Constructing a building or structure in the winter is a labor-intensive, but quite realistic idea. However, it is important to take into account the peculiarities of construction in winter, when it is necessary to use certain methods and techniques to build a strong foundation. Of course, it is best to carry out construction from April to October, however, emergency situations may arise and the foundation is needed in winter.
This page provides information about the features of arranging reinforced concrete foundations in winter. We will consider foundations suitable for construction in sub-zero temperatures, and the technological operations that accompany the process of their installation.
Only a professional approach and knowledge of laying technology will allow you to get a foundation that will not lose its qualities even in the most severe frosts and on frozen soil.
Features of foundation construction in winter
The installation of foundations in winter is often resorted to not only out of necessity, but also in order to save on the cost of building materials and workers’ services, the prices of which, out of season, are traditionally lower.However, practice shows that it is extremely difficult to achieve savings here; the reduction in costs is offset by the need to take additional measures to heat the foundation after concreting, the cost of which can reach up to 1 thousand rubles. rubles per day when using a heat gun.
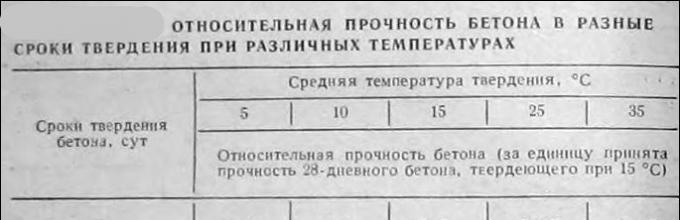
Important: according to SNiP, the permissible minimum temperature for the concrete mixture to gain strength is +5 degrees, when lowered, the quality of the concrete structure significantly deteriorates after hardening.

Rice
Difficulties in arranging the foundation in winter are associated with the following factors:
- Development of pits and trenches in frozen soil (feasible by using highly productive excavators);
- The need to heat the concreted structure (convection heating is used using a heat gun or electrical heating of the reinforcement laid in the foundation).
When the mixture freezes, the hardening of concrete slows down significantly, and at severe subzero temperatures it stops completely. Freezing water crystallizes and increases its volume; due to the expansion of concrete, the adhesion of the material to the reinforcement decreases, which is fraught with subsequent cracking and destruction of the foundation under heavy loads.
Important: concreting the foundation in winter should be done using concrete with anti-frost additives, which ensure the hydration process occurs in sub-zero temperatures. However, even anti-frost compounds require heating of the structure after pouring.

Rice
According to building codes, it is possible to allow concrete to cool to the temperature for which the additive is designed only after reaching a certain intermediate strength:
- Antifreeze concrete M200 - 30% of the design;
- M300 - 25%;
- M500 - 20%.
- M150 - 50%;
- M200 and M300 - 40%;
- M400 and M500 - 30%.
Important: if the structure after concreting will be subject to cyclic freezing and thawing, its cooling can be allowed only after reaching 70% of the design strength, regardless of the class of the mixture.
Concrete that has achieved the required intermediate strength does not continue to harden after cooling, but goes into a preserved state. It will receive its final design strength only after 28-30 exposures at above-zero temperatures. This means that if work on raising walls is also planned for winter, the foundation must be heated for a month.
Foundations suitable for construction in winter
For construction in winter, an important step is the choice of the type of foundation, since not every type is suitable for the conditions of a given time of year. Let's consider several construction options and types of foundation.Strip foundation in winter
 The most popular among developers is strip foundation. However, there are a couple of nuances, taking into account which this variety does not provide the desired result. So, for example, when laying a foundation in winter, it is necessary to perform a number of additional manipulations, and, accordingly, labor productivity increases, and as a result, financial costs increase significantly. Laying a strip foundation is characterized by so-called “wet operations,” which is not always possible, especially in cold weather. Consequently, if you use this type of foundation, then with the maximum number of ready-made structures made at the factory.
The most popular among developers is strip foundation. However, there are a couple of nuances, taking into account which this variety does not provide the desired result. So, for example, when laying a foundation in winter, it is necessary to perform a number of additional manipulations, and, accordingly, labor productivity increases, and as a result, financial costs increase significantly. Laying a strip foundation is characterized by so-called “wet operations,” which is not always possible, especially in cold weather. Consequently, if you use this type of foundation, then with the maximum number of ready-made structures made at the factory. Important: only deep strip foundations are allowed for construction in winter, the supporting base of which falls below the freezing level of the soil. Installation of a shallow-depth tape cannot be carried out in winter, since such a structure is placed in a layer of frozen soil, which changes its volume when thawed, which leads to settlement and deformation of the foundation in the spring.

Rice
If, after pouring and heating the foundation throughout the entire period of strengthening, cracks form on the surface of the structure, they must be blown out with compressed air and repaired using a homemade mixture of polymer glue and cement.
Foundation in winter based on concrete piles
 A foundation based on concrete piles is another method of construction in winter. So, it is best to use bored piles, which are driven into wells quite well using a breaker. However, before installation, a preparatory stage is necessary - drilling, and this is very difficult in frozen soil conditions.
A foundation based on concrete piles is another method of construction in winter. So, it is best to use bored piles, which are driven into wells quite well using a breaker. However, before installation, a preparatory stage is necessary - drilling, and this is very difficult in frozen soil conditions. The essence of the method is to develop wells into which reinforced concrete piles are installed. Modern drilling rigs, such as BM-811, are capable of effectively drilling frozen soil. The cost of creating a well 8-9 m deep in frozen soil, when using this machine, is 10-15 minutes.
Important: driving reinforced concrete piles into frozen soil has low efficiency. To increase the efficiency of piling hammers during the construction of pile foundations in winter, leader drilling technology is used.

