One of the most important parts of the house is the roof - its quality determines the warmth and comfort, noise level and frequency of repairs of the building.
Naturally, when planning a development, the question arises, what type of roof to choose, or which roof is better - cheaper, more expensive, broken or gable, or maybe hipped?
It is not enough for a roof to be simply durable and attractive. It must also have a number of important properties: provide good protection from rain and snow, protect from heat and cold, and be fireproof. Let's look at the main types of roofs and their characteristic features, because the choice of roofing material depends on the type of roof.
Main types of roofs
- Flat roofs. They are usually erected above utility and utility buildings, garages, bathhouses, sheds, as well as houses with a terrace on the roof.
- Pitched roofs. This type of roof is more widespread, and there are several classifications of pitched roofs, one of which we will present below. Among others pitched roofs can be divided into warm and cold, with and without an attic.
Let us list the main structural types of pitched roofs.
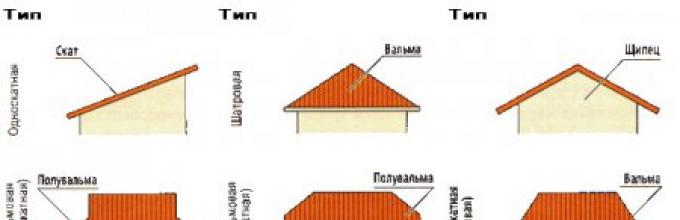
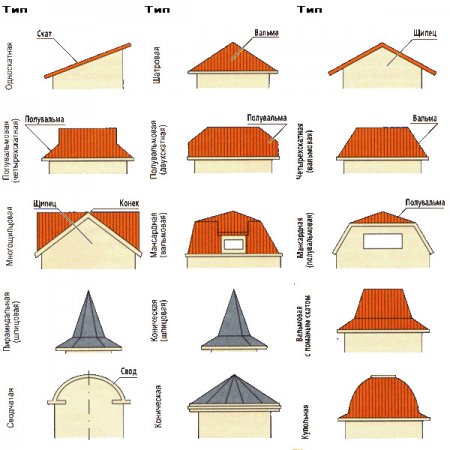
- Shed roofs
Their surface is a plane resting on opposite walls of different heights, i.e. is at an angle to the horizontal. - Gable roofs
They consist of two planes located at an angle and rest on opposite walls of the same height. This is perhaps the most common type of pitched roof. - broken roofs
Variety gable roof, in which each of the slopes consists of two rectangles located at an obtuse angle. - Cross-shaped roofs
They are a combination of several ordinary gable roofs, as if cut into each other at right angles. - Hip roofs
These are hip roofs with two long trapezoidal slopes and two short triangular ones. - Half hip roofs
A type of hip roof, sometimes called a Dutch roof, in which the end slopes do not reach the eaves. Thanks to this design, the house is better able to withstand the wind, and its gables are less exposed to precipitation. - Hip roofs
A type of 4-slope roof, consisting of four equal slopes of a triangular shape.
When choosing a roof type, you should take into account not only its intended operational properties, but also its decorative qualities. In low-rise buildings, the roof has a large relative volume and its appearance largely determines the architectural design.
In private houses, mainly the roofs of high structures are erected. This allows you to build an attic, and the house takes on a more presentable appearance. Also, steep slopes do not allow water and snow to linger on the roof. In areas with strong winds, it is preferable to build low roofs or high ones, with additionally reinforced rafter systems.
You should also consider which roof the developer can afford. Naturally, roofs of simpler designs are cheaper, and the most economical options are flat and pitched roofs. An additional convenience of a pitched roof is that it allows you to increase the internal volume of the building, and outbuildings at the same time serve as a ceiling.
If attic space will be used for household needs, it is better to erect a gable roof. In areas with strong winds best choice There will be a type of hip roof, but its construction will not be cheap. In addition, the construction of hip roofs requires high professionalism, and should only be trusted by experienced craftsmen.
In houses complex shape As a rule, cross-shaped roofs are used. This is a rather complex structure, consisting of many intersecting slopes. The difficulty of installing a cross-shaped roof is to ensure the tightness of the internal corners of the roof. Such roofs are expensive; they must be erected by experienced craftsmen and always from high-quality materials.
Roof structural elements
After choosing the type of roof, you can begin selecting materials. Therefore, let’s get acquainted with the main structural elements of roofs:
- Basic structure. Its type depends on the type of roof. It is usually constructed from wooden beams and rafters.
- Roof base. It can be constructed in the form of a lattice or be solid.
- Hydro- and heat-insulating layers.
- Roofing material.
