STATE SYSTEM OF SANITARY AND EPIDEMIOLOGICAL
REGULATIONS OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
FEDERAL SANITARY REGULATIONS, REGULATIONS
AND HYGIENE STANDARDS
2.4.2. SCHOOLINSTITUTIONS
HYGIENE REQUIREMENTS
TO THE CONDITIONS OF EDUCATION OF SCHOOLCHILDREN
IN VARIOUS TYPES OF MODERN
GENERAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS
Sanitary rules and regulations
SanPiN 2.4.2.576-96
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF RUSSIA
FOREWORD
1. Developed:- Scientific Center for the Health of Children, Adolescents and Youth of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences (N. N. Kuindzhi, B. Z. Voronova, V. I. Belyavskaya, G. M. Sapozhnikova, M. I. Stepanova, Z. I. Sazanyuk, M. A. Polenova, V. V. Butrov); - Center for State Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance of Moscow (D. V. Sinyakova, L. I. Pronina, Z. F. Stepanova); - St. Petersburg State Medical Academy (V. G. Maimulov, T. S. Chernyakina, L. T. Blinova, V. Yu. Andreeva, A. V. Suvorova); - Research Institute of Preventive Toxicology and Disinfection (L. S. Fedorova, A. I. Frolova); - Russian Institute of Public Buildings (V. I. Stepanov); - Nizhny Novgorod Research Institute of Pediatric Gastroenterology (I. E. Aleksandrova); Starring - Department of State Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (B. G. Bokitko). 2. Recommended by the Commission on State Sanitary and Epidemiological Rationing under the Ministry of Health of Russia. 3. Approved by the Decree of the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of Russia on October 31, 1996 No. 49. 4. Introduced instead of the "Sanitary Rules for the Arrangement and Maintenance of Secondary Schools", approved by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the USSR on September 29, 1974, No. 1186-a-74.RSFSR LAW
"ABOUT SANITARY-EPIDEMIOLOGICAL
WELFARE OF THE POPULATION»
Sanitary regulations, norms and hygiene standards(hereinafter - sanitary rules) - normative acts that establish criteria for the safety and (or) harmlessness for a person of environmental factors of his life. Sanitary rules are obligatory for observance by all state bodies and public associations, enterprises or other economic entities, organizations and institutions, regardless of their subordination and form of ownership, officials and citizens (Article 3). A sanitary offense is an unlawful, guilty (intentional or careless) act (action or inaction) that infringes on the rights of citizens and the interests of society, associated with non-compliance with the sanitary legislation of the RSFSR, including the current sanitary rules ... Officials and citizens of the RSFSR who have committed a sanitary offense may be brought to disciplinary, administrative and criminal liability (Article 27).
| 1. General provisions and scope. 2 2. Requirements for the conditions and organization of schoolchildren's education in various types of educational institutions. 3 2.1. Requirements for the placement of educational institutions. 3 2.2. Requirements for the site of educational institutions. 4 2.3. School building requirements.. 5 2.4. Requirements for the equipment of the premises. 8 2.5. Requirements to air-thermal regime. 9 2.6. Requirements for natural and artificial lighting.. 11 2.7. Requirements for water supply and sewerage. 12 2.8. Requirements for the premises and equipment of schools located in an adapted building. 13 2.9. Requirements for the organization of the educational process. 13 2.10. Requirements for the organization of medical care for students. 16 2.11. Requirements for the sanitary condition and maintenance of educational institutions. 17 2.12. Requirements for catering students in educational institutions. 18 Appendix 1 An approximate list of equipment and tools of the medical office of the school. 21 Annex 4 Approximate volume of physical activity of students. 23 Annex 5 Approximate scheme of three-combined acquisition of classes in an ungraded school. 24 Appendix 6 Hygiene requirements to the lesson schedule. 24 Annex 7 Regulations on preventive examinations of children attending educational institutions. 25 Annex 8 Sanitary and disinfection regime in educational institutions during the quarantine period. 26 Normative references. 27 |
Approved
Decree
Goskomsanepidnadzor of Russia
SanPiN 2.4.2.576-96.
2.4.2 SCHOOL INSTITUTIONS
HYGIENIC REQUIREMENTS FOR THE CONDITIONS FOR EDUCATION OF SCHOOLCHILDREN IN VARIOUS TYPES OF MODERN GENERAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS
HYGIENIC REQUIREMENTS FOR THE CONDITIONS OF SCHOOLCHILDREN'S STUDY IN DIFFERENT KINDS OF MODERN GENERAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS
Sanitary rules and regulations
SanPiN 2.4.2.576-96
1. GENERAL AND SCOPE
1.1. These Sanitary Rules and Norms (hereinafter referred to as the Sanitary Rules) are intended to prevent adverse effects on the body of schoolchildren of harmful factors that accompany them learning activities and determine the sanitary and hygienic requirements for: - placement of a general education institution; - the site of a general educational institution; - school building - equipment of the premises of a general educational institution; - air-thermal regime of educational institution: - natural and artificial lighting; - water supply and sewerage; - premises and equipment of schools located in adapted buildings; - organization of the educational process; - organization of medical care for students; - sanitary condition and maintenance of the educational institution; - catering for students. 1.2. Responsibility for the implementation of these Sanitary Rules rests with the administration of the educational institution. 1.3. Design, construction and reconstruction of educational institutions must be carried out in accordance with these sanitary rules and regulations. 1.4. References to the obligation to comply with the sanitary and hygienic requirements established by these Sanitary Rules should be included in state standards and other regulatory and technical documents that establish requirements for general educational institutions. 1.5. State sanitary and epidemiological supervision and control over the implementation of these Sanitary Rules is carried out by bodies and institutions of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Service Russian Federation, and departmental sanitary and epidemiological control - by the medical staff of the educational institution.2. REQUIREMENTS FOR THE CONDITIONS AND ORGANIZATION OF SCHOOLCHILDREN'S TRAINING IN DIFFERENT TYPES OF GENERAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS
2.1. Requirements for the placement of educational institutions
2.1.1. Buildings of educational institutions should be located on the intra-quarter territories of the microdistrict, remote from inter-quarter passages with regular traffic at a distance of 100 - 170 m. 2.1.2. The location of general educational institutions on intra-block passages with periodic (irregular) traffic is permissible only if the minimum gap from the border of the school site to the passage is increased from 15 to 25 m. 2.1.3. The placement of schools on intra-quarter and especially inter-quarter passages with regular traffic is unacceptable. 2.1.4. The construction of individual car garages near schools is unacceptable. Between the boundaries of school plots and garages, the minimum sanitary protection zone should be 25 m with a garage capacity of up to 20 cars and 50 m with a garage capacity of up to 50 cars. With a greater capacity of garages, the question of the degree of their removal from the school should be agreed with the bodies of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision. 2.1.5. Distances from the school building to various types of buildings (residential, industrial, etc.) must be taken in accordance with SNiP 2.07.01-89. 2.1.6. The service radius from the house to educational institutions located in the II and III building-climatic zones should be no more than 0.5 km of walking distance; in I climatic region (I subzone) for primary and secondary students school age(I - II stages of education) - 0.3 km, for older students (III stage) - 0.4 km; in the I climatic region (II subzone) for students of primary and secondary school age - 0.4 km, for older students - 0.5 km. It is allowed to place educational institutions at a distance of transport accessibility: for students of the 1st stage - 15 minutes (one way), for students of the 2nd and 3rd levels - no more than 30 minutes (one way). 2.1.7. In rural areas, the location of general educational institutions should provide for students of the 1st stage the radius of accessibility of no more than 2 km on foot and no more than 15 minutes. (one way) for transport services. For students of levels II and III, the radius of walking distance should not exceed 4 km, and with transport services - no more than 30 minutes. The maximum radius of service for students of II-III steps should not exceed 15 km. 2.1.8. Transport service students living at a distance of more than 3 km from the school are subject to. The transportation of rural schoolchildren is carried out by special school transport. The maximum pedestrian approach of students to the gathering place at the stop should be no more than 500 m. The transport stop should be equipped with a canopy, fenced on 3 sides, protected by a barrier from the roadway, have a hard surface and visibility of at least 250 m from the side of the road. 2.1.9. For students living at a distance exceeding the maximum allowable transport service, as well as in the event of transport inaccessibility during adverse weather conditions, a school boarding school should be provided at the rate of 10% of the total capacity of the institution.2.2. Requirements for the site of educational institutions