Rice
Screw piles in winter
 The solution to the problem is to use screw piles, which, thanks to their stability and unpretentiousness, are suitable even on soft soil.
The solution to the problem is to use screw piles, which, thanks to their stability and unpretentiousness, are suitable even on soft soil. A monolithic foundation is also suitable for winter construction, however, voids in the base and walls can cause serious freezing of the entire building and lead to destruction of the surface.
The installation of a screw foundation in conditions of sub-zero temperatures differs from the summer installation of the foundation in that it is exclusively more labor-intensive to screw in piles, for the implementation of which it is necessary to use mechanized equipment.
Tying screw supports with a grillage made of timber or rolled metal does not involve any complication of the technology; it can be implemented within 2-3 working days.

Rice
Related materials:
Advantages and disadvantages of building a foundation in winter
Before starting construction in the winter, it is worth finding out and comparing all the pros and cons of the future construction, because the future of the building or structure depends on it. As for the advantages of building a foundation in winter:- Significant discounts on building materials;
- Regarding summer work, winter work is much cheaper;
- There is no threat of pit collapse or erosion due to rain;
- The equipment will not get stuck in liquid soil on the way to the site.
Disadvantages of the foundation in winter
- Special equipment is required to dig a pit in frozen soil;
- Low labor productivity and a large number of additional work;
- The need for special strapping to protect against freezing;
- High risks of work stoppage due to severe weather conditions.
Mandatory measures applied during construction in winter
In addition to choosing the type of foundation, it is necessary to comply with construction technology. So, this process occurs with an artificial increase in the temperature of the post, for digging a trench, pit and drilling wells. For this purpose, a special tent with a heating unit is installed.Pouring the foundation
 Pouring the foundation in this case does not differ from the standard procedure in the summer. However, there is one caveat:
Pouring the foundation in this case does not differ from the standard procedure in the summer. However, there is one caveat: - Before pouring the foundation, a reinforced frame with a heating element is inserted into it.
- Upon completion of the installation, a canopy with a heat gun is built over the foundation to regulate the temperature.
- After several days, the canopy and cannon are dismantled, and the top layer of soil is sprinkled with a heat insulator to maintain the temperature of the heated base of the foundation.
- As a result, we get a complete basis for constructing a building in the winter.
When concreting the foundation in winter, the concrete preparation technology changes. It is necessary to increase the initial temperature of the composition to 30-40 degrees by heating the constituent components. Water is heated in boilers to a temperature of 90 degrees. In industrial conditions, aggregate (crushed stone) is heated in steam drums to 40 degrees. Cement cannot be heated.
The mixing time of the mixture in a concrete mixer increases by one and a half times.
When assembling the reinforced frame, the reinforcement stored outside must be heated to a positive temperature. The concreting itself is carried out at an accelerated pace, preventing the laid layer of concrete from setting and freezing before the next batch is poured.
Important: heating of the foundation can be realized in two ways: the “thermos” method and contact electric heating.

Rice
The “thermos” method involves installing it above the perimeter of the tent base and using a heat gun, which warms the air inside the tent to the required temperature (minimum +5 degrees).
When using a 10 kW heat gun in a tent with an area of 100 square meters, the temperature increases by 8-10 degrees compared to the street temperature. When working in frosts above 15 degrees, guns with a power of 25-30 kW are used.

Rice
The use of autonomous guns powered by gas or diesel fuel entails significant financial costs. A 30 kW device consumes up to 70 liters. gas per day, which at current prices is equal to 1 thousand rubles per day. Maintenance costs for electric generators connected to the home electrical network are significantly lower.

Rice
The method of contact electric heating consists of installing electrodes on the reinforced frame (placement step - 40 cm) or special cables, to which a welding generator is connected, supplying a voltage of 50-127 V (power is determined by thermal calculation). The average energy consumption for such heating is 70 kW per cubic meter of concrete. This method is used to heat massive slab foundations.
Ordering foundation work
Will carry out any work at any time of the year at a high level. Our staff of specialists and fleets of special equipment allow us to cope with absolutely any job.
Our company "Pile Installation" supplies and drives piles in the Moscow region -
Not so long ago, with the onset of frost, construction was also adopted to “freeze” in our latitudes. Moreover, no one undertook to start it. There could be no talk of constructing concrete foundations and reinforced analogues if the thermometer warned of a drop below +5º C during the daytime, and recorded negative temperatures at night. However, the length of the winter breaks in construction forced residents of the northern country to look for methods that would allow them to continue concrete work in the cold. This is how methods have emerged through which a durable monolithic foundation can be built at low temperatures. Having figured out how to pour a foundation during a difficult frosty period, you can safely begin building a bathhouse in winter.
The nuances of concreting in winter
It is not for nothing that winter was considered not the best period, both for pouring a monolithic structure and for constructing supporting elements of bored and pile types of foundations. The reason for this is the crystallization of water, one of the main components of the concrete solution. By turning into ice, water not only interferes with the normal course of the hydration process of the concrete mixture - that is, the formation of reliable molecular bonds due to its work. Due to the formation of ice crystals, the dimensions of which increase the initial volume of water by 10%, porosity increases. This fact in no way contributes to obtaining the planned strength of the foundation, but significantly reduces it.
Let's understand the mechanism of hydration
Concreting is the process of gradual transition of a mixture of cement with sand and crushed stone from the liquid phase into the solid stone state assigned to it by rank. At a temperature background of + 15º and at a humidity level favorable for setting, the following occurs:
- first, a kind of sodium hydrosilicate shell is formed on the surface of the poured structure;
- then the upper layers of the poured mass are involved in the reaction - the hard grains of cement gradually suck out the moisture, due to which the components of the solution “stick together”;
- then the outer shell, losing evaporating water, begins to shrink;
- then deeper layers react;
- and further in the same sequence, until after 28 days the concrete structure gains maximum strength.