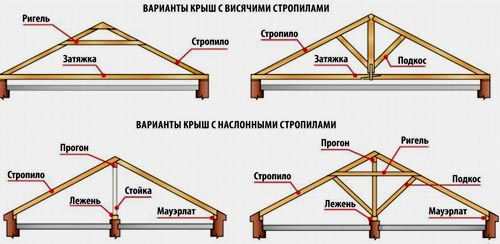
Rafters and their types
Rafters perform an important function in the roof structure. This is a support for the sheathing, taking on not only the weight of the roof, but also the wind load, as well as snow pressure.
- hanging, used for long length spans;
- inclined, used for span lengths up to 6.5 m. With additional support, the span length can increase to 12 m.
Design and construction rafter systems– jobs that require high qualifications. Its quality determines bearing capacity and therefore the strength of the roof.

Roof bases
The type of base for the roof is selected depending on the intended roofing material.
There are two main types of roofing base:
- sheathing(used for roofing made of metal tiles, slate or metal profiles)
- solid flooring(when using rolled materials)
Continuous flooring is constructed from two layers of boards. The first layer is called working, and the second – protective. The latter is located at an angle of 45 degrees relative to the worker and is constructed from narrow boards. Between these layers a windproof material is placed, usually roofing felt RRP-300 or 350.
When installing the sheathing, a number of rules are observed:
- all sheathing elements are securely fastened to the rafters;
- their joints are located staggered on the rafters;
- the distances between them must be maintained over the entire surface of the roof being constructed.
Roofing materials and works
The top part of the roof is called the roof. It is in direct contact with the external environment, taking on the full power of wind and precipitation. Therefore, the main qualities that it must have are strength and water resistance.
There are many roofing materials, and when choosing one of them, you should take into account its performance characteristics, as well as a number of other factors:
- climate;
- functional purpose of the building;
- durability of the material;
- cost of material;
- its noise-insulating and heat-saving properties;
- labor intensity and cost of roof maintenance;
- external attractiveness of the material.

It is difficult to give unambiguous and comprehensive advice on choosing which roofing material will be best, since it is influenced by all the listed factors, and ideal building materials, as we know, do not exist. In addition, the determining criteria may differ, for example, if there is insufficient funding, the price becomes the main thing, and all other factors are considered less meticulously. On the contrary, if consumer properties come to the fore, then price, as a rule, is not of decisive importance. For some, perhaps the main factor will be beauty or color, since according to the owners, the house should not be similar to the others.
The choice of material should be made at the stage of creating a house project, since the type of roof structure depends on it, and changes should be made to finished project it will be difficult and expensive.
conclusions
Selecting a roof structure and roofing material is an important stage in building a house. The best solution can only be found by taking into account a number of factors:
- purpose of the building;
- noise insulation and heat saving characteristics of the roof;
- construction budget;
- climate features;
- aesthetic impression.
Only by taking into account the listed factors and weighing each of them can you choose best option roofs and type of roofing material.
Having completed the construction of the walls, it is time to think about the structure that crowns the building. If we are talking about a small country house, garage or bathhouse, then its choice is not difficult to make. The simplest roof for such objects is single or gable. It can be calculated and built on your own, without involving a team of carpenters.
In this article we will look at common options for roofing structures, talk about important features their selection and installation.
Types of simple roofs and their main elements
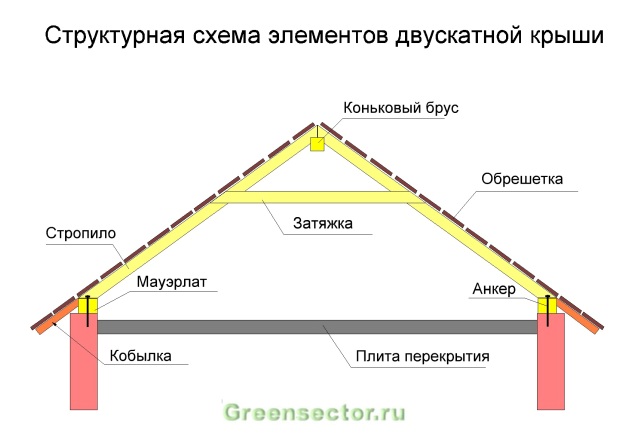
Any roof consists of a supporting frame and a protective roofing covering.
The frame includes the following elements:
- Rafters - inclined beams (serve as the load-bearing basis of the roof).
- Ridge beam (connects the upper connecting points of the rafters).
- Lathing is a flooring made of boards or OSB slabs, laid on the rafters and serving as a base for the roofing material.
- Counter-lattice - used when installing a warm roof (creates an air gap for ventilation of the insulation).