2.2.1. A general education institution must have an independent land plot with a distance of at least 25 m from the building of the institution to the red line. 2.2.2. Square land plots depends on the capacity of the institution and is accepted in accordance with SNiP 2.07.01-89. 2.2.3. The territory of the site must be fenced with a 1.5 m high fence and green spaces along it. 2.2.4. The site must be landscaped at the rate of at least 50% of its area. When landscaping the site, it is prohibited to plant trees and shrubs with poisonous fruits. 2.2.5. The following zones should be allocated on the land plot: educational and experimental, physical culture and sports, recreation, economic. 2.2.6. The training and experimental zone should not exceed 25% of the site area. In urban schools, it can be reduced through the construction of pavilions, greenhouses and greenhouses on the site, organically connected with the complex of biology and chemistry classrooms. 2.2.7. The physical culture and sports zone should be located at a distance of at least 25 m from the building of the institution, behind a strip of green spaces. It is not allowed to place it on the side of the windows of the classrooms. The equipment of the sports zone should ensure the implementation of training programs in physical education, as well as for conducting sectional sports and recreational activities. Sports and playgrounds must have a hard surface, a football field - a grass cover. It is forbidden to conduct classes on damp areas with bumps and potholes. 2.2.8. The recreation area should be located near the garden, green spaces, away from the sports and economic zones. It should include playgrounds for outdoor games and quiet recreation. Areas for outdoor games and recreation should be located near the exits of the building (for maximum use during breaks) and be divided for students at each level of schooling. 2.2.9. The economic zone should be located on the side of the entrance to the production premises of the canteen (buffet) on the border of the site at a distance of at least 35 m from the building of the educational institution, fenced with greenery and have an independent entrance from the street. In the absence of heating and centralized water supply on the territory of the economic zone, a boiler room and a pump room with a water tank should be provided. Garbage bins must have tight-fitting lids. They should be installed on a concrete platform at a distance of at least 25 m from the windows and the entrance to the dining room (buffet). 2.2.10. Entrances and entrances to the site, driveways, paths to outbuildings, to sites for garbage collectors, and in rural schools without sewerage - to yard latrines should be covered with asphalt, concrete, etc. hard coated. Approaches to the school building at least 100 meters away must also have a hard surface. 2.2.11. The site of the school must have outdoor lighting at the norm of illumination on the ground - 10 lux. 2.2.12. The land plots of rural schools should be expanded through the construction of greenhouses, greenhouses, conservatories, storage facilities for small-sized agricultural machinery, gardening equipment, etc.2.3. school building requirements
2.3.1. The number of children in the school should not exceed its capacity provided by the project according to which the building was built or adapted. The optimal capacity in urban educational institutions should not exceed 1,000 students. The occupancy of each class should not exceed 25 people. The capacity of rural schools should not exceed: for primary small schools - 80 students, for schools of I, II levels - 250 students, for schools of I, II, III levels - 500 students. 2.3.2. New types of general education institutions (lyceums, gymnasiums, private schools, etc.) should either have a separate building or be located in separate compartments with an isolated entrance on the basis of functioning general education schools. 2.3.3. Educational premises are prohibited from being located in the basement and basement floors of the building. 2.3.4. The number of storeys of the building should not exceed 3 floors. In conditions of dense urban development, the construction of schools with a height of 4 floors is allowed. When placing general educational institutions in previously built 4-5-storey buildings, the fourth and fifth floors must be allocated for classrooms rarely visited by students. 2.3.5. When placing a school in an adapted building, a set of premises, their area is determined in agreement with the territorial centers of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision in each case, based on the type of educational institution, the number and age of students, the number of classes, etc. 2.3.6. Wardrobes in schools should be placed on the 1st floor with the obligatory equipment of cells for each class. Wardrobes should be equipped with hangers for clothes and cells for shoes. It is strictly forbidden to arrange wardrobes in classrooms and recreations. 2.3.7. In order to properly organize quarantine measures in the event of infectious diseases, it is necessary to use all the entrances in the building on a daily basis. 2.3.8. The set of premises should create conditions for the study of compulsory academic disciplines (taking into account national and regional specifics), as well as additional subjects at the choice of students in accordance with their interests and differentiation in areas for in-depth study one, two or three things. Classrooms should not be located near premises that are sources of noise and odors (workshops, sports and assembly halls, catering facilities). 2.3.9. Pupils of the 1st stage in urban and rural schools should study in the classrooms assigned to each class, allocated in a separate block 2.3.10. Education of students of the II - III stage should be carried out according to the class-room system. The class-room system ensures the teaching of all subjects in a fixed class-room, into which textbooks and technical teaching aids (TUT) are transported. The number of classroom classes for the main disciplines is taken from the number of senior classes. Classrooms and laboratories are allowed to be placed on any floors of the building, except for the basement and basement. It is necessary to create specialized sections that unite classrooms for the disciplines of the natural-mathematical and humanitarian cycles. For creating best conditions for educational and extracurricular activities of schoolchildren of II-III levels, the number of classrooms and laboratories in the section should not exceed 6. In a rural school, with a small number of classes, it is allowed to use classrooms in 2 disciplines. The most favorable is the following combination of subjects: chemistry - biology, mathematics - drawing, drawing - drawing, history - geography, literature - a foreign language. 2.3.11. Educational premises should include: a working area (placement of study tables for students), a teacher’s working area, additional space for placing teaching aids, TCO, an area for individual lessons students and possible activities. 2.3.12. The area of the cabinets should be taken at the rate of 2.5 sq. m per 1 student with frontal forms of classes, 3.3 sq. m - with group forms of work and individual lessons. 2.3.13. The area and use of computer rooms must comply with the requirements of SanPiN 2.2.2.542-96. 2.3.14. Optimal dimensions the working area of students depends on the angle of visibility (associated with the distance from the board to the first side rows - desks). It should be at least 35 degrees for students of the II-III stage of the school and at least 45 degrees for students of 6-7 years old. 2.3.15. Each classroom or group of 2 - 3 classrooms should have a laboratory assistant (the presence of a laboratory assistant is obligatory in the classrooms of chemistry, physics, biology, computer class). 2.3.16. For an in-depth study of individual subjects and practical training, it is necessary to divide classes into 2-4 subgroups. 2.3.17. If there are educational workshops in the school building, they must be used for their intended purpose or can be re-equipped according to the profile of the new educational institution, as well as for extracurricular activities in technical creativity in agreement with the bodies of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision. 2.3.18. When building schools focused on in-depth and expanded content of education, for the versatile development of the personality of schoolchildren, it is necessary to provide for the allocation of premises for studios (universal halls) with dimensions of 12 × 12 m, as well as utility rooms for the department of artistic education and art: an aesthetics room with a split screen , circle rooms for fine arts, choreography, singing and music classes (70 - 108 sq. m), depending on the purpose of the new educational institution. In institutions with a technical profile, a universal room of 108 square meters should be provided. m (90 + 18) for technical creativity. Educational and art classrooms should have areas for watercolor painting, oil painting and drawing. Based on posture at work various types painting (according to watercolor painting and drawing - sitting, oil painting - standing), area per one workplace should be: for oil painting - 3.5 sq. m, watercolor painting and drawing - 2.0 sq. m. 2.3.19. The gym should be located on the 1st floor in the annex. Its dimensions should provide for the implementation of a full program of physical education for students and the possibility of extracurricular sports activities. The number and types of sports halls should be provided depending on the type of educational institution and its capacity. The areas of sports halls are accepted: 9 × 18 m, 12 × 24 m, 18 × 30 m with a height of at least 6 m. m depending on the area of the gym; dressing rooms for boys and girls with an area of 10.5 sq. m each; showers with an area of 9 sq. m each; latrines for girls and boys with an area of 8 square meters. m each; room for the instructor with an area of 9 sq. m. The composition of the premises for physical culture and sports purposes must include a room (zone) equipped with training devices, as well as, if possible, a swimming pool. 2.3.20. The dimensions of the assembly hall are determined by the number of seats at the rate of 0.65 sq. m per place and 60% of the total number of students in the school. At the assembly hall, artistic latrines with an area of at least 10 square meters should be provided. m each, film projection area of 27 sq. m, a warehouse of scenery and props, musical instruments with an area of 10 sq. m, a warehouse for storing costumes with an area of 10 sq. m. 2.3.21. In schools with in-depth learning content, there should be a lecture audience. Its dimensions are set according to the capacity in it of the age parallel of students, consisting of no more than 3 classes, at the rate of 1 sq. m per place. 