If the foundation has to harden on a hot, dry day, the rate of hydration increases. But the water also begins to evaporate more actively, leaving in its place pores unfilled with bound concrete. At low temperatures, the reaction slows down, but pores appear due to the formation of ice crystals. To avoid this, the foundation is poured in winter according to special rules that make it possible to obtain the temperature of the solution required for normal hardening inside the poured concrete mass or individual pillars.
Hydration is accompanied by a spontaneous increase in temperature. The greater the thickness and dimensions of the concrete structure, the more heat the concrete generates and the slower it cools. Therefore, you should not get carried away with pouring support pillars in cold weather; it is advisable to prefer tape or monolith. If you install heat-saving formwork from insulating mats or slabs around massive structures, with minor drops in temperature you can do without additional tricks.

Classification and analysis of concreting methods
Owners, puzzled by the problem of whether it is possible to fill the foundation in winter, receive a clear affirmative answer, but with many variations. Options for solving the problem of maintaining or creating the conditions necessary for normal hydration depend on:
- on the dimensions of the structure;
- on the chemical composition of the concrete mixture and on the proportions of the components;
- on the brand of binder cement and the fineness of its grinding;
- from climatic nuances;
- from the ability to heat water and filler.
Often the heat released during hydration is not enough to create the conditions necessary for concrete during the frosty period. Finely grinding the cement helps to slightly increase the temperature, due to which it reacts faster and releases more heat when combined with water. Heating the water and aggregate before mixing also helps.
Attention. Only water and fillers can be heated. Cement cannot be heated, otherwise it will lose its binding properties.
Usually in our latitudes, for winter pouring, a solution with a temperature above 21º C is not used, given that when moving from a concrete mixer to a place, it will release 4.5-5º C to the atmosphere. To obtain the working temperature of concrete, it is enough to heat the water to 32º. At temperatures above the specified value, hot water is first mixed with aggregates, then cement is added in portions.
Increasing the mixing period will help maintain the temperature of the solution. Thoroughly mixed concrete will quickly take its positions in the formwork and will cool less along the way. Therefore, builders recommend increasing the mixing time of concrete mixture components by 25% to optimize fluidity and using finely ground cement.
The simplest heating of concrete mixture
The option with separate heating of water, aggregate or the entire mixture in a concrete mixer by installing a brazier, a heat gun, or a gas burner next to it is suitable for those who are puzzled by the question of how to fill the foundation in winter with light frosts at night and positive thermometer readings during the day.

This scheme has strict rules:
- heating water max up to 80º C;
- initial mixing of water with aggregate and subsequent gradual introduction of cement, preferably with M from 400 to 500;
- the use of additives that increase the hardening rate.
Advice. The use of a vibration device is not a necessary condition for private buildings, but desirable. A construction vibrator is needed to compact the concrete mixture, to reduce air content, and reduce porosity.
After pouring, the concrete mass is immediately carefully covered with tarpaulins, bags, insulating mats, slag felt blankets or straw. Until strength gains, the temperature must be maintained by installing braziers or other heat-generating devices around the foundation. Then the heating is stopped and the formwork is dismantled. If the concrete cannot be fully cured, it can be allowed to freeze. All processes will be preserved, and after defrosting the reaction will proceed as usual minus the period between freezing and reverse action.
Attention. Stripping is carried out only after sufficient strength has been gained. According to SNiP III-15-76 regulations, the structure must gain 70%, regardless of the grade of concrete without additives.
Typically, “unfrozen” foundations built according to the rules do not lose more than 5% of their design value in strength properties if the water-cement mixture ratio was no more than 0.6.
Mixing concrete in frosty conditions is a difficult task. A justified decision by a reasonable owner would be to turn to the services of builders or purchase a ready-made solution with modifying additives at the factory. There the proportions will be calculated and weather conditions will be taken into account. With a ready-made solution, solving the question “how to properly fill a foundation with your own hands in winter” will no longer be an impossible task.