- Mauerlat - wooden beam (mounted on longitudinal walls). The lower parts of the rafters (rafter legs) are attached to it.
- Vertical posts, horizontal ties and struts (used to strengthen the truss structure).
- Fillers are boards nailed to the lower ends of the rafters to create a roof overhang.
Gable roof for a summer house and bathhouse (span width no more than 6 meters)
The design of a simple roof for a house is determined by several factors:
- width of the span to be covered;
- purpose of the attic space (residential or non-residential, walk-through or non-passage);
- type of interfloor covering ( wooden beams, reinforced concrete panels).
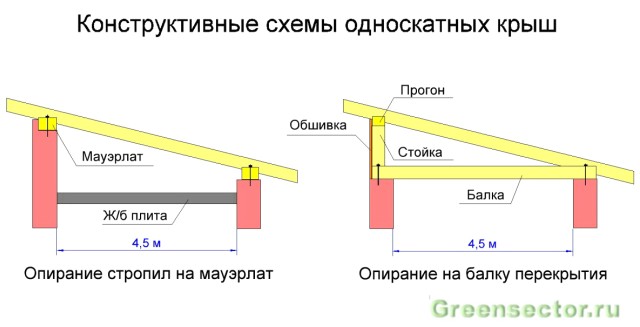
If the building width is small (up to 4.5 meters), and there are no plans to arrange a living space in the attic, then you can choose the option of a pitched roof. It is economical and easy to install.
The rafters of such a roof can be supported directly on the walls. To do this, one of them needs to be made higher than the other. This will create the slope necessary for rainwater to drain.
If you decide to install a pitched roof on walls of the same level, then to create a slope, you need to include wooden posts in its design. After installation is completed, they are sheathed with siding, OSB board or blockhouse.
Options pitched roofs for garage, barn, gazebo and bathhouse
For asbestos-cement slate, the roof slope must be at least 22 degrees. For metal tiles, ondulin, bitumen shingles The roof slope should be at least 15 degrees. Making the calculation simple one pitched roof, remember that snow load is a serious factor. To reduce it, it is recommended to make the slope steeper. IN otherwise you will have to increase the cross-section of the rafters and sheathing, which will lead to an increase in the cost of the structure.
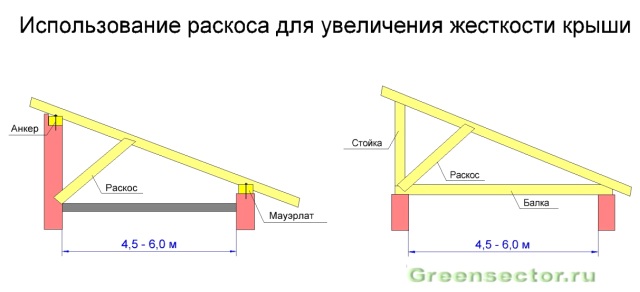
If the span width is from 4.5 to 6 meters, then the rafters need to be reinforced with braces (inclined racks made of timber). They will reduce the deflection of the rafter legs under the influence of snow load. The lower ends of the braces are embedded in the masonry, and when using vertical support posts, they are attached to them using staples, nails or jagged metal plates.
Shed roofs are most often used for small structures such as garages, sheds, bathhouses or gazebos. A gable structure with a large elevation angle is the best option for arranging an attic space.
Main docking points
The main condition for the strength of any roof is the proper joining of all its parts. Therefore, when drawing up a sketch drawing, you need to pay attention to the nodes (connection of the mauerlat to the wall, rafters to the ridge and floor beams).
The installation of a simple roof begins with laying a horizontal wooden beam- a mauerlat on which the rafters will rest. It is attached to the masonry through threaded steel anchors (in brick walls) or to studs concreted in an armored belt (gas silicate masonry, expanded clay concrete, foam block).
The floor beams are fixed to the wall using anchor pins, and the Mauerlat is attached to them with nails or long screws.