2.3.22. The type of library depends on the type of educational institution and its capacity. In schools of a new type, the library should be used as a reference and information center, equipped with all types of TCO, providing conditions for individual studies of students. The area of the library - information center must be taken at the rate of at least 0.6 square meters. m per student. The following zones should be provided in the library premises: reading places, information point (issuing and receiving literature), places for working with catalogs, open access funds, funds closed storage , an area with booths for individual lessons with TCO and boxes for storing mobile carts. 2.3.23. During the construction and reconstruction of modern educational institutions, preference should be given to recreational facilities of the hall type. 2.3.24. The medical center of a general educational institution should include the following premises: a doctor's office with a length of at least 7 m (to determine the acuity of hearing and vision of students) with an area of at least 14 square meters. m; Dentist's office with an area of 12 sq. m, equipped with a fume hood; treatment room with an area of 14 sq. m; psychologist's office with an area of 10 sq. m. At the first-aid post there should be an independent bathroom. An approximate list of equipment and tools for the medical office of the school is given in Appendix 1. 2.3.25. On each floor there should be sanitary facilities for boys and girls, equipped with cabins with doors without locks. The number of sanitary appliances should be at the rate of 1 toilet bowl for 20 girls, 1 washbasin for 30 girls; 1 toilet bowl, 0.5 trough urinal and 1 washbasin for 30 boys. The area of sanitary facilities for boys and girls should be taken at the rate of at least 0.1 sq. m per student. There should be a separate bathroom for staff. For students of the II and III levels, personal hygiene rooms for girls should be organized at the rate of 1 cabin for 70 people with an area of at least 3 square meters. m. Entrances to the bathrooms should not be located opposite the entrance to the classroom or in close proximity to them. On each floor, rooms equipped with pallets and supplying cold and hot water to them should be provided for storage and processing of cleaning equipment, preparation of disinfection solutions. 2.3.26. In the premises of primary classes, laboratories, classrooms, workshops, medical facilities, teachers' room, technical staff room, wash basins must be installed. 2.3.27. In educational institutions, 2 hot meals a day for children of extended day groups and hot breakfasts for other children should be organized. Meals can be organized in the dining room, working on raw materials or semi-finished products, as well as in the buffet-distributing. According to the requirements of SanPiN 42-123-5777-91, canteens should be provided in schools with more than 100 students. The school canteen, working on raw materials, should have the following set of equipment and premises: workshops - hot, cold, meat and fish, confectionery, vegetable; washing for table and kitchen utensils; pantries for dry foods and vegetables; refrigerated and low-temperature chambers for storing meat and especially perishable products; amenity premises for catering personnel; boot-tare; washing for containers; refrigerator for food waste; bathroom for employees of the dining room. The structure of the premises of the school canteen, working on semi-finished products, should include: a hot shop, pre-cooking, washing for table and kitchen utensils, pantries for dry foods and vegetables, refrigerators for semi-finished products, household premises for catering staff, loading and packaging, washing for containers , refrigerator for food waste. The premises of the buffet-distributing room should include: a loading room equipped with a stove for heating food, refrigerated cabinets; distributing, equipped with food warmers; dishwasher; utility rooms, household rooms for staff, rooms for washing containers. At school buffets and canteens, a dining room with an area of 0.7 square meters must be provided. m per seat in the hall, based on the landing of 100% of students in the 3rd queue. At dining rooms, washbasins should be installed at the rate of 1 tap for 20 seats. Washbasins are placed in widened aisles, corridors leading to the dining room, or in separate room next to the dining room. 2.3.28. In rural schools (secondary, incomplete secondary) the requirements for catering are the same as in urban ones. In small schools (up to 50 students), it is necessary to allocate rooms for eating with minimum set equipment: 2-socket electric stove, dishwashing sink, refrigerator, electrotitanium.2.4. Room equipment requirements
2.4.1. Depending on the purpose of the classrooms, student tables (single and double), classroom, drawing or laboratory tables can be used. The arrangement of tables should be, as a rule, three-row, but options are possible with two-row or single-row (interlocked) arrangement of tables. 2.4.2. Each student is provided with a comfortable workplace at a desk or table in accordance with his height and the state of sight and hearing. For the selection of furniture according to the growth of students, its color marking is made. It is forbidden to use stools or benches instead of chairs. Desks (tables) are placed in classrooms by numbers: smaller ones are closer to the blackboard, larger ones are farther away. For children with impaired hearing and vision, the desks, regardless of their number, are placed first, and students with reduced visual acuity should be placed in the first row from the windows. Children who often suffer from acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis, colds should be seated further from the outer wall.Table 1
DIMENSIONS OF FURNITURE AND ITS MARKING ACCORDING TO GOST STUDENT TABLES AND STUDENT CHAIRS
|
Furniture numbers according to GOST 11015-93 11016-93 |
Height group (in mm) |
Height above the floor of the cover of the edge of the table facing the student, according to GOST 11015-93 (in mm) |
Marking color |
Height above the floor of the front edge of the seat according to GOST 11016-93 (in mm) |
|
orange |
||||
|
violet |
||||
2.5. Air-thermal requirements
2.5.1. Heating, ventilation, air conditioning in educational institutions should be provided in accordance with SNiP 2.08.02-89. Heat supply of buildings should be provided from CHP, district or local boiler houses. Steam heating is not allowed. As heating devices, radiators, tubular heating elements built into concrete panels can be used, and convectors with casings can also be used. Heating appliances should be protected by removable wooden grates, located under window openings and have temperature controls. It is not allowed to install fences made of chipboards and other polymeric materials. The average surface temperature of heating devices should not exceed 80 degrees Celsius. 2.5.2. When designing air heating combined with ventilation in a school building, automatic control of systems should be provided to maintain the calculated levels of temperature and relative air humidity within 40 - 60% in the room during working hours. During non-school hours, the temperature in the room must be maintained at least 15 degrees Celsius. The air temperature maintained in the air heating system during working hours should not exceed 40 degrees Celsius. Air recirculation in air heating systems of educational premises is not allowed. Separate exhaust ventilation systems should be provided for the following rooms (groups of rooms): classrooms and classrooms (in the absence of air heating), laboratories, assembly halls, swimming pools, shooting ranges, a canteen, a first-aid post, a cinema room, sanitary facilities, rooms for processing and storing cleaning inventory. Air exchange in school canteens should be calculated for the absorption of excess heat generated by the technological equipment of the kitchen. Do not use in educational institutions asbestos-cement air ducts. 2.5.3. Stove heating is allowed only in one-storey small rural schools (no more than 50 students). The firebox should be located in the corridor. It is forbidden to install iron stoves. To avoid indoor air pollution with carbon monoxide, the chimneys are closed no earlier than the complete combustion of the fuel and no later than two hours before the students arrive. 2.5.4. The area of transoms and vents in classrooms must be at least 1/50 of the floor area. Transoms and vents should function at any time of the year. 2.5.5. Educational rooms should be ventilated during breaks, and recreational rooms during lessons. Before the start of classes and after their completion, it is necessary to carry out through ventilation of the classrooms. The duration of through ventilation is determined by weather conditions according to table 2. On warm days, it is advisable to conduct classes with open transoms and vents.table 2
DURATION OF THROUGH VENTILATION OF LEARNING ROOMS DEPENDING ON OUTDOOR AIR TEMPERATURE
|
Outside temperature in degrees Celsius |
Duration of ventilation of the premises (min) |
|
|
in small changes |
during big breaks and between shifts |
|
| from + 10 to + 6 | ||
| from + 5 to 0 | ||
| from 0 to - 5 | ||
| from - 5 to - 10 | ||
| below - 10 | ||
2.6. Requirements for natural and artificial lighting
