Any building is unthinkable without a roof. She is the barrier that protects interior spaces from atmospheric precipitation and prevents heat leakage. How comfortable living in the house will be depends largely on the solidity of the roof. Previously, in order to create a tight roof, clay and sheet iron were used. These methods were not very durable, and the roof needed regular repairs. With the development of the construction industry and the invention of new materials, the situation has changed. A new technology has emerged.
To create a reliable roof waterproofing, welded roll materials are usually used.
What is waterproofing for?
Perhaps the most important thing in the construction of the roof is waterproofing. It is she who protects the roof from leaks. Thus, not only the qualities of the materials from which the rafters are made are preserved, but also. The waterproofing layer always consists of those products of the construction industry that have water-repellent properties. Manufacturers of roofing materials offer a wide range of products that will help ensure the durability of the house, and comfort in living in it.
The choice of waterproofing roofing depends on the type of device of the roof itself. Private houses are usually built with a gable or sloping roof. As a waterproofing layer, membranes based on polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride, as well as rolled roofing material, are often used here. The situation is different in buildings that have a flat roof. In the vast majority of cases, welded roll materials are used to create a waterproofing layer of the roof.
Types of roll materials for roofing
Bitumen-based materials, when laid, sealing is created using special mastics, of which there are two types: cold and hot (molten bitumen).
Materials with a bottom adhesive layer protected by a thin polyethylene-based film.
Materials that are welded onto the surface of the roof. The technology of their use involves working with a gas burner.
All rolled materials are divided into coatings intended for single-layer and multi-layer carpets. The former, as a rule, consist of a much larger number of layers of fiberglass, polymer components and bitumen. They have an upper decorative layer in the form of powder, which is made of basalt, sand, foil, slate. Hydrostekloizol, stekloizol, rubiteks, stekloelast, prorofikr, masterkrom are most in demand in the roofing device.
Roll roof properties

Working with a rolled roof allows you to quickly and without much effort to carry out work on the installation of the coating.
Although these types roofing difficult to call elite, they are often indispensable in modern construction. The simplicity of their laying allows you to work at a fairly fast pace. The undoubted advantage of these materials is that they can be laid on flat and sloping roofs up to 11 degrees of slope, which is impossible when using ondulin and other coatings. elastic and, as a result, not subject to cracking. It has high strength characteristics and acts as a sound insulator. These materials comply with all fire safety standards and are made from environmentally friendly components. They retain their high thermal insulation properties even with prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Roofing technology using rolled materials
Built-up roof
The technology of laying rolled material has its own characteristics. Its main manufacturers are TechnoNIKOL and Isoflex. The vast majority of roll coatings are built-up. They are not used on roofs with wooden floors and rafters. Their purpose is to serve as a covering for flat and sloping roofs. Most often, for these purposes, a built-up roofing material (euroroofing material) is used. This material consists of fiberglass coated on both sides with bitumen. Unlike the outdated version with a cardboard layer, modern roofing material is durable and strong. How to make these works?

The rolled roof is elastic, and therefore damage to it is minimized.
- Preparatory stage. First of all, the concrete or other surface must be cleaned of debris and dirt. It is desirable that even fine sand does not remain. In the event that the roof is being repaired, the old coating is removed.
- Cracks and chips in the concrete surface should be repaired with a cement-sand mortar.
- Priming the base with a bituminous primer.
- The gluing of the roofing material occurs due to the softening of the lower layer of the canvas. This can be done with a gas burner or white spirit.
- The rolled material is rolled out in such a way that its direction is perpendicular to the flow of water. Laying should begin from the lower parts of the roof or from its edge if the roof does not have a slope.
- Warming up the lower layer of material, the roll is gradually rolled forward. Such a coating will last at least a quarter of a century.
- Proper gluing of canvases and strengthening of corners is done with bitumen-based mastics.
Roofing felt with bituminous mastic
- The base on which the material will be laid should be cleaned of dirt.
- Hot bituminous mastic is being prepared. Then, at a distance of 0.7-1 m, the roof surface is smeared with it.
- The manufacturer treats the lower layer of the rolled material with talc to prevent the layers from sticking together. Therefore, as the work progresses, it is carefully swept by hand with a brush with stiff bristles. This must be done, otherwise the adhesion of the roof to the roof surface will not be strong enough.
- Rolled roofing material is gradually rolled up to the distance that has been treated with bitumen.
- Those places that lay on the mastic are carefully aligned, starting from the middle. You need to make sure that there are no “bubbles”.
- When the canvas is completely rolled out, you need to walk on its surface with a special, rather heavy roller. This is done to improve the adhesion of the material to the roof surface.
- The next roll is laid in such a way that an overlap of 10-15 cm is formed.
Multilayer roofing device
It is known that the roof has to withstand significant loads: wind, rain, snow layer, temperature changes. Therefore, the strength of the coating should be as resistant to them as possible. For this purpose, a multi-layer cake made of roofing felt or other rolled material is arranged. Its thickness depends on the slope of the roof. Depending on this factor, the number of layers can be from 2 to 5.