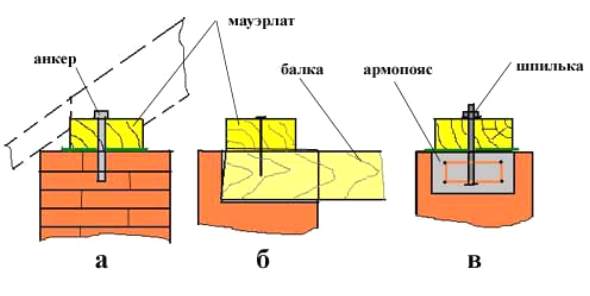
Methods for attaching the Mauerlat to the wall: a - with an anchor; b - nail; c - with a pin concreted in an armored belt
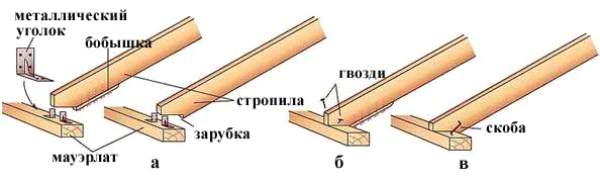
Options for fixing the rafters to the mauerlat: a – with metal corners, a thrust block (boss) or a notch; b - nails; c – steel bracket
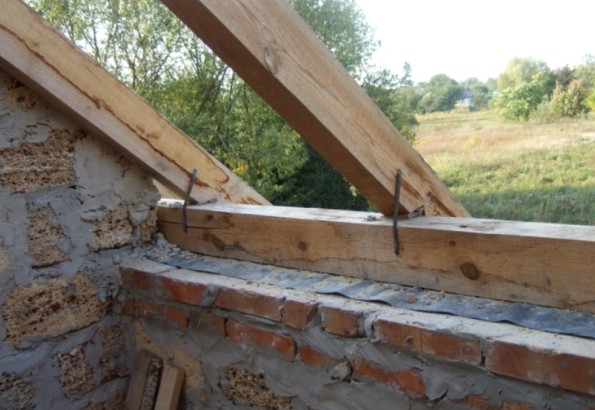

Fastening the rafters to the mauerlat with a bracket and a notch
Note also that the roof small house, barn or garage can be installed without a Mauerlat, fixing the lower ends of the rafters directly to the floor beams.
The next important unit is fastening the upper ends of the rafters to each other and connecting them to the ridge beam.
There are several ways to create this node. The rafter beams can be connected with a bolt and tightened with a nut (node 1). You can use a piece of OSB board (node 2) or secure them with a metal toothed plate (node 3). For closer contact of the rafters with the ridge beam, notches are made on them.
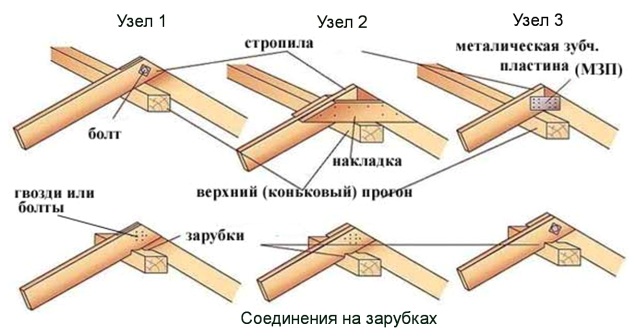
It should be noted that ridge beams, which increase structural rigidity, are most often used on large roofs. It is also installed in buildings with gables made of brick, block or logs, which serve as supporting walls for it. Building a small bathhouse, garage or country house, you can do without this element. A small roof will be provided with sufficient rigidity by lathing or decking made from OSB boards.
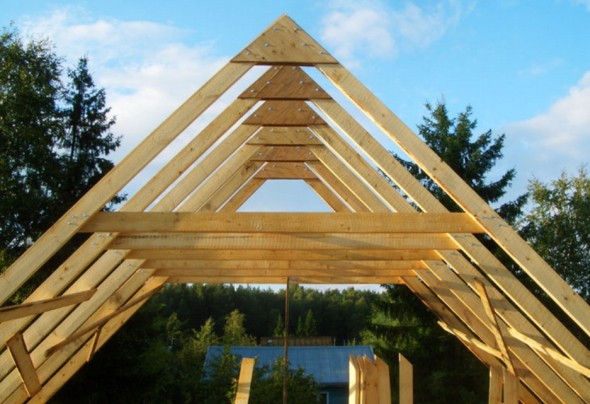

Option for a simple gable roof without a ridge beam
About to do simple roof with your own hands, you should familiarize yourself with the recommended sections of rafter legs (Table No. 1).
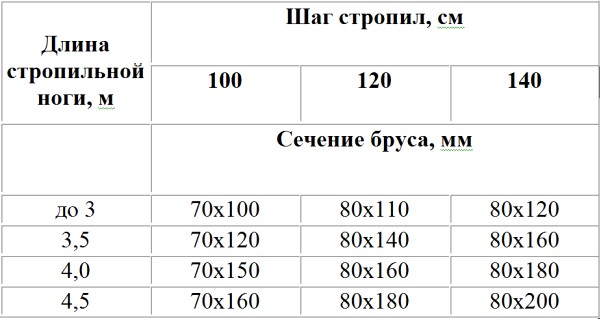
Table No. 1 Design sections of rafters depending on the selected pitch
The cross-sectional dimensions of other elements of a simple roof can be taken from table No. 2
Features of constructing a simple roof
The installation of the roof begins after the completion of the walls, installation of beams or floor slabs. Having aligned the outer rafters, they are attached to beams or mauerlat and fixed with temporary ties. After this, a beacon cord is pulled between them. Ordinary rafters are placed along it and secured one by one using lathing.