2.6.1. Daylight. School classrooms should have daylight. Without natural lighting, it is allowed to design: shell, washrooms, showers, latrines at the gym; showers and restrooms for staff; storerooms and storage rooms (except for rooms for storing flammable liquids), radio centers; film and photo laboratories; book depositories; boiler, pump water supply and sewerage; ventilation and air conditioning chambers; control units and other premises for installation and control of engineering and technological equipment of buildings; facilities for storage of disinfectants. In classrooms, lateral left-hand lighting should be designed. With two-sided lighting, which is designed with a depth of more than 6 m in classrooms, a right-sided lighting device is required, the height of which must be at least 2.2 m from the ceiling. In this case, the direction of the main light flux in front and behind the students is unacceptable. In training and production workshops, assembly and sports halls, two-sided lateral natural lighting and combined (top and side) can also be used. In school premises, normalized KEO values must be provided in accordance with SNiP 23-05-95. In classrooms with one-sided side natural lighting, KEO should be 1.5% (at a distance of 1 m from the wall opposite the light opening). The unevenness of the natural lighting of the premises intended for the classes of students should not exceed 3: 1. The orientation of the windows of the classrooms should be on the southern, southeastern and eastern sides of the horizon. The windows of the drafting and drawing rooms, as well as the kitchen room, can be oriented to the northern points of the horizon, the orientation of the computer room is to the north, northeast. The light openings of the classrooms should be equipped with: adjustable sun protection devices such as blinds, fabric curtains in light colors that match the color of the walls and furniture. It is forbidden to use curtains made of PVC film. In the non-working state, the curtains must be placed in the piers between the windows. To finish the classrooms, finishing materials and paints should be used that create a matte surface with reflection coefficients: for the ceiling - 0.7 - 0.8 for the walls - 0.5 - 0.6 for the floor - 0.3 - 0.5 Should be used the following paint colors: - for the walls of classrooms - light colors of yellow, beige, pink, green, blue; - for furniture (desks, tables, cabinets) - colors natural wood or light green; - for blackboards - dark green, dark brown; - for doors, window frames - white. For maximum use daylight and uniform lighting of classrooms, it is recommended: - plant trees no closer than 15 m, shrubs - no closer than 5 m from the building; - do not paint over window panes; - do not arrange flowers on the windowsills. They should be placed in portable flower beds 65 - 70 cm high from the floor or hanging planters in the window piers; - cleaning and washing of glasses should be carried out 2 times a year (in autumn and spring). 2.6.2. artificial lighting. In classrooms, normalized levels of illumination and indicators of lighting quality (discomfort indicator and pulsation coefficient of illumination) must be provided in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 23-05-95. In classrooms, predominantly fluorescent lighting should be designed using lamps: LB, LHB, LEC. The use of incandescent lamps is allowed (in this case, the illumination standards are reduced by 2 steps of the illumination scale). It is forbidden to use fluorescent lamps and incandescent lamps in the same room. The use of new types of lamps and fixtures must be coordinated with the local Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision Centers. In classrooms, a general lighting system should be used. Luminaires with fluorescent lamps should be placed parallel to the light-bearing wall at a distance of 1.2 m from the outer wall and 1.5 m from the inner one. For general lighting of classrooms and training workshops, fluorescent lamps of the following types should be used: LS002 - 2 × 40, LP028 - 2 × 40, LP002 - 2 × 40, LP034 - 4 × 36, TsSP-5 - 2 × 40. Other luminaires of the type given with similar lighting characteristics and design can also be used. The blackboard should be equipped with spotlights and illuminated by two mirror lamps of the LPO-30-40-122 type (125) installed parallel to it. These lamps are placed 0.3 m above the top edge of the board and 0.6 m towards the classroom in front of the board. When designing a system artificial lighting for classrooms, it is necessary to provide separate switching on of the lines of lamps. In classrooms, classrooms, laboratories, illumination levels must comply with the following standards: on desktops - 300 lux, on a blackboard - 500 lux, in technical drawing and drawing rooms - 500 lux, in display classes on tables - 300 - 500 lux, in assembly and sports halls (on the floor) - 200 lux, in recreations (on the floor) - 150 lux. In the classrooms of technical teaching aids, if necessary, combine the perception of information from the screen and keeping records in a notebook - the illumination on the students' tables should be 300 lux. When using slide and film projectors, the illumination on the tables of students should be 500 lux. In this case, either only one local lighting should be used, or a system of “functional” artificial lighting should be created with a “dark corridor” in front of the screen. It is necessary to clean the lighting fittings of luminaires at least 2 times a year and replace burned-out lamps in a timely manner. It is forbidden to involve students in this work. Faulty, burned-out fluorescent lamps must be collected and removed from the school building. Their storage in unsuitable premises of educational institutions is prohibited. Preventive ultraviolet irradiation of children should be carried out in areas north of 57.5 degrees N. sh. and in polluted areas. To do this, it is recommended to use long-term or short-term irradiation installations (photoria) in accordance with the methodological recommendations "Prophylactic ultraviolet irradiation of people using sources of ultraviolet radiation."2.7. Requirements for water supply and sewerage
2.7.1. Buildings of general educational institutions must be equipped with systems of domestic and drinking, fire-fighting and hot water supply, sewerage and drains in accordance with SNiP 2.08.02-89. 2.7.2. Water supply and sewerage in educational institutions should be centralized. In cases of absence in locality sewerage and water supply, water supply and the method of removing sewage and waste in each case is consistent with the local Centers of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision. 2.7.3. Educational institutions must be provided with good-quality drinking water in accordance with SanPiN 2.1.4.559-96 “Drinking water. Hygienic requirements for water quality of centralized drinking water supply systems. Quality control". 2.7.4. The use of filters for drinking water purification in educational institutions must be agreed with the local Centers of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision. 2.7.5. Hot water supply should be provided for the production premises of the catering unit, showers, washrooms, hygiene cabins for girls, and premises for the medical office. 2.7.6. In non-sewered areas, educational institutions should be equipped with internal sewerage, subject to the installation of local treatment facilities. 2.7.7. In non-canalized areas, it is allowed to equip small rural schools with a capacity of up to 50 students with backlash closets or cesspools (with the organization of waste disposal). It is forbidden to pour water into the cesspool from under the washbasins and after cleaning the premises.2.8. Requirements for the premises and equipment of schools located in an adapted building
2.8.1. When placing a school in an adapted building, it is necessary to have a mandatory set of premises: classrooms, premises for physical education classes, a canteen or buffet, a first-aid post or a room for medical support, administrative and utility rooms, bathrooms, recreation and a cloakroom. The areas of the premises should be determined in each specific case, based on the direction of the general education institution, the number and age of students, the number of classes, in accordance with the requirements of these sanitary rules and in agreement with the bodies of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision. 2.8.2. Leasing school premises to other organizations for purposes not related to educational processes is not allowed. 2.8.3. The premises of the dining room or buffet should be located on the 1st floor and have a separate exit. In small schools (with the number of students less than 100), in the absence of a catering unit, it is allowed to organize meals for children in a specially designated room in agreement with the bodies of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision. 2.8.4. A sports or physical education hall should be located on the 1st floor and removed from the classrooms, the teacher's room and the doctor's office. At the gym, there should be changing rooms and showers for boys and girls, equipped with clothes hangers. If it is not possible to equip your own gym, it is allowed to use sports facilities located near the educational institution, provided that they comply with the requirements for school gyms. 2.8.5. The medical center should be located on the ground floor and include a doctor's office and a treatment room. 2.8.6. The walls of classrooms must be smooth, allowing them to be cleaned with a wet method. 2.8.7. The floors must be without gaps and have a plank, parquet or linoleum flooring on an insulated base. The floors of toilets and washrooms should be lined with polished ceramic or mosaic tiles. Do not use cement, marble or similar materials. 2.8.8. When choosing polymeric materials for finishing floors and walls of premises, one should be guided by the list of polymeric materials and products approved for use in construction.2.9. Requirements for the organization of the educational process
2.9.1. The curriculum is developed in each educational institution independently, but taking into account the observance of the norms of the maximum allowable load of schoolchildren. 2.9.2. For all educational institutions, regardless of the language of instruction, the following maximum allowable number of hours per week is set, taking into account its duration (Table 3).Table 3
THE MAXIMUM ALLOWED NUMBER OF HOURS PER WEEK FOR DIFFERENT DURATIONS.