Use of concrete with modifying additives
The introduction of antifreeze additives into the solution is also aimed at increasing the thermal energy generated by the concrete itself. In addition to this stimulating effect, modifiers lower the “threshold” for water crystallization. Due to this, the hydration of concrete will take place according to the usual scheme at a temperature lower than for standard conditions.
In order to develop anti-frost properties, concrete is enriched mainly with calcium chloride. No more than 2% of the total mass can be added to the solution, otherwise the compressive strength of the concrete structure will significantly decrease. When the thermometer readings are stable below zero, the solution is mixed with sodium chloride (ordinary salt), potash, sodium nitrate, which ensures trouble-free concreting at -15º below zero. Despite the availability of additives, craftsmen looking for methods on how to pour a foundation for a bathhouse in cold weather should not experiment with solution formulas. It is better to purchase a ready-made composition without the risk of irretrievably losing all the money invested.
When using anti-frost modifiers, you can begin dismantling the formwork when:
- a solution with M200 will gain 40% strength;
- concrete with M to 300 will gain 30%;
- concrete marked M400 and above will gain 20%.
Most often, the use of concrete with modifiers is combined with artificial heating methods. When combining improved concrete, for example, with electric heating, it is necessary to take into account that urea will decompose at + 40º C, and due to potash heated to 30º, the strength will be reduced by 30%.

Technically complex methods of winter concreting
Let us briefly consider methods of artificial heating of concrete in formwork, the purpose of which is to increase the rate of setting of the mixture. Depending on the possibility of using electrical appliances, the availability of insulating materials and the financial framework of construction, the owner of a country estate can choose, or rather, order from a construction organization:
- concreting using the thermos method. Leakage of thermal energy and cooling of the body of the concrete mass are eliminated by the insulating sheathing constructed around the formwork. It is a metal casing with an electric, steam or water circuit that heats hardening concrete;
- pouring the foundation with steam heating. To implement concreting with steam heating of the solution, you will need powerful equipment and a considerable amount of water. It is necessary to accurately calculate the number of pipes installed in the formwork and build a pipeline supplying steam, which will forever remain in the body of the structure. Due to the considerable cost and complexity of implementation, few private owners prefer steam heating.
- installation of a greenhouse around a poured foundation It’s also not the cheapest way, because you need to build a large tarpaulin or plastic tent. It is necessary to maintain a constant temperature inside the tent and monitor the humidity so as not to dry out the concrete. The greenhouse is heated with portable stoves, cannons, and electrical equipment. A separate project is created for the construction of the greenhouse; it is dismantled after the formwork is removed.
- concreting with electric heating, carried out by starting current through wires with a steel core located in fresh concrete. The formwork or reinforcement structure is “entangled” with a wire with a calculated pitch, or the heating cable is simply laid in the concrete. Compared to the above options, this is the most economical and easiest to implement method, and therefore the most common.
- infrared and induction electric heating options, arranged by analogy from tubular heating elements, carborundum rod emitters or cables that create magnetic fields in reinforcement or steel formwork.
All of the methods listed do not belong to the category of work that should be undertaken without knowledge and qualifications. You need calculations of the amount of energy supplied, the design of additional devices, and the skills of a good electrician for electrical methods.

General rules to follow
Let's start with the fact that everyone who wants to know whether it is possible to fill the foundation in parts in winter conditions will probably be disappointed with the answer. A definite no. And until the filling is completed you will have to work around the clock. Laying should be done in segments that are small in height and length, immediately covering them with the next layer to avoid temperature loss. If for some unforeseen reason a helium shell begins to form on the surface of the poured concrete, it must be chipped off.
It is important to properly prepare the object for pouring:
- clear the pit or trench of snow, chip and remove ice from the bottom and from the reinforcement. To prevent freezing and icing of the bottom, you need to cover the trench or foundation pit with straw immediately after digging and laying the sand cushion;
- warm the bottom between the walls of the formwork approximately 30 cm. Do not pour concrete on top of frozen soil! Thawing under the mass of the solution, the soil will settle. It is not a fact that the settlement will be uniform. Moreover, there is no certainty that the foundation will not sag too much;
- provide access to the formwork from all sides.
There are few rules for safe, effective concrete pouring in winter, but they must be strictly observed. It is much easier to be diligent before pouring and during the process than to waste time and money on dismantling and alterations.
In the summer, building both the foundation and the structure itself is faster, easier and cheaper. But this is not always possible. This is due either to personal employment or to the short duration of the warm period. Thanks to the use of modern materials and the implementation of new technological solutions in practice, the question of whether it is possible to pour a foundation in winter has practically lost its relevance. These works are successfully carried out at sub-zero temperatures. Today, the effectiveness of concreting in frosts is being discussed from the point of view of economic and labor costs.
Features of foundation construction in winter
Making a foundation at low temperatures is not an easy process. Workers will have to work in the cold. Winter is generally considered not the best time to create a monolithic structure of slab or strip type, or to build piled and bored types of foundations. The main reason for this is that water, which is one of the main components of the working solution, crystallizes at temperatures below zero.
The formation of ice interferes with the normal process of formation of reliable bonds between concrete molecules - its hydration. Also, the expansion of water when freezing leads to a significant reduction in the strength of the foundation. This occurs due to the formation of pores in the concrete by ice crystals.