If there is a capital pediment, installation is simplified, since the ridge beam laid on it serves as a support and beacon for installing the rafters.
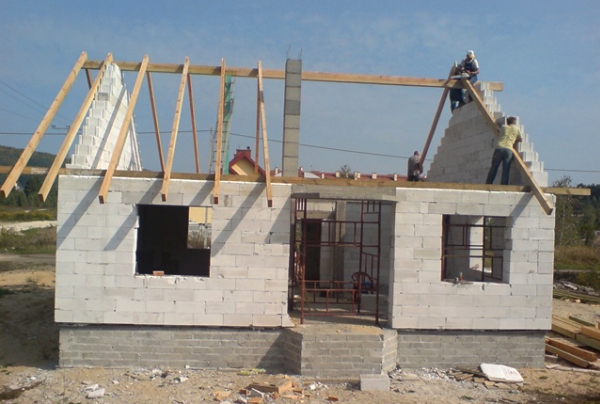

Installing a roof frame at height is a labor-intensive task. When erecting a small roof, it is more convenient to assemble trusses on the ground. In this case, on the walls you will only have to connect them using lathing into a single structure. Having assembled one truss, it can be used as a template for marking and cutting rafters, tie rods and beams.
When preparing to build a roof, be sure to make a detailed diagram indicating the dimensions of all elements and detailed elaboration of the components. It will be useful to you for calculating the purchased lumber and will help you complete the installation efficiently and quickly.
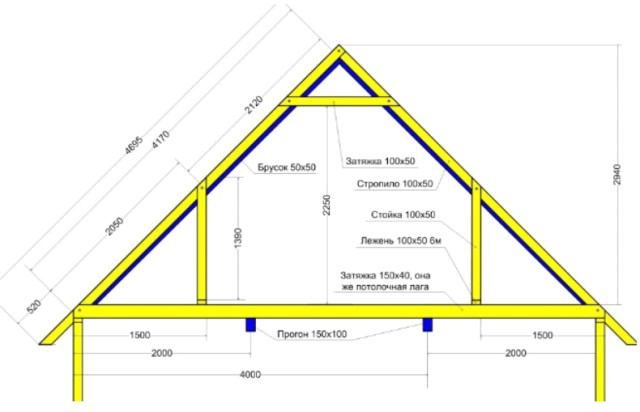
A detailed drawing is an important condition for efficiency and quality of work
If the attic space is residential, then the roof structure must include not only insulation and vapor barrier, but also a counter-lattice - a wooden block with a cross-section of 30x50 mm. It is nailed to the rafters on top of the vapor barrier film to create a ventilation gap, and the main sheathing is attached on top. Without this “trifle,” the insulation will become wet from diffusion moisture in the cold season, and the wooden parts of the structure will begin to rot.
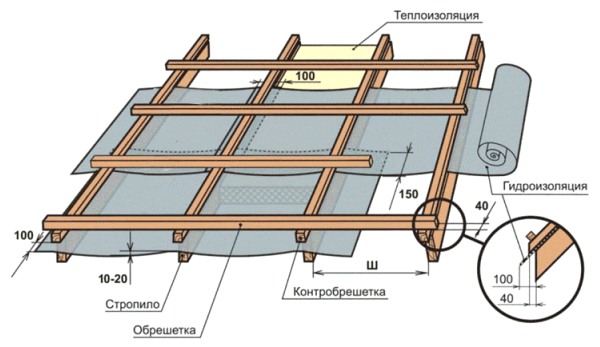
Structural diagram of an insulated roof
If a solid OSB board deck is used when installing an insulated roof, then a counter-lattice is placed under it.
To protect the walls from rainwater, any roof needs overhangs. For a lean-to structure, they are made not only in the lower part, but also in the upper part. If the length of the rafter legs is not enough to form eaves overhangs, then they are extended by nailing “filly” boards.
The minimum size of roof overhangs must be at least 20 cm. To protect the gables from moisture, the length of the roof on each side is increased by 20-30 cm, creating front overhangs. The ends and lower planes of the overhangs are sheathed with wind boards.