|
Maximum allowable weekly load in hours |
||
|
at 6 day week |
at 5 day week |
|
|
3-year primary school: |
||
|
4-year primary school: |
||
Table 4
DURATION OF CONTINUOUS USE IN THE LESSONS OF VARIOUS TECHNICAL TEACHING TOOLS
|
Viewing time (min.) |
|||
|
filmstrips, slides |
movies |
TV shows |
|
2.10. Requirements for the organization of medical care for students
2.10.1. All educational institutions must be staffed with qualified paramedical workers and pediatricians. 2.10.2. Students of any educational institution must be provided with medical examinations in accordance with Order No. 186/272 of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation (Appendix 7). 2.10.3. In all types of educational institutions, a comprehensive rehabilitation of children with deviations in health should be organized, with the inclusion of psychological and pedagogical correction in its structure. 2.10.4. In the absence of a medical worker, the school management concludes an agreement with a nearby polyclinic on medical care for children. 2.10.5. All school employees must undergo mandatory preventive examinations in accordance with current orders. 2.10.6. When children with chronic diseases enter their school, the administration and medical staff of educational institutions with in-depth training should explain to parents that studying in such schools is an additional risk factor for the health of a sick child. 2.10.7. When considering the issue of exemption from final certification graduates of grades 9, 11 (12) should be guided by the order of the Ministry of Health and Medical Industry of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation No. 268/146 dated 18.07.94.2.11. Requirements for the sanitary condition and maintenance of educational institutions
2.11.1. During the period of epidemiological well-being in institutions, daily wet cleaning of the premises is carried out using soda, soap or synthetic detergents. Cleaning classrooms and other educational and auxiliary premises carried out after the end of the lessons open windows or transoms. If the school has two shifts, cleaning is done twice. They wash the floors, wipe the places where dust accumulates (window sills, radiators, etc.). Conducted once a month general cleaning premises with the use of not only detergents, but also disinfectants. For these purposes, use a 0.5 - 1% solution of bleach, chloramine or calcium hypochlorite, 0.2% solution of sulfochloranthin, 3% ampholan solution, 1% (according to DV) polysept solution, 1% (according to DV) peramine solution, 3 % (according to DV) hydrogen peroxide solution with detergent. Windows outside and inside and window openings are washed 2 times a year (in spring and autumn). Common areas (toilets, canteen, canteen and medical office) are always cleaned with disinfectants. Sanitary equipment is subject to daily disinfection, regardless of the epidemiological situation. Toilet seats, cistern handles and door handles are washed with warm soapy water. Sinks, toilet bowls are cleaned with quaches or brushes with cleaning and disinfecting agents: Shine-2, Sanita, Belka, PCHD, Desef, Desus, Sanitary, etc. - in accordance with the instructions on the label or wiped twice with a rag soaked in one of the disinfectants ( Appendix 8). 2.11.2. The dining room is cleaned after each visit by its children (breakfast, lunch, afternoon tea). After each meal, the tables are washed with hot water and soap or soda. Washing of dishes is carried out mechanically or manually. With the manual method of washing dishes, a three-cell bath is used. The tableware freed from food residues is washed with a brush in water having 50 degrees Celsius, with the addition of detergents (1 bath). After that, the dishes are immersed in one of the disinfecting solutions (0.2% solution of chloramine, sodium or calcium hypochlorite) - 2 baths, rinsed with hot running water at a temperature of 65 degrees Celsius (3 baths) and dried in special cabinets or grates. Glassware after mechanical cleaning is washed using approved detergents (1 bath), rinsed with hot running water (2 baths) and dried on special grids. Cutlery after mechanical cleaning and washing with detergents (1 bath) is rinsed with hot running water (2 baths) and disinfected by a physical method in air sterilizers for 2-3 minutes. Clean cutlery is stored in metal cassettes in a vertical position with the handles up. 2.11.3. During quarantine, the order of dish processing processes changes. First, after being freed from food debris, the dishes are immersed in one of the disinfectant solutions listed in Appendix 8, or boiled in a 2% soda solution for 15 minutes. After that, the dishes are washed, rinsed with hot water and dried. When using a dishwasher, the dishes are processed according to the regime specified in the documentation for the machine. 2.11.4. Washcloths, brushes for washing dishes, rags for wiping tables after use are boiled for 15 minutes in water with the addition of soda or soaked in a disinfectant solution (0.5% chloramine solution for 30 minutes), then rinsed, dried and stored in a special labeled container. 2.11.5. Food remains are disinfected by boiling for 15 minutes. or covered with bleach or any of the following: heat-resistant bleaching lime 200 g/kg or NGK or DOSHA 100 g/kg. 2.11.6. In the premises of the catering unit (kitchens, pantries, etc.), the rules for storing food and food waste must be observed and the fight against flies, cockroaches and rodents must be carried out. 2.11.7. In the medical office, in addition to disinfecting the premises and furnishings, it is necessary to disinfect reusable medical instruments by immersion in one of the solutions specified in the appendix, or use physical disinfection methods (boiling, dry hot air), patient care items are disinfected by wiping or immersion into a disinfectant solution (Appendix 8). 2.11.8. In cases where sterility is required, disposable products must be used. 2.11.9. During the quarantine period, all rooms where there were children from the quarantined class are subject to daily disinfection. When carrying out disinfection, special attention is paid to the processing of objects that play a decisive role in the transmission of this information. With drip infections - frequent airing of classrooms (at each change), thorough removal of dust in the premises, disinfection of dishes; for intestinal infections - disinfection of dishes, surfaces of dining tables, sanitary equipment, washing hands with soap and water after each visit to the toilet and before eating. 2.11.10. In order to detect pediculosis, medical personnel need to conduct examinations of children at least 4 times a year after each vacation and monthly selectively (four to five classes). Examinations (of the hairy part of the body and clothing) are carried out in a well-lit room, using a magnifying glass and fine combs. After each inspection, the comb is doused with boiling water or wiped with a 70-degree alcohol solution. 2.11.11. The site is cleaned daily. Garbage is collected in metal bins with lockable lids. They are located at a distance of at least 25 m from the main building on a concrete or asphalt base. Waste bins are cleaned when they are 2/3 full. After emptying, the bins are disinfected. Disinfection of garbage bins, garbage pits, dustbins is carried out by irrigation with a 10% solution of bleach (or heat-resistant whitewash), a 5% solution of NGK or a 1% solution of VGK with a disinfection time of 60 minutes. Garbage is poured with one of the solutions: 10% solution of bleach in a ratio of 2: 1 for 120 minutes, 20% chloride-lime milk 2: 1 for 60 minutes, 5% solution of NGK 2: 1 for 120 minutes. 2.11.12. In order to prevent the breeding of flies and destroy them in the development phase in the waste, once every 5 to 10 days, the waste collection sites are treated with one of the means proposed by the Guidelines for the fight against flies. There should be no stray animals on school grounds.2.12. Requirements for catering for students in educational institutions
2.12.1. Requirements for the diet of students. For students of all educational institutions, a one-time hot meal (breakfast) should be organized. At the request of parents, students can also be provided with lunch. Students of extended day groups should be provided at the place of study with two hot meals a day (breakfast and lunch), and for a long stay at school, and an afternoon snack. 2.12.2. The organization and diet of students in educational institutions are subject to mandatory coordination with the bodies of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision. 2.12.3. When catering for schoolchildren, one should be guided by the following documents: - SanPiN 42-123-5777-91 "Sanitary rules for enterprises Catering, including confectionery shops and enterprises that produce soft ice cream”; - SanPiN 42-123-4147-86 "Conditions, terms of storage of especially perishable products"; - Guidelines on the organization of rational nutrition of students in general education schools. 2.12.4. The cases of food poisoning and acute intestinal infections among students and staff in the school must be reported to the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision authorities in a timely manner. 2.12.5. In the nutrition of students of educational institutions it is forbidden to use: - flask, barrel, unpasteurized milk without heat treatment (boiling); - cottage cheese and sour cream in its natural form without heat treatment (cottage cheese is used in the form of casseroles, cheesecakes, cheesecakes; sour cream is used in the form of sauces and in the first dish 5-10 minutes before readiness); - milk and curdled milk "samokvas" in its natural form, as well as for the preparation of cottage cheese; - green pea without heat treatment; - pasta with minced meat(navy style), pancakes with meat, jelly, okroshka, pastes, mincemeat from herring, jellied dishes (meat and fish); - drinks, fruit drinks without heat treatment, kvass; - mushrooms; - pasta with chopped egg, fried eggs; - cakes and cream cakes; - deep-fried pies, donuts; - unknown powders as dough rippers. 