The hydration process itself occurs with heat release. Moreover, the larger the size of the concrete structure, the higher the heat transfer, and the cooling of the pour occurs more slowly.
In general, in winter, construction is carried out in the following cases:
- when the summer period is short, which is typical for cold northern regions;
- if it is necessary to erect the building as quickly as possible by the planned date;
- The reason for this may also be the properties of the soil at the construction site.
It is also taken into account that some building materials can be purchased cheaper in winter than in summer (during the work season). For builders, cold weather is a period often characterized by small volumes of orders or their absence. Mostly employed are those who specialize in interior decoration. Due to the increased supply of services, prices for them fall. They also pay attention to this when starting construction in winter. But there are no significant savings, because the work is carried out using more complex technologies.
The disadvantages of pouring concrete in winter are:
- complexity of the work;
- the need to attract heavy equipment;
- difficulties with organizing the heating of the foundation being built;
- increased costs for purchasing additives that increase the frost resistance of the solution.
Due to the release of heat by concrete during hardening, when working in frosty periods, preference is given to strip or slab (monolithic) types of foundations rather than columnar ones. When erecting them, if the ambient temperature is slightly below zero, then you can even do without special additives and heating, using thermal insulating formwork and a special covering (made of mats).
When starting construction, you should take into account that it will not be possible to carry out excavation work on frozen ground yourself, manually. This will require the use of technology.
Concreting technologies
It is possible to make a foundation in winter using various technologies. The choice of option for creating and maintaining the conditions necessary for the concrete hydration process to proceed normally depends on the following factors:
- from the chemical substances included in the working concrete solution, their proportional relationships;
- dimensions of the structure being created;
- climate characteristics of the area;
- availability of power supply network;
- brand of cement used;
- Possibility of organizing heating of water and liquid additives.
The more crushed the cement particles are, the faster it enters into a chemical reaction, releasing heat.

Normal work is facilitated by heating the aggregate and water to 32 degrees immediately before mixing. The temperature of the working solution in this case will be approximately 21º C. It must be taken into account that the cement cannot be heated, because it will lose its binding properties.
The solution must be mixed thoroughly. It is also recommended to increase the mixing time by approximately 25% compared to summer.
Application of concrete additives
The main method that allows pouring a foundation during cold weather is the introduction of antifreeze additives into its composition. Their introduction causes an increase in the amount of heat independently generated by concrete. Supplemented with increasing heat transfer, modifiers lower the crystallization temperature of the liquid. Thanks to this, the hydration process of poured concrete at lower temperatures proceeds in the usual way.
Calcium chloride is often used as an additive that increases frost-resistant properties. It is introduced into the working solution in an amount not exceeding 2% of the total mass. If this proportion is exceeded, the compressive strength of the created base is significantly reduced.

At a stable temperature level around -15 degrees, the following substances are used to add to concrete:
- table salt (sodium chloride);
- sodium nitrate;
- potash.
The use of concrete modifiers is often combined with the organization of artificial additional heating of the base.
If anti-frost fillers are used, the formwork is dismantled when M400 concrete reaches 20% strength. For M and M300 this figure should already be 30%, and for M200 – 40%.
It is not recommended to independently experiment with adding available components to filling compositions. It is better to use ready-made building materials.
Warming up the poured base
In practice, different methods of heating a poured base are used. The simplest option is to preheat the water and aggregate, or the entire solution. Suitable for these purposes:
- fryer;
- heat gun;
- burners of various types;
- an ordinary fire.
Modifiers are added to concrete to speed up the hardening process. After pouring it, the entire structure is covered using the following materials:
- bags;
- tarpaulin;
- straw;
- thermal insulation mats.
You can also cover with rags or unnecessary blankets. Braziers or other heat-producing devices are installed around the base. They are used until the concrete reaches the required strength.
You can make a kind of tent around the structure, which will contribute to more efficient energy consumption. But in this case, it is necessary to monitor the humidity level so as not to dry out the poured concrete. You will also need to draw up a separate project for the structure and dismantle it after the work.
After the monolith reaches the required strength (according to SNIP III-15-76 it is 70% and does not depend on the brand), the formwork and insulation are dismantled. If the concrete has not completely hardened, it can be allowed to freeze. After defrosting, all processes will continue in the right direction, and the strength will be lost by approximately 5% of that calculated according to the project.
Alternative heating methods and their implementation are presented in the table below.
| № | Method of heating poured concrete | Practical implementation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | creation of a "thermos" | To do this, a heat-generating casing is installed around the perimeter of the formwork, consisting of a metal casing with a steam or electric or water circuit located inside it |
| 2 | heating the fill with steam | This method is implemented by laying the required number of pipes in the formwork, through which steam is supplied from a specially created pipeline |
| 3 | use of electricity | To implement this option, a steel wire is used to heat the poured solution, fixed in a certain way in the reinforcement frame or on the formwork, or simply laid directly in the concrete, through which an electric current is passed |
| 4 | use of induction heaters | such devices located along the perimeter of the foundation warm it up by heating reinforcement or metal formwork with an electromagnetic field |
Infrared heaters are also used in practice. Steam heating is an expensive and labor-intensive method that is used quite rarely.

The point of all methods is to speed up the setting of the solution.
Of all the methods considered, the most accessible are simple insulation of the base with various materials (followed by heating it) and installation of an electric heating circuit. Carrying out heating work requires the performer to have a certain level of qualifications in this field of activity, so specialists should be involved.
Pouring a foundation in winter requires strict adherence to a number of nuances. The rules for carrying out the work are as follows:
- It is not allowed to fill the base in parts: the formwork mounted under it should be completely filled with mortar;
- in order to avoid heat losses when laying concrete, the layers must be made of small height and length, immediately overlapping them with the following ones;
- when a helium shell forms on the surface of the fill, it must be chipped off;
- during the preparation of trenches for the foundation or foundation pit, they should be thoroughly cleared of snow and any existing ice should be knocked off the reinforcement;
- immediately after digging and laying the sand cushion, you need to lay straw on the bottom: such a cover will prevent it from icing;
- It is impossible to pour concrete on frozen soil; it must be pre-warmed;
- it is imperative to ensure free access to the formwork from all sides;
- if, after digging, water appears at the bottom of a trench or pit, then it must be removed;
- it is better to use formwork with increased thermal insulation properties;
- Until the concrete reaches a sufficient level of strength, it is necessary to heat the entire poured structure, maintaining a positive temperature.