The roof is an element that encloses the upper part of the building and is considered one of the most important in the design of the building. The roof consists of load-bearing elements: trusses, rafters, purlins and roofing. The supporting structure is designed to transfer the load to the walls, and the roof protects the building from the external environment. The roof allows you to provide the house with high-quality waterproofing, creates a kind of thermal protection and protects the building from the wind.
Main types of roofs
Roofs of buildings are divided into several categories depending on their shape and design features. They are selected after taking into account nuances such as the amount of precipitation, wind strength, and the characteristics of the house itself. Let's look at what types of roofs are used in private houses today, and which option is most preferable in a given case.
The variety of different roof options used for the construction of private buildings is amazing. Besides protective functions, roofs can also carry a decorative load, and can also be made more functional. Roofs can be classified according to many properties, the most common of which is the slope of the slopes. 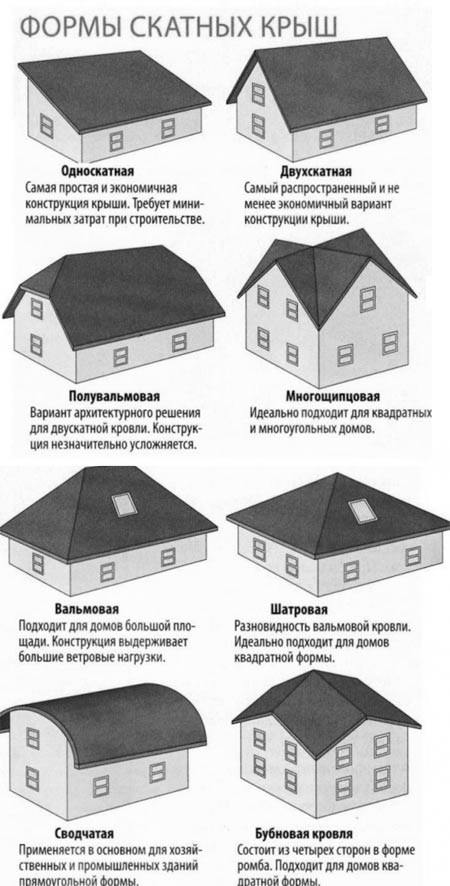
Flat roofs
This option is the easiest to implement and the cheapest. Based on the name, it is not difficult to guess that the angle of inclination of the slopes in such a roof is almost absent, and it rests on walls of equal height. As a rule, the slope of such a roof is made very small, up to three percent. Its main design feature is also its most significant drawback.
Due to the fact that the roof is sloped very poorly, precipitation in the form of snow accumulates on it and, ultimately, it may leak. In order to prevent these problems, it is necessary to promptly remove snow from the roof, which accordingly obliges the owners to carry out periodic maintenance.
It is worth noting that in the construction of private residential buildings such roofs are not particularly popular, which cannot be said about industrial buildings, where this roof option is used very often.

Flat roof house project
Now about the advantages of roofs of this design. If you compare flat and pitched roofs, you can definitely see significant differences in size. This fact allows flat roofs to be the most budget-friendly, and their use significantly reduces installation costs and the purchase of materials. In addition, flat structures are easier to install, because you don’t have to climb the slopes and risk your health. Maintenance of such a roof is also convenient, because there is no need to stock up on climbing equipment and balance at height.
IN in some cases flat roofs allow the owners of buildings to acquire a larger usable area without resorting to expanding the outline of the building.
To do this, the roof will be converted into a mini-garden or walking area. An example of this use is in European countries, where flat roofs of high-rise and private houses are used in a similar way.
The design of a flat roof is as follows.
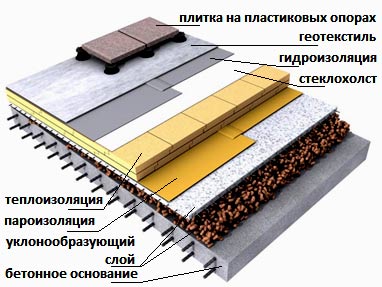
Flat roof design diagram
The basis for everything is a load-bearing element in the form reinforced concrete floor or a profiled sheet on which vapor barrier, thermal insulation and a layer of waterproofing materials are alternately laid. In order not to worry about the service life of such a structure, you should not neglect any of these layers. Deviations from generally accepted recommendations are possible only with a thorough study of the local climate and the properties of the materials used.
Pitched roofs
The design of the roof shape that is most familiar to the eye is considered the most popular in the construction of suburban buildings. It gets its name because it consists of slopes, which are inclined planes. Pitched structures are made with attics and without attics. and roofs assume that there will be useful space between the interfloor ceiling and the roof, and the attic structures themselves represent an upper-level ceiling.