2.12.6. Requirements for compliance with the rules of personal hygiene by employees of the catering department. Healthy persons who have undergone a medical examination in accordance with the current orders and instructions, as well as those who have attended a hygiene training course with passing a test, are allowed to work at the catering unit. Control over compliance with the deadlines for passing medical examinations rests with the school health worker. Each employee must have a personal medical book, which includes the results of medical examinations, information about infectious diseases, sanitary minimum. The staff of a public catering enterprise is obliged to observe the following rules of personal hygiene: - come to work in clean clothes and shoes; - leave outerwear, headgear, personal items in the dressing room; - cut nails short; - before starting work, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water, put on clean sanitary clothes in a specially designated place, after visiting the toilet, wash your hands thoroughly with soap, preferably disinfectant; - when signs appear colds or intestinal dysfunction, as well as suppuration, cuts, burns, inform the administration and contact a medical institution for treatment; - report all cases of intestinal infections in the employee's family. In the catering departments of schools it is strictly forbidden: - when preparing dishes, culinary and confectionery products, wear jewelry, varnish nails, fasten sanitary clothing with pins; - eat, smoke at the workplace. Eating and smoking are allowed in a specially designated room or place. Every day, before the start of the shift, the health worker conducts an inspection of open surfaces of the body for the presence of pustular diseases in all workers. Persons with pustular skin diseases, festering cuts, burns, abrasions, as well as catarrhs of the upper respiratory tract are not allowed to work, but are transferred to another job. The results of the inspections are recorded in the journal of the established form. Each catering unit should have a first aid kit with a set of medicines for first aid.ANNEX 1
(required)
EXAMPLE LIST OF EQUIPMENT AND INSTRUMENTS OF THE MEDICAL ROOM OF THE SCHOOL
- Desk 1 - 2 pcs. - Chairs 4 - 6 pcs. - Screen 1 pc. - Daybed 1 pc. - Stationery cabinet 1 - 2 pcs. - Pharmacy cabinet 1 pc. - Medical table with a glass cover: a) with a set of grafting tools 1 pc. b) with funds for emergency care 1 pc. - Refrigerator (for vaccines and medicines) 1 pc. - Washbasin (washbasin) 1 pc. - Bucket with pedal cover 1 pc. - Medical scales 1 pc. - Height meter 1 pc. - Spirometer 1 pc. - Manual dynamometer 1 pc. - Table lamp for ophthalmological and otorhinolaryngological examinations 1 pc. - Table for determining visual acuity, placed in the Rotta apparatus 1 pc. - Tonometer 1 pc. - Phonendoscope 2 pcs. - Bix small 2 pcs. - Bix big 2 pcs. - Rubber harness 4 - 6 pcs. - Disposable syringes with needles 2.0 10 pcs. 5.0 10 pcs. 10.0 5 pcs. - Tweezers 1 pc. - Medical thermometer 20 - 25 pcs. - Scissors 2 pcs. - Rubber heating pad 1 - 2 pcs. - Bubble for ice 1 - 2 pcs. - Reniform tray 5 pcs. - Metal spatula 40 pcs. - Tires (Kramer, Dieterikhs, plastic, for upper limbs) 10 pieces. - Stretcher 1 pc. - Tube quartz 1 pc. - Glasses in a children's frame (Drr 56 - 58 mm) with lenses of 1 diopter 1 pc. - Polychromatic tables for the study of color perception by E. B. Rabkina 1 pc. - Wooden plantograph (can be made in the school workshop) 1 pc. - Rug (1 m × 1.5 m) 1 pc.COMPLEX OF EXERCISES OF PHYSICAL MINUTES (FM)
School classes, combining mental, static, dynamic loads on individual organs and systems and on the whole organism as a whole, require FM in class to relieve local fatigue and FM of the general impact. FM to improve cerebral circulation. 1. Starting position (ip) - sitting on a chair. 1 - 2 - take your head back and gently tilt back, 3 - 4 - tilt your head forward, do not raise your shoulders. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is slow. 2. I. p. - sitting, hands on the belt. 1 - turn the head to the right, 2 - and. p., 3 - turn the head to the left, 4 - and. n. Repeat 6-8 times. The pace is slow. 3. I. p. - standing or sitting, hands on the belt. 1 - swing your left hand over your right shoulder, turn your head to the left. 2 - i. p., 3 - 4 - the same with the right hand. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is slow. FM to relieve fatigue from the shoulder girdle and arms. 1. I. p. - standing or sitting, hands on the belt. 1 - right hand forward, left up. 2 - change the position of the hands. Repeat 3-4 times, then relax down and shake your hands, tilt your head forward. The pace is average. 2. I. p. - standing or sitting, hands with the back on the belt. 1 - 2 - bring your elbows forward, tilt your head forward. 3 - 4 - elbows back, bend. Repeat 6-8 times, then arms down and shake relaxed. The pace is slow. 3. I. p. - sitting, hands up. 1 - clench the hands into a fist 2 - unclench the hands. Repeat 6-8 times, then relax your arms down and shake your hands. The pace is average. FM to relieve fatigue from the body. 1. I. p. - stand legs apart, hands behind the head. 1 - sharply turn the pelvis to the right. 2 - sharply turn the pelvis to the left. During turns, the shoulder girdle should remain motionless. Repeat 6 - 8 times. The pace is average. 2. I. p. - stand legs apart, hands behind the head. 1 - 3 - circular movements of the pelvis in one direction. 4 - 6 - the same in the other direction. 7 - 8 - hands down and shake your hands relaxed. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is average. 3. I. p. - stand legs apart. 1 - 2 - tilt forward, the right hand slides down along the leg, the left, bending, along the body up. 3 - 4 - and. n., 5 - 8 - the same in the other direction. Repeat 6 - 8 times. The pace is average. FM of the general impact are completed from exercises for different muscle groups, taking into account their tension in the process of activity A set of exercises FM for younger students in the classroom with elements of writing. 1. Exercises to improve cerebral circulation. I. p. - sitting, hands on the belt. 1 - turn the head to the right, 2 - and. p., 3 - turn the head to the left, 4 - and. p., 5 - gently tilt your head back, 6 - and. p., 7 - tilt your head forward. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is slow. 2. Exercises to relieve fatigue from the small muscles of the hand. I. p. - sitting, hands raised up. 1 - clench the brushes into a fist, 2 - unclench the brushes. Repeat 6-8 times, then relax your arms down and shake your hands. The pace is average. 3. Exercise to relieve fatigue from the muscles of the body. I. p. - stand legs apart, hands behind the head. 1 - sharply turn the pelvis to the right. 2 - sharply turn the pelvis to the left. During turns, the shoulder girdle should remain motionless. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is average. 4. Exercise to mobilize attention. I. p. - standing, arms along the body. 1 - right hand on the belt, 2 - left hand on the belt, 3 - right hand on the shoulder, 4 - left hand on the shoulder, 5 - right hand up, 6 - left hand up, 7 - 8 - clapping hands above the head, 9 - lower the left hand on the shoulder, 10 - the right hand on the shoulder, 11 - the left hand on the belt, 12 - the right hand on the belt, 13 - 14 - clapping hands on the hips. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace - 1 time slow, 2 - 3 times - medium, 4 - 5 - fast, 6 - slow.COMPLEX OF EXERCISES GYMNASTICS FOR THE EYES
1. Blink quickly, close your eyes and sit quietly, slowly counting to 5. Repeat 4-5 times. 2. Close your eyes tightly (count to 3), open them and look into the distance (count to 5). Repeat 4-5 times. 3. Stretch your right hand forward. Follow with your eyes, without turning your head, the slow movements of the index finger of the outstretched hand to the left and right, up and down. Repeat 4-5 times. 4. Look at the index finger of the outstretched hand at the expense of 1 - 4, then look into the distance at the expense of 1 - 6. Repeat 4 - 5 times. 5. At an average pace, do 3 - 4 circular movements with the eyes to the right side, the same in left side. After relaxing the eye muscles, look into the distance at the expense of 1 - 6. Repeat 1 - 2 times.APPROXIMATE VOLUME OF STUDENTS' MOTOR ACTIVITY
|
Daily amount of time (h) |
Cultural and recreational activities |
Physical education lessons per week (h) |
Extra-curricular forms of classes per week, sports sections, physical education circles, general physical education groups (h) |
School events |
Independent physical education at least (min) |
|||||
|
Gymnastics before training sessions (min) |
Physical education minutes at the lessons (min) |
Moving changes (min) |
Sports hour in an extended day (h) |
Participation in competitions in academic year(once) |
Days of health and sports |
|||||
|
Monthly |
||||||||||
EXAMPLE SCHEME OF THE THREE-COMPLETE COMPOSITION OF CLASSES IN A SMALL SCHOOL
Note: the duration of the combined lessons is reduced to 40 minutes, the last lessons - to 35 minutes. In the 1st grade, the duration of the lessons is 30 minutes in the first half of the year, and 35 minutes in the second. The second break (20 min.) is used for feeding children, the third (20 min.) - for outdoor games. In option 2, in the first grade, after the 3rd lesson, a 2.5-hour break is held, during which lunch, sleep, and games are organized. In conditions of full combination, lessons of physical education, labor, singing, drawing are held.