The maximum number of layers of material is mandatory when covering flat roofs. In this case, without damage to itself, it can withstand the weight of a person and objects heavier than him.
A four-layer cake is used on slopes whose slope does not exceed 2-3 degrees.
Ruberoid in 3 layers is needed where up to 10 degrees. If the slope exceeds this slope value, then you can safely use 2 layers of roofing material: underlying and outer.
One of the main advantages roll roofing is that it can be installed on roofs of any shape. Despite this, this type of roof is affordable for most people. Other advantages make it even more in demand.
- Light weight and easy installation;
- Strength and durability;
- Fire safety and high thermal protection;
- Hydro - and soundproof properties;
- Tightness and environmental friendliness;
It will be possible to take full advantage of all the advantages with proper installation of the material. Mistakes made can lead to a decrease in the service life of the roofing from welded roll materials.
UNION construction company uses the most modern version installation of a rolled roof - built-up. Unlike traditional ones, when the installation of sheets of rolled materials (based on bitumen-impregnated fiberglass) required their surface treatment with mastic, modern welded rolled roofing is convenient and easy to install. The role of mastic is performed by the lower layer of the sheet in the roll - when exposed to high temperature it melts and sticks tightly to the base of the roof. Thanks to total absence seams (even between the sheets they are fused), the roof is as tight as possible. Well, the polymer mixed with bitumen forms a wear-resistant hydrophobic layer that lasts for decades.
Roof design and installation guide_general (PDF, 14.19 Mb)The device of flat roofs from the built-up materials. TechnoNIKOL
Installation of a soft roll roof
When sticking a roll being rolled out, the brushman is in front and on the side and with a brush or a spatula puts the mastic on sections of 50-60 cm. The mastic is first applied along the edges of the panel with two longitudinal strokes, and then with transverse movements - in the interval between these strokes.
If the roll is skewed during the sticker and the overlap has decreased, the material is cut off, and as a result of fitting, the roll is given a new direction and the sticker is started again, strictly observing the overlap.
To reduce distortions, an approximate roll can be rolled up from both ends to the middle and the sticker can be led from the middle - first to one end, and then to the other.
The overlap of adjacent panels on each other on the planes of the roof is done in the lower layers of 5-7 cm, and in the upper 7-10 cm. This operation is performed with a spatula due to the mastic protruding along the edges. In this case, the seams are not painted with mastic.
When sticking, the roll must be carefully rubbed from the middle to the edges and immediately rolled with a cylindrical hand roller weighing 80-100 kg with a soft lining. The use of a replaceable tarpaulin cover greatly facilitates the cleaning of the skating rink from mastic adhering to it.
The direction of movement when sticking rolls in windy weather should be chosen in the direction of the wind, that is, so that mastic splashes cannot fall on the worker rolling the roll. When sticking the top layer, it must be borne in mind that the direction of the seams perpendicular to the cornice overhangs and ridges must correspond to the direction of the prevailing winds in the construction area. This is done so that the wind cannot blow dust and sand into the seams and tear off the rolled material.
When sticking rolled materials, it is necessary to systematically control the temperature of the mastic, not allowing it to cool below 160 ° with bituminous mastic and below 120 degrees with tar mastic, because the quality of the rolled carpet sticker largely depends on this. In order to maintain the temperature of the mastic supplied to the place of work for a longer time, a special insulated transport container is used. Electric boilers are used to heat mastic on the roof.
The work on sticking the carpet is always carried out in such a way that the area between the watersheds can be completely sealed with at least one layer of rolled material. If at the same time the rolled material is used without cover (glassine, hydroisol, only leather), the surface of the pasted layer must be painted with a continuous layer of mastic. This allows you to immediately put the roof into operation and ensures the safety of the glued layer, screed and insulation.
In case of unfinished installation of ventilation and other devices; as well as in adverse weather, all layers of the roof should not be glued at once.
On these sections of the roof, it is necessary to stick only one layer of roofing felt with fine dressing (or roofing felt with a roofing roof), and glue the remaining layers after finishing installation work and in good weather.
To fill the supply tank with mastic, the arcuate handle of the machine leans forward and thanks to this the tank rises so that mastic can be poured into it; the roller is tilted forward to open the filling slot. The mastic is poured into each of the 10 sections of the tank into which it is divided so that the mastic does not merge to one edge of the tank when working on inclined surfaces.
The consumption of mastic for machine gluing is about 1 kg/m2, which is 2 times lower than for manual gluing. The quality of the machine sticker due to the reduction in the thickness of the gluing layer and the careful immediate pressing of the glued panel with an elastic roller is higher than with manual sticker.