If you lay concrete directly on frozen soil, then under the influence of heat generated as a result of hydration of the solution mass, the soil will begin to thaw and sag. In this case, the settlement may be uneven and the foundation will be deformed.
There are few rules for the correct, effective implementation of concrete pouring work. But they require strict compliance. It is easier and more economically feasible to perform them during preparation and during pouring than to redo everything afterwards.
Methods for pouring a foundation in winter are shown in the videos below.
It is possible to build a concrete foundation in winter. A high-quality result is achieved by using anti-frost modifiers or creating a heating system, or combining these two methods. In this case, it is recommended to use ready-made additives sold in construction stores from well-known manufacturers and finely ground cement. An important point is careful adherence to the technology of work and the nuances of the process.
Due to the long winter period, in most regions of the Russian Federation, in industrial and residential construction, pouring the foundation in winter is practiced. For individual developers who prefer to do all the work themselves to save budget, these technologies do not bring tangible benefits. The costs of ensuring the minimum possible strength gain of cement stone are increasing sharply.
The main disadvantages of winter concreting are traditionally the following factors:
- at 0 – minus 2 degrees, the hydration process inside the mixture stops completely;
- it requires the introduction of additives into concrete, heating of the formwork and the mixture itself;
- it is almost impossible to prepare normal concrete in a building spot in frosty conditions;
- When delivering the mixture by mixers, laying must be carried out quickly.
At the initial stage, it is necessary to decide how to maintain a positive temperature inside the formwork for 3–5 days so that hydration is completed by at least 70%, after which freezing of the structure is no longer so scary. After thawing, the processes will continue, and the concrete will be able to gain its design strength on its own.
If you freeze the structure immediately after laying the concrete, there can be no talk of any performance characteristics. The developer will receive crumbling, loose material that will have to be completely destroyed, removed from the site and disposed of.
What to do if for some reason the foundation still needs to be poured in frosty weather? The main methods of winter concreting are:
- insulation of the structure;
- introduction of antifreeze additives;
- heating of the building area or formwork elements and reinforced concrete mass.

Option for a greenhouse for a slab foundation.
Attention! Regardless of the technology chosen, fillers are steamed (sand, crushed stone, water is heated), and anti-frost additives are introduced. Otherwise, the concrete will simply freeze in the mixer or dump truck upon delivery. It is strictly forbidden to heat cement - it will lose its properties.
Insulation
At the initial stage, it is necessary to plan the work and draw up some kind of PPR schedule. It is mandatory to carry out operations in the specified sequence:
- preparation of covering material - the best option is a 0.15 mm polyethylene film for stretching around the entire perimeter like a greenhouse (the so-called greenhouse, consists of wooden posts, beams, beams, and film or awning), the foundation tape and formwork are wrapped in polystyrene foam, mineral wool or straw mats;
- warming up the underlying layer - laying the mixture on frozen soil is prohibited, since in the lower reinforced layer the concrete will freeze even before hydration begins, this is done immediately before the arrival of the mixers so that the ground does not have time to freeze again;
- heating the reinforcement frame - in case of frost below 15 degrees, the rods are heated with electric current to +5 degrees.

A variant of a greenhouse for a strip foundation.
The thickness and amount of heat insulation is chosen depending on how many degrees it is outside. Do-it-yourself work is not recommended below minus 5 degrees, since before freezing without heating, the concrete will gain strength:
- at -2 degrees – 63%;
- at -5 degrees – 18%;
- at -15 degrees – 0%.
In cold weather, work is carried out continuously (sometimes around the clock), which also affects the cost of the foundation.
Supplements
The main purpose of chemicals is to lower the freezing point of water. The rise in price of concrete is 10–16%, depending on the additive (potash, chloride salts, sodium nitrite). Other reagents can only be used according to special instructions.
The minimum possible strength gain to comply with the mixture classes B 15 - B 30 in the first three hours is 20 - 30%. The structure must be heated in the first three days (minimum) before stripping, after which the concrete can be frozen - hydration will continue after spring thawing.
Attention! When using additives, according to the standards, it is necessary to use galvanized reinforcement, because additives make concrete chemically aggressive, which can lead to accelerated corrosion of unprotected reinforcement.