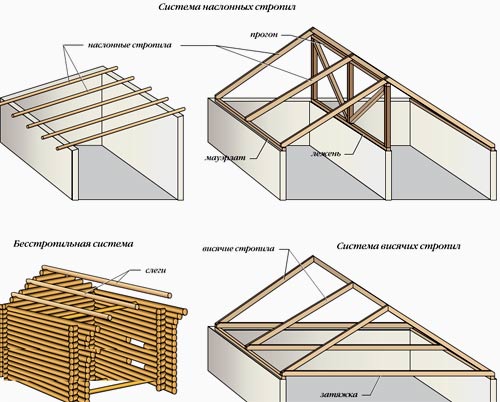
Various schemes for installing pitched roofs
A feature of a pitched roof is the presence of load-bearing elements that are designed to take the load from the structure, as well as the load from external factors. The slope present in this type of roof favors the removal of precipitation from the structure.
Which slope to choose in a particular case depends on several factors:
- Amount of precipitation in winter time. The steeper the roof, the better it removes snow, and the less load there will be on the load-bearing elements. There are special tables that describe the indicators for snow falling in winter, which greatly facilitates the choice;
- What type of roofing material is planned to be used;
- Architectural view of the future building.
Roofs that have one slope are called shed roofs. Bearing structures Such roofs rest on walls of different heights, which creates the necessary slope. Due to the ease of installation and low cost, such roofs are widely used in the construction of outbuildings.

Project two-story house with pitched roof
Can be used as a roof for pitched roofs Various types materials, such as roofing felt, corrugated sheets, ondulin, slate, etc. Due to the fact that precipitation flows in one direction, the storm drainage system can be significantly simplified. The only disadvantages of such a roof are the absence of an attic and some restrictions in creating the exterior of the house.
- Rafters and other auxiliary elements for arranging the frame (struts, crossbars, racks, etc.);
- Waterproofing;
- Thermal insulation;
- Lathing;
- Various types roofing materials.
Gable roofs
These types of roofs are used quite often in the private sector. Structurally, it consists of two slopes resting on opposite walls of equal length. The construction of such roofs is more difficult compared to the previous type, however, it is much easier when compared with other types.
Device drawings of various options gable roofs
It is safe to say that types of gable roofs can withstand severe gusts of wind and are very durable in use.
Visually, such a roof looks more familiar and correct, and various types can be used as protective materials. The design of gable roofs includes rafters and a mauerlat, as well as various auxiliary elements. In addition, like other types of roofs, their design includes various protective and roofing types of materials.
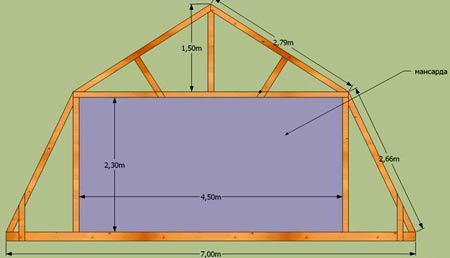
Mansard roofs
Types of mansard roofs can be called a variety gable roofs. Usually, mansard roof It has broken slopes, which is why it is sometimes called that. You can change the angles of the slopes in different ranges, which allows you to increase the usable space by .
Detailed diagram with dimensions mansard roof
Despite the fact that such designs have some features, their installation does not cause difficulties. Most often, such roofs are used for protection country houses and cottages when the owners plan to save space on the site. During construction, it is necessary to pay attention to roof insulation work and the choice of insulating materials, because the roof will be the only obstacle against the penetration of cold into the living space.
Roof height starting from interfloor covering to the ridge is usually about three meters, because if you make this distance smaller, the slopes will “eat up” the usable space in the attic much more. Thanks to the use of a mansard roof, you can not only increase the functionality of the house, but also embellish it and give it an unusual shape.
Hip roofs
These types of roofs are distinguished by the presence of four slopes, two of which have the shape of an isosceles trapezoid, and the other two, called hips, are triangles. The hip roof is excellent at removing precipitation, and despite the fact that its slopes are quite steep, it perfectly withstands strong gusts of wind. The presence of steep slopes makes it necessary to install a drainage system. It is very difficult to make such a roof with your own hands, because it has a complex rafter system.
If there is a need to install such a roof, it is best to seek help from professional builders.