The direction of rolling rolls for machine gluing on the planes of the roof is the same as for manual gluing.
roll sticker
The roll is rolled out to its full length and tried on in place. Then the end of the roll is folded over and the machine is installed in this place in the filling position. If necessary, they immediately fill the supply tank with mastic and then put the end of the roll on the tank and press it with a roller. In this state, the machine can be put into working position and, moving along the roll, stick it.
You can paste in two ways. If the weather is not windy, the roll can not be rolled up. In this case, the machine is moved forward along the roll. If the weather is windy and the bale moves because of this, it can be rolled up tightly and placed on the storage tank. In the latter case, it is more difficult to withstand
a given direction and it is somewhat harder to move the car, but in windy weather this method of sticker is more convenient. Regardless of how the roll is applied, the end of the roll should be glued first. This is done by pushing the machine forward as soon as the machine is in working position; at the same time, in order to prevent the shift of the panel, it is necessary to step on the end of the roll with your foot.
The correctness of the given direction and the amount of overlap depends on the correct sticker of the end of the roll; therefore, the rolls must be carefully tried on in place and the machine must be correctly installed in the working position, and then the end of the roll must be glued.
Cold mastic is used for gluing double-sided roofing felt on roofs with slopes of up to 25%.
Roofing on cold mastics is arranged according to cement; wooden or asphalt concrete bases. Since asphalt concrete bases soften from the solvent, they are made on bitumen with a softening temperature increased by 10-15 °, compared with the softening temperature of bitumen, determined by the selection of asphalt concrete of the required heat resistance.
For bases made in advance from cast or compacted asphalt concrete, i.e., selected on bitumen with a normal (not elevated) softening temperature, they must be painted twice with a cold primer of a 1: 1 composition of BN-V bitumen and an easily evaporating solvent (gasoline, benzene, etc.) with a total consumption of 400-500 g/m2 or hot bitumen grade BN-V.
Cold mastics are used at air temperature. + 10° and above without heating; at a lower temperature, the mastics must be heated so that at the time of application to a cold base, their temperature is not lower than + 10 °. "Mastics are heated to a temperature not exceeding 70 °, but not on an open flame, but, for example, in a water or sand bath .
Before use, cold mastic should be intensively mixed (for example, with a chain or paddle mixer driven by an electric drill); it is recommended to mix the mastic directly in the factory container until the required workability is obtained.
The mastic is poured with a bucket and leveled over the pasted surface with a special rake with a rubber gasket so that there are no uncovered areas and there is no excess that is easily removed by the rake.
The consumption of cold mastic when sticking the first layer is allowed up to 1 kg/m2, when sticking the remaining layers it should not exceed 0.7 kg/m2, since at a higher consumption roofing material may slip or the mastic may flow out. To control the consumption of mastic, it should be supplied to the workplace in containers of 6 (12) kg and this amount should be distributed over an area of 10 (20) m2 in an even layer in the direction of rolling the roll.
Ruberoid is glued by rolling the roll onto the layer of mastic, and this rolling is carried out in a forward-backward movement, i.e. with the reverse rolling of the roll, so that the panel fits better to the base and sticks.
In addition to lapping by hand, the roofing felt must be rolled with a cylindrical roller weighing 80-100 kg with a soft elastic lining. The sticker of the next layer of roofing material is made the next day.
The sticker of rolled materials on cold mastic is also allowed to be carried out separately, in which the roofing material is not glued immediately, but after 30-45 minutes. after applying the mastic to the surface to be glued. This method is only recommended for summer time.
Valleys, junctions and drain funnels are also pasted over with cold mastic. In this case, special attention should be paid to the smoothness of transitions from a vertical surface to a horizontal one, since roofing material may lag behind in these places. Lapping of roofing material to a vertical surface should be done immediately after rolling it onto a layer of mastic and repeated the next day.
Air bubbles found before sticking the next layer of roofing material are pierced with an awl so that all the air around the puncture comes out. The roofing material around the puncture should be tightly compressed and carefully rubbed. Lap seams must be carefully puttied with mastic, rubbed and rolled.
Cost of work
| Name of works | Unit rev. | Volume | Unit cost in rubles | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dismantling of roofing from rolled materials (up to 4 layers) | m2 | 150 | 0 | ||
| Device for leveling cement-sand screed 30-40 mm thick | m2 | 330 | 300 | 0 | |
| TOTAL for scope of work | 0 | ||||
Rolled materials cannot be called aesthetically attractive. Nevertheless, there are such conditions in which rolled roofing is almost the only option for covering the roof. This is a flat roof, a single-pitched or multi-pitched roof with a small slope - up to 30 degrees. The device of a roll roof provides tightness and water tightness of such roofs. Garages, warehouses, hangars, commercial premises, enterprises and high-rise buildings are covered with rolled materials. Roll roof installation technology depends on many factors, including the type of material and the slope of the roof. A minimum of three people will be required to complete the work. How the installation takes place, what you should pay attention to and what rules to follow, we will tell in this article.