HYGIENIC REQUIREMENTS FOR THE LESSON SCHEDULE
Modern scientific research has established that the biorhythmological optimum of mental performance in children of school age falls on the interval of 10-12 hours. During these hours, the greatest efficiency of assimilation of the material is noted at the lowest psychophysiological costs of the body. Therefore, in the schedule of lessons for younger students, the main subjects should be taught in 2-3 lessons, and for middle-aged and older students - in 2, 3, 4 lessons. The mental performance of students is not the same on different days of the school week. Its level increases towards the middle of the week and remains low at the beginning (Monday) and at the end (Friday) of the week. Therefore, the distribution of the study load during the week should be built in such a way that its largest volume falls on Tuesday and (or) Wednesday. On these days, the school schedule should include either the most difficult subjects, or subjects of medium and light difficulty, but in greater numbers than on the other days of the week. The presentation of new material, tests should be carried out at 2-4 lessons in the middle of the school week. Subjects that require a lot of time for home preparation should not be grouped on the same day of the school schedule. When scheduling lessons, we recommend using the table of I. G. Sivkov (1975), in which the difficulty of each subject is ranked in points.|
Item |
Number of points |
| Mathematics, Russian language (for national schools) | |
| Foreign language | |
| Physics chemistry | |
| Story | |
| Mother tongue, literature | |
| Natural science, geography | |
| Physical training | |
| Work | |
| Drawing | |
| Drawing | |
| Singing |
APPENDIX 7
(required)
Extract from the Order
Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation
and Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation
No. 186/272 dated 06/30/92
REGULATIONS ON PREVENTIVE EXAMINATIONS OF CHILDREN ATTENDING GENERAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS
|
Tipping periods |
Pre-medical stage (screening and laboratory examination) |
Medical and pedagogical stage |
Specialized Stage |
|
|
Teacher, psychologist |
||||
|
Before entering preschool |
Middle health worker of a medical institution |
Inspection with analysis of screening test data and laboratory examination. Distribution by health groups |
Neurologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedic surgeon, dentist, speech therapist (from 3 years old), psychiatrist and other specialists according to indications |
|
|
One year before starting school |
Examination with analysis of screening test data and laboratory examination |
Determination of functional readiness for learning at school |
Neurologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedic surgeon, dentist, speech therapist, psychiatrist |
|
|
Before entering school |
Paramedic preschool |
Inspection with analysis of screening test data and laboratory examination. Distribution per medical groups for physical education |
Definition of functional readiness for school |
|
|
End of first year |
School nurse |
Neurologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedic surgeon, dentist, according to indications psychiatrist, speech therapist |
||
|
Transition to subject education |
School nurse |
Assessment of neuropsychic and physical development, determination of the biological age of the child and compliance with the passport |
Adaptation assessment |
|
|
Pubertal period (14 - 15 years) |
School nurse |
Neurologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedic surgeon, dentist, psychiatrist, speech therapist and gynecologist according to indications |
||
|
Before graduating from an educational institution (10 - 11 cl. 16 - 17 years old) |
School nurse |
Medical professional advice, transfer of information on young men of pre-conscription age to military registration and enlistment offices |
Teacher, psychologist Medical and professional consultation |
Neurologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedic surgeon, dentist, psychiatrist, speech therapist and gynecologist according to indications |
APPENDIX 8
(required)
SANITARY AND DISINFECTION REGIME IN GENERAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS DURING THE QUARANTINE PERIOD
|
Object name |
Method and mode of disinfection |
| 1. Premises (floor, walls, doors, window sills, etc.), hard furniture | The treatment is carried out by wiping with a rag soaked in one of the disinfectant solutions: 0.5% chloramine solution - 60 min; 0.5% solution of bleach or white heat-resistant lime - 60 min; 0.25% solution of NGK, DOSHA - 60 min; 0.2% solution of sulfochloranthin - 60 min; 3% (according to active ingredient) solution of hydrogen peroxide with detergent (0.5%) - 60 min; 1% (according to active ingredient) peramine solution - 60 min; 1% (according to active ingredient) polysept solution - 60 min; 3% ampholan solution - 60 min; 0.5% solution of catamine AB - 30 min |
| 2. Carpets | Brush twice with a brush moistened with: 0.5% chloramine solution; 0.2% solution of sulfochloranthin; 1% peramine solution; 0.5% solution of catamine AB and remove for the period of quarantine. |
| 3. Dishes freed from food residues | Boiling in water or in a 2% soda solution - 15 minutes. Immersion in one of the disinfectant solutions for 60 minutes: 1% chloramine solution, 1% clarified bleach solution, 0.5% NHA solution, 0.2% sulphochloranthin solution, 3% ampholane solution, 1% catamine AB solution. Wash, rinse and dry the dishes after disinfection. |
| 4. Leftover food | Boiling - 15 min. Falling asleep with bleach (or white heat-resistant lime) 200 g/kg - 60 min. NGK, DOSHA 100 g/kg. |
| 5. Sanitary equipment (sinks, toilet bowls, etc.) | Clean toilet lids with hot soapy water. Wipe toilets, bathtubs, sinks twice with one of the solutions specified in paragraph 1, or wipe with a cleaner and disinfectant: Protein, Shine-2, Sanita, PCHD, Sanitary, Desus, Desaf, etc., - in accordance with the recommendations for use means on the label. Used kvacha, cleaning material is immersed in a 0.5% solution of NGK or 1% solution of bleach for 30 minutes, rinsed and dried. They store clean kwachas and cleaning material in a special labeled container in a utility closet. |
| 6. Medical products made of glass, metal, rubber, plastics | chemical method: immersion or wiping with one of the disinfectant solutions: 1.0% chloramine solution - 30 min; 2.5% (0.5% DV) solution of chlorhexidine bigluconate - 30 min; 3% (according to AI) hydrogen peroxide solution with 0.5% detergent solution - 80 min. physical method(except for plastic products): boiling in water or 2% soda solution - 15 minutes; dry hot air 120 degrees Celsius - 45 min. |
| 7. Staff hands | For hygienic disinfection, hands are treated with a cotton swab for 2 minutes. one of the solutions: 2.5% (0.5%) aqueous solution of chlorhexidine bigluconate; 1% iodopyrone solution; 0.5% chloramine solution and then washed with soap. |
NORMATIVE REFERENCES
These sanitary rules use references to the following documents: 1. Law of the RSFSR "On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population." 2. Law of the Russian Federation "On Education". 3. "Regulations on State Sanitary and Epidemiological Rationing", approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of June 5, 1994, No. 625. 4. Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation "Improving the system of medical support for children in educational institutions" of 06/30/92 , No. 186/272. 5. "Classifier of sanitary-hygienic and epidemiological normative and methodological documents", approved by the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of the Russian Federation on 09.04-93. 6. Guide R I. I .004-94 “State system of sanitary and epidemiological regulation of the Russian Federation. General requirements to the construction, presentation and execution of sanitary-hygienic and epidemiological regulatory and methodological documents”, approved by the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of the Russian Federation on 09.02-94. 7. GOST 11015-93 “Student Tables”. 8. GOST 11016-93 "Student chairs". 9. SanPiN 2.1.4.559-96 “Drinking water. Hygienic requirements for water quality of centralized drinking water supply systems. Quality control". 10. SNiP 23-05-95 "Natural and artificial lighting", approved by the USSR State Construction Committee in 1995. 11. SNiP 2.08.02-89 "Public buildings and structures", approved by the USSR State Construction Committee in 1989. 12. SNiP 2.07.01 -89 "Planning and development of urban and rural settlements", approved by the USSR State Construction Committee in 1989. 13. SanPiN 2.2.2.542-96 "Hygienic requirements for video display terminals and personal electronic computers and organization of work", approved by the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of the Russian Federation on 14.07.96 14. SanPiN 42-125-4216-86 “Sanitary and hygienic rules and norms for organizing the education of children from the age of six”, approved by the USSR Ministry of Health and the USSR Ministry of Education in 1986. 15. SanPiN 42-123-4147-86 “Conditions , shelf life of especially perishable products”, approved by the USSR Ministry of Health in 1986 17. Guidelines for the organization of rational nutrition of students in secondary schools, approved by the Ministry of Trade of the USSR on December 28, 1985, No. 315. 19. Methodological recommendations "Organization and mode of operation of after-school groups and schools", approved by the Ministry of Health of the USSR on 12.12.1979, No. 2111-79. 20. Guidelines for the fight against flies, approved by the USSR Ministry of Health on January 27, 1984, No. 28-93. 21. A comprehensive program for physical education of students in grades X - XI, approved by the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation in 1992. 268/146.Currently, there are several types of schools (Table 135):