Potash is potassium carbonate or potassium carbonate.
When choosing antifreeze additives, you must consider:
- independent mixing is not allowed, since it is necessary to accurately calculate the W/C (water-cement) ratio, which is only possible with mortar units equipped with special dosing devices;
- chloride salts require an increase in the protective layer (5 - 7 cm), which is not always possible in small sections of MZLF tapes of private construction;
- Potash is not recommended when using galvanized reinforcement, but it is the only reagent for concreting at minus 25 degrees.
The amount of reagent depends on the weight of cement in the mixture and is regulated by GOST 24211 of 2008:
- to accelerate the hardening of the material – 1 – 2%;
- to reduce the freezing point of water by 7 - 10 degrees - 3 - 5%;
- for guaranteed absence of freezing – 10 – 15%.
This is the most budget option for winter concreting compared to other technologies.
Heating
You can provide heating for the concrete placed inside the formwork with your own hands using several methods:
- “thermos” - can be made for MZLF with a simple configuration; the mixture along with the formwork is enough to be covered with mineral wool, polystyrene foam, straw or sawdust;
- steaming - around the formwork you can make a cage of panels, roofing felt, under which steam is supplied (temperature 50 degrees, pressure 0.5 - 0.7 atmospheres), increasing the temperature within 10 degrees every hour, then cooling at the same gradient rate;
- electric heating - supplying voltage to electrodes, strings, reinforcement frame.

When steaming, the following concrete heat treatment modes are used:
- curing after laying the mixture in the formwork;
- heating to 50 – 80 degrees at a speed of 15°C/hour;
- gradual cooling at a rate of 15°C/hour.
Electric heating can be done in several ways:
- internal - longitudinal reinforcement bars serve as electrodes;
- through - for narrow MZLF strips within 0.5 m, 15 mm strips or 6 mm strings are mounted along the inner edges of the formwork;
- electrode - current passes between the electrodes, through the thickness of the concrete, heating individual areas; the method is used for heating pilasters, corners, and protrusions.
At minus 5 - 10 degrees, IR heating is more often used. A feature of infrared radiation is the transformation of energy (radial into thermal) within the materials themselves that are exposed to it. The air between the IR gun and the heater practically does not heat up, the formwork and concrete remain warm.
Induction heating is not used in private construction due to the high cost of delivery and the use of large, energy-intensive equipment in cold weather.
Possible options for filling at negative temperatures
The optimal method of winter concreting, which can be used for a relatively small cottage foundation in cold weather, is a “warmhouse”:
- a timber frame is constructed over the building site;
- immediately after laying the mixture and compacting it with the tips of deep vibrators, a canopy made of materials that retain elasticity in cold weather is put on;
- There are several heat guns inside that maintain a positive temperature for 3–5 days.

Tepljak is a greenhouse for pouring the foundation in cold weather.
The main difficulty of this DIY technology lies in the need for round-the-clock duty to control the temperature in cold weather and provide a wet compress to the upper surface of the foundation. You can rent heating formworks with heating elements built into the panels, but this is unreasonably expensive for the limited budget of an individual developer.
For slab foundations, a heating cable and underfloor heating systems are used (USHP slab with ready-made communications). If the cable is laid inside a floating slab, it becomes irremovable and remains in the concrete for its entire service life, which increases the cost by 20 - 30%.
In an insulated Swedish slab, the contours of the heated floor are intended for further use, so additional costs can not be taken into account here. However, the slab must be sanded to achieve its final strength. This is difficult to do in cold weather, especially when snow falls immediately after pouring.
At the same time, it is necessary to take into account that in 70% of cases, the contours of a water heated floor are laid in the USP, into which there is nowhere to supply boiling water in winter. Electric heating is always more expensive, so it is less in demand among individual developers, even as additional heating.
Possible consequences
It is possible to carry out concreting with your own hands at subzero temperatures only using the specified technologies in compliance with the requirements of the sequence of operations and the timing of their implementation.
Attention! The statement that the processes of hydration of cement stone will continue after the concrete has thawed is fundamentally incorrect. The water necessary for this molecular process freezes out over the winter, and the mixture will not be able to reach its design strength. Before freezing, concrete must gain at least 70% strength.

Consequences of non-compliance with technology when concreting in winter.
It is to gain 70% strength in the first few days that you need to do everything necessary to maintain a positive temperature of the mixture and the formwork around it, through which the main heat losses occur. If frost strikes suddenly, a temperature of minus 10 degrees or more will lead to dire consequences:
- the most affected will be the outer surfaces, the side edges of the base of the tape, rising above the ground;
- crumbs and individual layers can be swept away with a broom after warm spring weather sets in;
- further hydration in this damaged material is impossible in principle.

Again, from a different angle.
Reinforced concrete is a complex chemical composite, the properties of which depend on the water-cement ratio of the mixture laid in the formwork. With an increase in the W/C ratio and a decrease in the grinding fineness of cement, concrete is able to gain the required 70% strength much faster, subsequently increasing this characteristic, exceeding the brand strength by 20%.
In other words, when pouring in cold weather, you can achieve not a decrease, but an increase in the strength of the structure. Another thing is that this can only be entrusted to professionals with the appropriate education or to practitioners who have poured a lot of foundations of varying complexity in the winter. In 80% of cases, an individual developer will not be able to achieve anything other than a decrease in design strength and an unjustified increase in the construction budget in the off-season, even if he wants to.
Construction of a foundation in winter is quite labor-intensive and troublesome, but doable. It is believed that the time from April to November is the most favorable period for installing the foundation of any structure. But there are situations when work occurs in winter. Thanks to modern construction technologies, it is possible to build a reliable foundation that will not be inferior in its characteristics to the foundation laid in the warm season. From this article you can find out what pouring a foundation in winter is, whether it can be poured and how to make such a foundation.
When is winter foundation pouring necessary?
With careful adherence to all construction rules, the construction of a strong foundation is quite feasible even in severe frosts and, as a consequence, frozen soil. Pouring the foundation in winter is not always necessary, it all depends on the project. Most often, the decision to start construction during the cold period is related to the characteristics of the soil. There are areas where the soil crumbles in summer, and only in winter, when the ground is well frozen, can a good pit be dug. In this case, it is an excellent solution to accomplish the task. In many regions of Russia, winter is the main season of the year, and summer practically does not exist. Therefore, there is simply no other period for the construction of the foundation. In addition, it is believed that the costs of materials and labor in winter are much lower than in the summer months, although serious savings are unlikely to be counted on. Sometimes pouring a foundation in winter is necessary when the construction process needs to be completed as quickly as possible.