Types of roll materials
Gone are the days when roofing material and roofing felt were the only roll materials for roofing. Their service life did not exceed 5 - 7 years, since the cardboard base quickly collapsed under the action of water, the bitumen cracked under the action of sunlight and temperature changes. Modern technologies made it possible to significantly improve the characteristics of bituminous materials, extend their service life up to 15 - 25 years and make them more versatile.
Modern rolled materials have stronger bases, a complex structure, have increased plasticity and frost resistance and can be attached to the base in various ways.
Rolled roofing materials are not the same, they differ in the base material, the binder and the material and fraction of the dressing.
As the basis of the roll material are used fiberglass, fiberglass And polyester. The most durable, reliable and expensive material is polyester-based.
As a binder use oxidized bitumen And polymerized bitumen. Polymeric materials are more resistant to temperature changes, more elastic, which allows them to be used on roofs with complex terrain, and more resistant to tensile forces. Various substances are used as polymer additives, but styrene butadiene styrene is considered the best.
Sprinkling on the surface of roll materials differs not only in the type of material, but also in the size of the fractions. Distinguish coarse-grained, medium-grained, fine-grained, pulverized And flake powder. The main function of dressing is to protect bitumen from direct sunlight, increase its strength and resistance to mechanical stress, therefore, in most rolled materials, dressing is only on the front side of the material.

Separately, I would like to note materials that have no basis. They are called "unfounded". Such materials are obtained by heat treatment of polymer binders with various additives and fillers, then the resulting composition is rolled into webs.
In total, 4 generations of roll materials can be distinguished:
- Ruberoid. As already mentioned, the material is not durable, but it continues to be used to cover the roofs of non-responsible objects.
- Embedded roofing material. It differs from the usual roofing material in that on its basis there is already a layer of bitumen, when melted, a sheet of material is glued.
- Glass roofing material. Fiberglass or polyester is used as a base. Glass roofing material is more durable than ordinary roofing material, its service life reaches 12 - 15 years. It is not afraid of temperature changes and frosts, as well as ultraviolet rays. It is considered a more reliable option for arranging a roll roof. Fastened by welding or mechanical fastening.
- Membrane roll material- the most modern at the moment. The service life of the membrane material reaches 20 - 25 years. It uses the most reliable and durable binders, fiberglass as a base, as well as colored sprinkle granules. The main difference between membrane roll materials is that they are self-adhesive. On the underside there is a special protective film, which hides the adhesive layer. It is enough to remove the film, roll out the material, level it and it will stick by itself when the sun's rays heat up the adhesive layer of the base.
When choosing roll material, pay attention to the markings. There are such types of coatings:
- P - lining;
- K - roofing;
- E - elastic.
Appropriately labeled material may only be used under certain conditions. For example, the underlay material can only be used as the first underlay. Roofing material can be used as a top layer, and elastic is convenient to use for bypassing complex vertical elements.
Roll roofing: arrangement technology and fastening methods
The technology of laying a rolled roof depends on several factors: first of all, on the slope of the roof slope.
For example, the number of layers of roll material should be:
- 2 layers are enough if the slope is more than 15%;
- 3 layers if the roof slope is 5 - 15%;
- 4 layers if the roof is flat, slope 0 - 5%.
Maximum allowable slope roofing, in which roll materials can be used, is 25%.
looks like that:
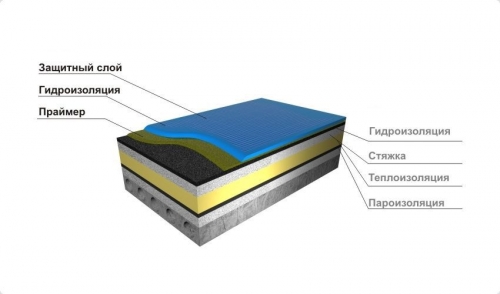
- base in the form concrete slab overlaps;
- Vapor barrier film to protect the insulation from wet vapors coming from the premises;
- Thermal insulation material. The most commonly used stone mineral wool in slabs and extruded polystyrene foam;
- Screed layer 2 - 7 cm;
- Rolled roofing material in 2 - 3 or 4 - 5 layers.
If the roof is made of metal profile, then the layers of the pie look like this:

- Roofing material - corrugated board;
- Thermal insulation material;
- Roll roofing material.
Basically, this method of laying roll roofing is used to cover hangars and other storage facilities. Please note that the base must not allow vapors from the heated room to pass through. Also, laying the roll material on top of the insulation is not the most good option, as the resource of the heater is reduced. But this method is still used, since most often it is not recommended to overload such roofs with a screed.
Roll roofing technology pitched roof :
- Vapor barrier film inside the attic or attic;
- Thermal insulation material between the rafters;
- Waterproofing superdiffusion membrane;
- Solid lathing in the form of OSB sheets or moisture-resistant plywood;
- Roll roofing material.
All layers of rolled material must be laid with an offset so that the joints and overlaps do not coincide.