Structural components of a hip roof:
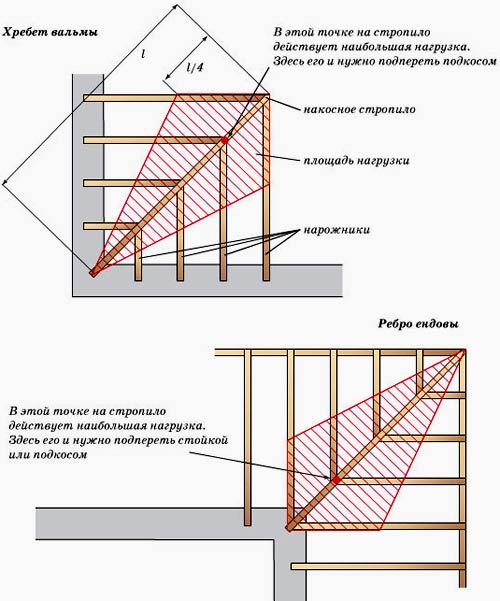
As you can see, the design of a hip roof is very complex, and the slightest miscalculations can lead to dire consequences.
Half hip roofs
This roof can be described as a hybrid of a gable and hip roof. The design of half-hip roofs does not involve sharp corners, which makes them highly resistant to wind. This feature is useful when constructing buildings in areas where strong gusts of wind are normal.

Project of a cottage with a half-hip roof
Depending on the region in which the house is planned to be built, the roof design can be changed in terms of arranging steep slopes or large overhangs.
Hip roofs
This type of roof is considered a variation of the previous option. In order for it to be possible to build such a structure, you must have a house correct form. Then all the slopes will be in the form of triangles and will close in one place. The right kind Such a roof transforms the structure and makes it unique. As with hip roofs, hip roofs are very difficult to construct and require extensive knowledge of the construction industry to do the DIY job.
Multi-gable roofs
This type of roofing is used in the construction of houses irregular shape with many outbuildings.

Ready-made house project with a multi-gable roof
The presence of many angles, both internal and external, requires you to approach the arrangement of the roof very carefully, so you cannot do without the help of qualified specialists.
Dome type roofs
This know-how in the construction industry is gaining increasing popularity among developers. A special feature of buildings with domed roofs is the unusual ratio of the heights of the walls and the roof. As a rule, the walls in such houses occupy only a fifth of the building's height, and the rest is allocated for the roof.
The frame of such structures will be curved, and flexible or soft types of roofing, such as galvanized steel, roofing felt, etc., should be used as roofing materials.
Roof selection
When planning the arrangement of the roof, it is necessary to take into account the style in which everything is done so that the overall appearance is harmonious, although everything depends on the wishes and preferences of the customer.
Let's consider some points that will be useful when choosing roof shapes.

When building any house, you need to pay a lot of attention to such a structural element as the roof. The degree of its reliability, protection from bad weather, and negative external conditions depends on it. The roof of the house can have a variety of shapes - it all depends on appearance home, architectural requirements.
- Folded roofs are structures where individual elements of a trapezoidal shape are connected - folds.
- Domed in shape resembles half a sphere, which rests on cylindrical walls.
- Cross vaults are four connected arched vaults. They are rarely used for the main residential building; most often these are gazebos, terraces, etc.
- The multi-pincer form is one of the most complex designs, it is inevitable a large number of valleys, which greatly complicates installation and maintenance. But it is these roofs that are most often used for attic installations. The resulting premises are unusual shapes, spacious and attractive.
- Flat roofs are the simplest structures, supported by load-bearing walls that are the same height.
- Oblique forms are one of the varieties of gentle slopes that rest on load-bearing walls that have different height levels.
- The spire-shaped roof consists of steep triangular slopes with a connection point at the top.
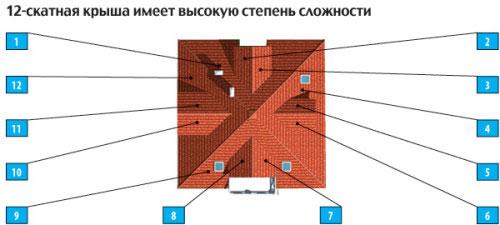
An example of a multi-pitched roof. This design consists of twelve slopes.
Today, for private residential construction, any of the structures listed above is used, it can be a complex roof, or an ordinary straight surface with a small slope or without it, which allows you to create a comfortable open terrace on the roof surface. Such a straight roof is becoming increasingly popular today; on top you can create not only a cozy place to relax, but also real green areas!
Today, a variety of types of roofs can be used for private houses, including attics, spiers, arches, domes and other unusual elements. The main thing, even at the planning stage, is to clearly determine what exactly the roof will be, to calculate truss structure, waterproofing, insulation, roofing. Without this, construction at the very beginning will be doomed to failure; it is much cheaper and easier to immediately provide for all the nuances than to disassemble structures and reassemble them during the construction process.