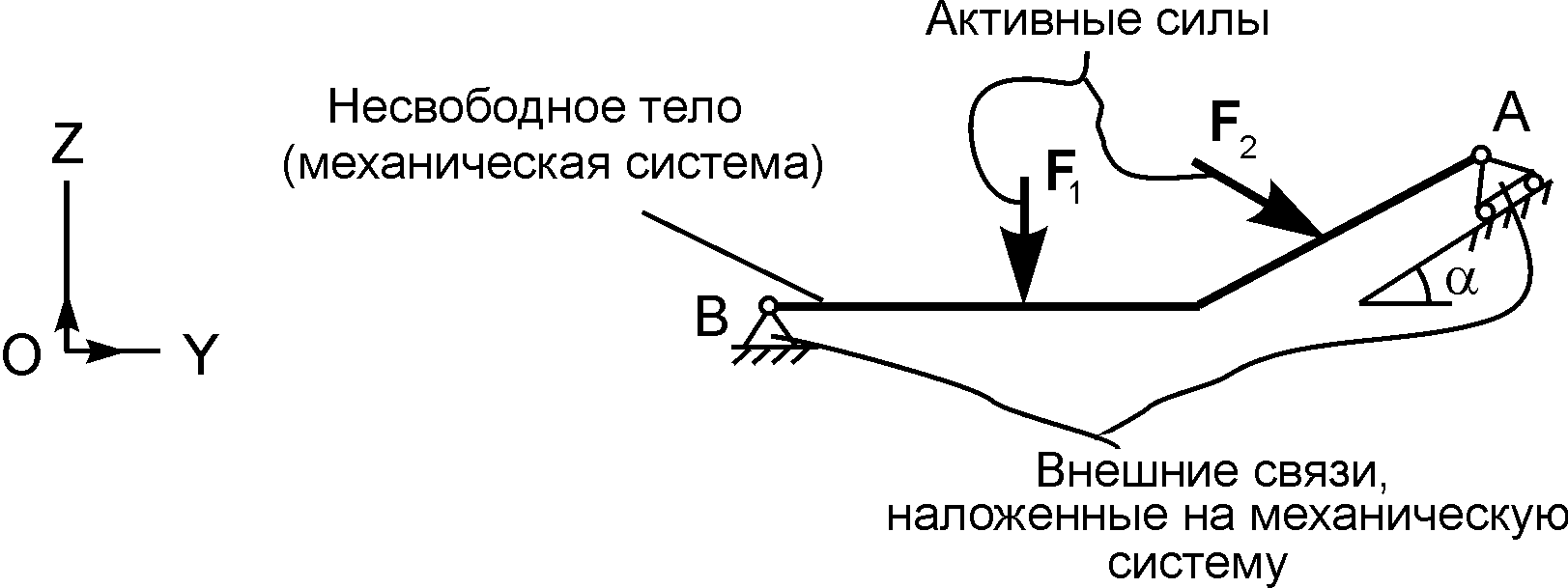
IN

Beam AB is in equilibrium under the action of active forces F 1 ,F 2 and reactions Z b, Y b, R A external relations. reaction R It is advisable to decompose A into components of the force along the coordinate axes.
It must be emphasized once again that the decomposition of the force into components of the force is carried out only at the point of application of the force.
Questions and tasks for self-control
"non-free body" .
Formulate a definition of the term "connections" .
Formulate a definition of the term "bond reactions" .
Formulate a definition of the term "smooth connection" .
Formulate a definition of the term "flexible connection" .
Formulate a definition of the term "weightless rod" .
Formulate a definition of the term "free body" .
Formulate axiom of connections .