The cost of laying a rolled roof depends not only on the price of the material used, but also on the laying technology and on the method of fastening. For example, laying material in 2 layers on a finished base will cost 7 USD. per 1 m2, if it is necessary to perform a screed and lay insulation, then such work will cost 40 USD. per m2. Laying the membrane material mechanically, even on a finished base, will cost 14 USD. per m2.
There are several ways to fasten rolled roofing materials:
- mechanical method with roofing nails. Usually used to secure the first underlayment.

- Welding material. A gas burner is used, with the help of which the lower bituminous layer of the material is melted and the canvas is glued to the base.
- Bonding on bituminous mastic. The base is carefully smeared with an adhesive - cold-applied bituminous mastic, and then rolled material is glued onto it. In this way, all layers of the roof are attached, from the first lining to the last roofing.

- Self-adhesive materials. As already mentioned, there are materials whose bottom layer is adhesive. It melts and acquires adhesive properties from heating under the sun's rays. It is enough to simply fix such materials with a roller in places of overlap and joints.
The most common method of fastening rolled roofing material is fusing. The last category of self-adhesive materials belongs to expensive materials, therefore it is used less frequently. But in commercial and residential buildings with a flat roof, membrane-type materials are increasingly being used.
Roll roof laying: scheme
The location of the webs of rolled material depends on the slope of the roof.
On a flat roof, the laying of roll materials starts from the lowest place.
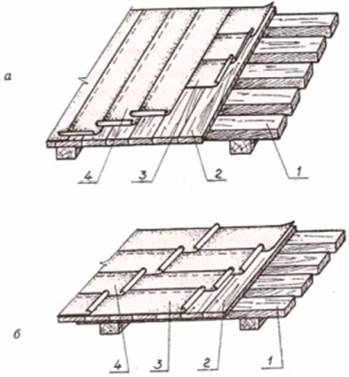
On pitched roofs with a slope of less than 15% laying is carried out parallel to the ridge. You need to start from the bottom, from the overhang and move up. After laying the material on the roof slopes, the canvas is cut off and placed on the roof ridge so that the water flows down.
On pitched roofs with a slope of more than 15% laying is done across the ridge. The upper edge must necessarily be thrown over the ridge, and the lower edge must fall on the overhang by 15 cm. The second slope is covered in the same way. The top edge should be thrown over the skate.
The size of the overlap also depends on the slope of the roof. If the slope is more than 5 °, then the overlap between the sheets of the inner layers should be 7 - 8 cm, and between the sheets of the outer layer - 10 - 15 cm. If the slope is less than 5 °, then the overlap in any layers should be at least 10 cm.
It is forbidden to lay layers in transverse directions. This is especially true for flat roofs. Laying the roll material in layers should be carried out in only one direction, and the overlaps should be located with an offset of 10 cm.

Laying welded-on method is most often used for arranging flat roofs. Laying technology is a certain sequence of actions that must be followed, without excluding any of the stages.
Stages of laying a roll roof:
- Drainage arrangement.
- Creation of a breakout.
- Drainage installation.
- Laying vapor barrier material.
- Laying of thermal insulation material.
- Laying reinforcing mesh.
- Laying cement-sand screed.
- Laying roofing around water intake funnels and aerators.
- Installation of roofing on parapets and other vertical and complex elements.
- Priming of the screed and all junctions to the vertical elements with a primer.
- Fusing of rolled material - 1 layer.
- Welding of material at the junctions.
- Fusing of rolled material - 2 layers.
- Clamp plate installation.
- Installation of an apron on vertical elements - galvanized.
- Installation of a galvanized parapet.
Foundation preparation
The concrete base must first be cleaned of debris, dust and dirt. If there is an old coating on the surface, it must be removed. All chips, cracks, ruts are sealed with a repair compound. All further work should begin after the repair composition is completely dry. At this time, you can do the installation of the storm water inlet and gutters.
Laying vapor barrier materials
Film or membrane materials are used as a vapor barrier. It is necessary to lay them with an overlap of 10 - 15 cm. All joints are glued with construction tape. The vapor barrier material is brought to all vertical elements to such a height that it ultimately turns out to be higher than the location of the future thermal insulation material.
Laying of thermal insulation materials
For thermal insulation of flat roofs, mineral wool in slabs and extruded polystyrene foam are used. The heat-insulating material is laid in two layers to block the cold bridges formed by the joints of the plates. By the way, the joints between the insulation plates should be spaced apart.
Thermal insulation boards can be glued to the base, or they can be fixed with special dowels.
After laying the insulation, a leveling screed is poured with a layer of 2 cm to 7 cm. It is imperative to perform temperature-shrinkage seams in a 5 mm thick screed. The linear dimensions of the seams should be 6x6 m.
In those places where the roofing material will adjoin the vertical elements, the sides must be made 10 cm wide and 10 cm high. They can be done using cement mortar. Just fill in the corner formed by the vertical element and the base.