in winter
To arrange the foundation of any structure in winter, there are several types of foundations. Let's look at them in more detail:
1. The most common among developers is a strip foundation. In this case, experts advise reducing the so-called “wet” operations, for example, using ready-made ones for laying them in a pit.
2. Foundation made of concrete piles. This type of foundation is ideal for light buildings, in particular wooden houses. By following construction technology and adhering to the basic rules, you can get a durable pile foundation that is not inferior in quality to other types. Further from the article you can learn everything about pouring the foundation in winter.
How to pour a foundation using piles? First of all, you need to distinguish between their types. Concrete piles are either bored or drilled. Screw pile foundations are ideal for winter work. Suitable for any difficult soil.
Preparation of concrete mixture
When arranging the foundation, the question often arises: “Is it possible to pour a foundation in winter using ordinary concrete?” No you can not. For these purposes, one that contains special modifiers is suitable. Thanks to additives, concrete has time to gain the necessary qualities; it does not set ahead of time. In addition, modifying additives make it much easier to pour concrete into the formwork.
When choosing modifiers, you should pay attention to frost resistance indicators and the rate of hardening of concrete. The required amount of the substance is determined according to the scale indicated on the packaging.

How to apply modifiers?
When using modified additives, it is necessary to focus on some basic points:
The use of frost-resistant substances allows you to reduce the amount of water consumed by 10-15% when making concrete mortar.
The minimum temperature at which the use of modifiers is acceptable is 25 degrees below zero.
When air humidity reaches 60%, the use of additives is prohibited.
It is necessary to take into account factors in which individual components of modifiers interact with certain metals.
The use of additives does not negate some additional measures when arranging the foundation during the cold period. When the air temperature is low, additives alone that affect the frost resistance of concrete are not enough. It is necessary to warm up the concrete and install additional thermal insulation to maintain a certain temperature of the finished structure.

The use of additional means that make it possible to fill the foundation in winter
Another way in which the answer to the question of whether it is possible to fill a foundation in winter will be positive is to ensure that the foundation is warmed up. It is known that concrete gains its highest strength during the first two days. It is during this period that the foundation especially needs protection from low temperatures. To heat the base along the entire perimeter, special equipment is used - a thermal gun. With its help, the temperature required for hardening of the concrete solution is ensured and maintained. The larger the foundation, the higher the power of the device should be
You can also heat the foundation using electronic current. This method allows you to maintain the temperature required for hardening by transferring heat (from hot to cool). The concrete is heated by reinforcement rods to which an electric current (380 V) is supplied.
Negative aspects of pouring a foundation in winter
So, the answer to the question “is it possible to pour a foundation in winter” is obvious. However, despite many positive arguments in favor of this process, there are also some negative aspects:
Although the savings in the cost of building materials are obvious, at the same time, the price of excavation work in frosty weather increases greatly. You will also incur additional costs for heating the concrete solution and structures, so in general, the savings in construction in winter are very doubtful.
The efficiency of work in winter is much lower than in summer, since working in cold weather is much more difficult.
The price of additives and modifying substances that affect the properties of concrete is low, but to build even a small foundation, quite a lot of them are required. And therefore the price of building materials increases significantly.
Sometimes it is necessary to use special equipment, in particular for digging a pit.
Therefore, before thinking about whether it is possible to pour a foundation in winter, you need to calculate all the costs and consider all the pros and cons of this idea.

List of basic materials and tools for creating a foundation
To arrange and pour the foundation, the following materials and tools are required:
- shovel;
- sawdust;
- building level;
- hacksaw;
- Master OK;
- cement and concrete mortars;
- modifying additives;
- thermal insulation;
- reinforcing mesh;
- crushed stone

How to properly pour a foundation in winter?
Is it possible and is it worth doing? These questions often bother newcomers to construction. After all, it is very difficult to carry out any work in the cold; snow and frost can interfere. Expert advice will tell you how to properly fill the foundation in winter with your own hands. The rules of work are as follows:
First of all, a trench or pit is dug, while the ground moisture that will collect at the bottom is controlled. At sub-zero temperatures, water freezes and ice forms, which must be removed, since nothing can be placed on such a base.
The next step is the installation of formwork and reinforcement frame. The formwork is filled with concrete mixture. The required positive temperature must be maintained for a certain period of time (to accelerate the setting process) using heating equipment. Immediately after pouring, the foundation can be insulated using roofing material or polyethylene film. You can sprinkle a layer of sawdust (20-30 cm) on top. As a result, we have a ready-made foundation in winter.

Is it possible to fill it for the winter? The answer is yes. But it is still recommended to build walls on such foundations at positive temperatures, since the concrete solution needs a certain time to acquire strength. By preparing the foundation in winter (taking into account all the rules and nuances), you can get a strong and durable structure.