After laying the screed, wait 4-6 hours, and then cover its surface with a primer, which is bitumen diluted in half with kerosene. You can also buy ready-made primer.
After the screed and primer have dried, you can start laying the rolled roofing material.
Installation of built-up roof
To begin with, it is necessary to waterproof the temperature-shrinkage seams. To do this, strips 15 cm wide are cut off and glued to the base using bituminous mastic. Next, you can lay the sheets of the rolled roof:
- Laying starts from the lowest point. The roll is unwound and placed at the place of future installation. Before you start fixing it, you need to check its integrity.
- First of all, the edge of the roll web is fixed. To do this, the edge is heated by a gas burner and pressed against the very edge of the area where it will be fixed.
- The canvas is again rolled up into a roll to the attachment point.
- Now you can heat the canvas itself with a burner. The gas burner is held so that it heats the surface of the base where the canvas will be attached, as well as bottom surface the canvas itself. As a result of heating, a bitumen roller with a layer of 2 cm should form in front of the web.
- The technology of work is as follows: one person heats the canvas with a burner, the second one unfolds the canvas with a hook in the course of gluing, and the third one rolls it with a roller. More details can be seen in the photo.
Laying a roll roof: a photo - an example

- If the canvas is heated correctly, then bitumen 2 cm thick should protrude along the edges.
- It is undesirable to walk on newly laid rolled material.
- The person rolling the roller must carefully remove all air bubbles. After gluing, it is advisable to check the fastening of the edges of the material. Poorly fastened edges must be torn off with a spatula and heated again with a gas heater and pressed to the base.
- The edges of the roll must be rolled with special care. The movements of the roller along the rolled material should be at a certain angle, starting from the middle of the web and moving towards the edges.
- Cloths are glued with an overlap: longitudinal overlap - 10 cm, end - 15 cm.
- To lay the rolled material on the parapets, you must do the following: cut off a piece of the required length, then mechanically attach its upper edge to the parapet, then glue the fabric by fusing to the base.

- For laying the material in the corners - internal and external - it is necessary to cut a larger sheet and glue it with an overlap.
- To lay the material around the receiving funnels of the drainage system, it is necessary to cut off pieces of the canvas and glue them so that squares of 70x70 cm are formed around the funnels.
- The second and third layers of roll material are attached in exactly the same sequence. Do not forget about the junction with vertical objects, parapets, funnels. After each layer, additional layers are laid in these places.
Remember that the roll material should only be laid in one direction.
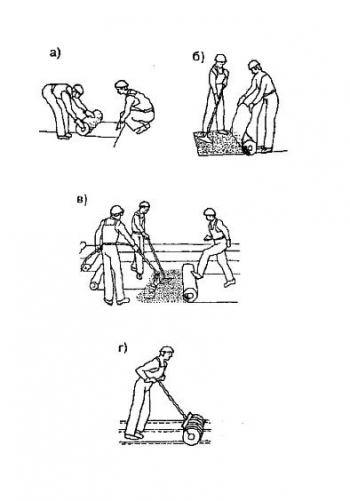
The cold laying of roll roofing is somewhat different from the hot method. Let's note the most obvious differences in technology:
- Before laying the roll, it must be rolled out and left in this position for at least a day. If this is not possible, then it is necessary to roll out the roll, and then roll it in the opposite direction.
- The laying of the first roll is carried out as follows: the roll is rolled to the middle, the dimensions of the web are checked, whether it is enough to the place where the laying began, then the unfolded part of the web is rolled into a roll again. The result should look like this: a roll divided in half into two rolls.
- Then one person coats the base with mastic where the rolled material will be laid. It is enough to process an area of no more than 1.5 m2 at a time.
- The second person rolls out the roll on a base smeared with mastic.
- The overlap of the roll material should be: longitudinal 8 - 10 cm, end - 15 cm.
In addition to laying rolled roofing on mastic, there is another method of cold laying. If membrane roll materials are used, they can be laid either on glue or mechanically.
Laying membrane roll materials on glue is quite expensive, so mechanical laying is more often used. Welding of the membrane roof panels between themselves is carried out using special welding equipment.
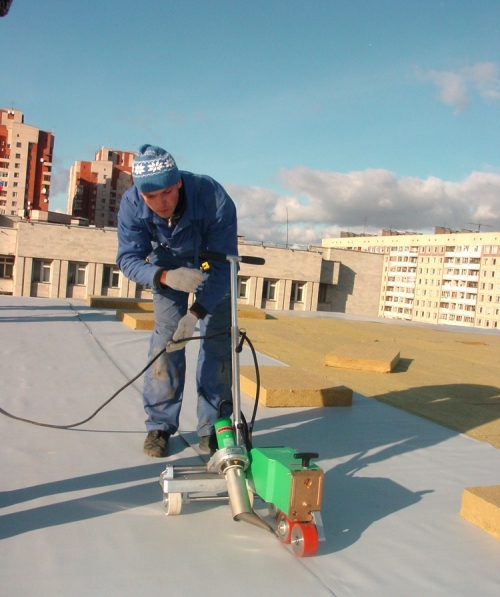

Thermoplastic panels are well fastened with hot air at a temperature of 600 ° C. The edges are rolled hot with a special roller-skating rink. The adjunction of the canvas to the vertical elements is carried out using a building hair dryer.

The junctions of the rolled roof to the vertical elements are considered the most difficult, since there is a high probability of water getting under the material. Laying roll material in such places is carried out in at least 2 layers:
- The first piece is cut so wide that its upper edge extends at least 25 cm onto the vertical element.
- The upper edge is fixed mechanically - with nails or self-tapping screws.
- The rest of the canvas is glued to the base.
- A second piece is cut off of such a width that its upper edge extends 35 cm onto the vertical element.
- The upper edge of the piece is folded into a small roll 5 cm, applied to a vertical base and secured with a mounting plate.
- The rest of the canvas is heated and glued to the base.
Pitched roll roofing: installation technology
A feature of the installation of a roll roof on a pitched roof is that a solid crate made of OSB or plywood is used as the base. It is also worth paying close attention to cornices, overhangs, valleys, vertical elements and the ridge.
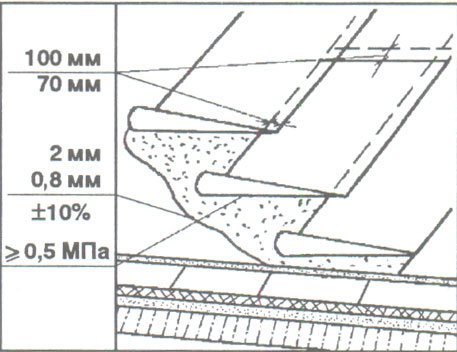
As already mentioned, if the roof slope is less than 15%, then the material must be laid parallel to the ridge. The first canvas is laid at the very bottom from the edge, the bypass to the cornice overhang should be at least 12 - 15 cm. This hanging edge is then fixed with a pressure board. Further laying is done from the bottom up. All subsequent rows are laid with an overlap of 10 cm. The last canvas is laid with an overlap on the ridge of at least 25 cm. Then they are laid on the second slope using exactly the same technology.
If the roof slope is more than 15%, then the material can be laid across the ridge. To do this, roll it tightly from top to bottom, and the overlap on the ridge should be at least 30 - 40 cm.

Attach roll material to pitched roof can be both welded on and glued to the mastic. For mechanical laying, a gluing machine is used to join the edges of the sheets.
To cover the valleys and grooves, the material is laid in 4 - 5 layers. The first 3 layers are laid immediately, overlapping 10 cm. The fourth and fifth layers are laid, alternating them with layers of rolled material on the slope. If the width of the valleys is less than 60 cm, then the canvases are glued along them. If the width is more than 60 cm, then the canvases are cut into pieces and glued across. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure that the flow of water is carried out unhindered. To do this, the material begins to be laid from the bottom up.
In places of overhangs and cornices, the material is laid with a margin of 10 - 15 cm. Then the edge is wrapped and fixed with roofing nails. From above, the edges of the cornices on the sides of the building are covered with roofing steel. In places of overhangs, grooves for a drain must be mounted.
Roll roofing is one of the most simple way cover the roof. The main thing is to follow the technology, make sure that there are no air bubbles under the material, and the edges are firmly fixed.
Laying a roll roof: video - an example
590
Roof waterproofing is necessary in order to completely exclude the penetration of moisture into the room. It also helps to protect the truss system, the roof base, and the heat-insulating layer from snow, rain, condensation and dust. To create a reliable waterproofing carpet, rolled bitumen-polymer materials are used. Modern rolled roofing materials, when properly installed, completely prevent leaks, create a durable and strong waterproofing layer, and isolate roof joints.
Roll waterproofing IKOPAL
ICOPAL produces various new generation roll waterproofing materials based on SBS-modified bitumen. Roll waterproofing produced by ICOPAL has a long service life (up to 50 years), does not lose its consumer characteristics in a wide temperature range and is easily mounted by welding or free laying. Work can be carried out independently, without involving specialist builders.
The ICOPAL line includes different kinds roofing roll materials, making it easy to choose the solution that is optimal for your situation. IKOPAL roll roofing can be successfully used both for residential buildings and for industrial and commercial buildings.
ICOPAL VILLATEX. Roll insulation material on a durable non-woven polyester backing. Reliable waterproofing qualities are given to it by SBS-modified bitumen. For high-quality and fast deposition, the surface of the sheet is equipped with a ribbed profile and covered with a thin flammable film. The outer surface is covered with coarse-grained quartz dressing. Applicable:
- when repairing an old bituminous roof,
- for vapor barrier.
Produced as a two-layer system in rolls with marking:
- ICOPAL VILLATEX N,
- ICOPAL VILLATEX V.
It is successfully operated at a frost to - 25 °C. Weighs 4.5 kg/sq. m.
IKOPAL rolled roofing materials are produced in the form of single-layer and two-layer systems. Two-layer systems are supplied in rolls of two types:
- IKOPAL N. The letter H in the marking means that this is a roll for the lower layer of the roof (it is laid first, a roll marked B is laid on it).
- IKOPAL V. The letter B in the marking means that this roll is intended for the top layer of the roof (it is laid on top of the roll marked H).
ICOPAL SOLO. A single-layer waterproofing system based on a durable polyester base coated with SBS-modified bitumen and sprayed with granular quartz dressing. On the reverse side there is a ribbed profile that simplifies installation and a light-burning film.
Applicable:
- for waterproofing non-exploited roofs and floors,
- when repairing an old bituminous roof (no replacement of the old coating is required),
- for vapor barrier.
IKOPAL SOLO does not lose its waterproofing characteristics at temperatures up to -35°C, it has increased tensile strength. Weighs 6.5 kg/sq. m.
IKOPAL ULTRA. Two-layer waterproofing system made of SBS-modified bitumen on a durable non-woven polyester base, equipped with a protective profile for reliable fusing. On top is a decorative and protective quartz granular layer.
Is used for:
- roof waterproofing,
- waterproofing of an unused roof,
- foundation waterproofing,
- old roof repair.
IKOPAL ULTRA does not lose its waterproofing characteristics at temperatures up to -30°C, it has heat resistance up to +100°C. Weighs 5 kg/sq. m.
The technology of work on the device of a flat roof using rolled materials
Foundation preparation. When installing flat roofs, the waterproofing carpet is laid on a dry, even concrete base with a slight slope. Before starting work, the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe base must be prepared: repair all irregularities, clean from dirt and dust.
A general recommendation when fusing vapor barriers and roofing materials: to improve the adhesion of the fusing materials to the base surface, it is advisable to coat it with a primer. You can find ready-to-use primers in the ICOPAL product line.
Installation of vapor barrier. To protect the heat-insulating layer of the roof from condensate coming from the under-roof side from attic space, a vapor barrier layer is required. As a vapor barrier, you can use ICOPAL VILLATEX N roll material, which is mounted by fusing on the base. The welding method is the same as described below (see "Installation of welded roofing").
Thermal insulation installation. For thermal insulation of the roof, plate insulating materials made of mineral wool, foam glass, extruded polystyrene foam are used. It is also possible to insulate the roof with a monolithic layer of lightweight concrete or perlite (vermiculite) backfill with cement or bituminous binders. A separating layer of roofing material or glassine is laid on the thermal insulation. A leveling screed is poured on top, which should be treated with a primer and wait for it to dry completely. A rolled roofing material is welded onto the prepared screed. If you do not plan to insulate the roof, then the roofing material is mounted directly on the base prepared and treated with a primer.
Before installation, roll roofing materials are recommended to be rolled out, allowed to rest for several hours for alignment and rolled up again at both ends.
Installation of built-up roof:
- Welding is carried out evenly and consistently, with a gas burner with an overlap of 10 cm of waterproofing sheets.
- The roll of roofing waterproofing must be thoroughly heated so that when fusing on the sides of the sheet, the bituminous mass flows out evenly (by about 1 cm). Neighboring rolls must be displaced in such a way that there is a gap of about one meter between them.
- On the vertical elements of the roof, rolled roofing materials are welded from the bottom up.
- On a roof with a small slope, the coating is laid in 3-4 layers (with a displacement of the joints of each subsequent layer).
The technology of laying a rolled roof on a pitched roof
The specificity of a pitched roof is that its base is a continuous crate made of wood materials, and the thermal insulation layer is mounted with inside roofs (where the attic is located) - between the elements truss system. Rolled waterproofing is laid from the outside and does not come into contact with the insulation. When constructing a roof with a counter-lattice, waterproofing is laid over the rafters, on a continuous crate (and below the counter-batten).
With a roof slope of more than 15 degrees, rolled waterproofing materials are evenly welded from top to bottom perpendicular to the ridge with an overlap of 40 cm on it. The overlap between the rolls should be 10 cm. A bypass of 15 cm is made on the cornice overhang, which is fixed with a clamping rail and self-tapping screws. Since moisture does not accumulate on a pitched roof, it is enough to lay the coating in two layers (the seam of the joints of each subsequent layer must be displaced).
With a pitched roof slope of less than 15 degrees, roll materials are laid parallel to the ridge in three layers. The canvases are welded from the bottom up, the bypass on the cornice overhang is also fixed. The last canvas on the slope is laid with an overlap on the ridge of 30 cm.
On a pitched roof, special attention should be paid to waterproofing joints, vertical elements, valleys, etc., in order to completely eliminate leaks. To enhance the waterproofing of complex junctions, you can use bandage tape and specialized IKOPAL waterproofing mastics.