1) mass general education, in which children are 4-5 hours daily;
2) an extended day school, where not only the educational process, but also the educational process is carried out and where schoolchildren spend 8-10 hours a day;
3) a boarding school with round-the-clock stay of students, where the share and importance of the educational process is even more increased;
4) evening shift schools for work
melting adolescents, where classes are held 3-4 times a week for 4-5 hours, either in the evening or in the daytime.
Despite the unified curricula and programs, there are differences in the composition of the premises and the structure of the buildings of these types of schools, which are determined by the specific weight of the educational process and the length of stay of schoolchildren in an educational institution.
Depending on the health status of the contingents of students, three types of schools have been identified:
1) mass general education for practically healthy children;
2) schools for children with developmental disabilities - the blind and visually impaired, hearing impaired and deaf and dumb, mentally retarded;
3) sanatorium-type schools for children with poor health - neurotics, suffering from chronic rheumatism, survivors of poliomyelitis, with tuberculosis intoxication, etc.
IN last years there was a need to classify schools according to specialization: teaching in a foreign language, mathematics, etc. Each of these schools has its own teaching characteristics and requires the creation of special types of school buildings.
The listed types of schools have their own characteristics of the pedagogical process, education and health work, differ in the types of school buildings. At h and with t ok school. The area of the plot of schools should be as follows (see Table 135).
Table 135. Types of schools
| School type | General students | Square | Type | schools | General students | Square | ||
| Initial: | ||||||||
| for 4 classes | 40 | on | 10 | classes | 392 | 2,0 | ||
| " 4 " | 80 | 0,5 | » | 12 | » | 464 | 2,0 | |
| Eight year olds: | » | 16 | » | 624 | 2,0 | |||
| for 8 classes | 192 | 1,2 | » | 20 | » | 784 | 2,2 | |
| " 8 " | 320 | 1,7 | » | 30 | » | 1176 | 2,8 | |
| » | 40 | » | 1568 | 3,0 | ||||
| for 50 classes | 1960 | _____ 4th______ | ||||||
Under reconstruction inhabited place the area of school plots may be reduced, but not more than by 20%, while the area of the plots must be at least 0.5 ha.
The site must be fenced, landscaped and divided into zones: educational and experimental, physical culture and sports, a recreation area and an economic zone (yard).
The landscaping area should be 40-50% of the area of the site. The width of the green strip along the boundaries of the land plot is taken to be at least 1.5 m, and from the side of the street - at least 6 m. Planting trees and shrubs with poisonous fruits, and thorny bushes and fruit trees near sports grounds is not allowed.
The sports zone should be located in the depth of the site. The main element of the sports area is a gymnastic ground, which is equipped with hanging equipment (poles, rings, rope), a gymnastic wall, uneven bars, etc. A sports ground for ball games should be placed at a distance of at least 10 m from the windows of other premises of the school building and school- boarding school or separated from them by a protective strip of green spaces. Near the exits from the school buildings, playgrounds for outdoor games should be located, divided for students in grades 1-2, grades 5-8 and grades 9-10. All sites must be flat, with earth-sand or natural turf cover. In the dry season, the grounds must be watered '/g - 3 hours before the start of the game. Playgrounds located near the school building are recommended to be sown with low, hard-to-trample grass (a mixture of clover, timothy grass, ryegrass and meadow mint).
Economic yard it is recommended to locate on the side of the entrance to the production premises of the school canteen and adjacent to the training and experimental area, with a separate entrance from the street. The sites for the placement of waste bins must be insulated with a dense strip of green spaces at least 3 m wide and have an asphalt or cemented surface. Garbage bins are located at a distance of at least 25 m from the school building.
The entire area must be cleaned daily: in spring and summer, water it with water, winter time to clear the common playground and paths from snow. In winter, in the sports zone, slides for sledding and a skating rink are arranged. The path to the yard toilet, as well as the approaches to the building at least 100 m before the building, must have a hard surface (asphalt, crushed stone, concrete).
In the evening, it is necessary to provide illumination of the territory of the site, based on the norm of 20-40 lux on the ground.
In the absence of sewerage and water supply, water supply and disposal of sewage and waste are handled in the same way as in preschool institutions.
All regulatory provisions for the arrangement and equipment of the territory, buildings and premises of newly built and reconstructed schools should be adopted in accordance with the requirements of SNiP P-L-65-73 "General education schools and boarding schools" and "Sanitary rules for the arrangement and maintenance of general education schools" , No. 1186-a-74.
Based on pedagogical and hygienic requirements, the structure of the school building should provide:
1) the maximum division of the children's team into age groups to differentiate the educational process, due to the peculiarities of the development and functional state of children;
2) separation of educational premises from general school premises, which are sources of noise, dust and other air pollution: gymnastic and assembly halls, workshops, catering department, utility rooms;
3) convenient and fairly short connections between educational and recreational premises, especially primary classes, with wardrobes and land plot used for recreation of children during recess;
5) favorable conditions natural lighting and ventilation of educational and recreational facilities;
6) the possibility of isolating certain groups of children in the event of infectious diseases in order to prevent their spread to the entire team.
The building and premises of the school. School buildings are currently being designed with three floors. The composition and area of the premises are established on the basis of the curriculum of the general education labor polytechnic school, depending on the capacity of the building, taking into account special premises for organizing an extended day for some students. For grades 1-4, classrooms are provided according to the number of classes, for grades 5-10 - study rooms. In order to provide students in classrooms with furniture appropriate for their height, large schools should have
2-3 classrooms per subject, each for 2-3 ages.
School buildings should have groups of premises for: a) grades 1-4; b) classrooms of 5-10-x (11-x) classes; c) labor training; d) educational, sports and cultural purposes; e) organization of an extended day, including a section of sleeping quarters; f) for general school purposes: a canteen, a library, administrative and economic, medical support, etc. Sanitary units for boys and girls are located on each floor of the block of educational premises. Depending on climatic conditions, vestibules (double or triple) are arranged at the entrances to buildings.
To place classrooms in the school building, it is recommended that the principle of age be predominantly with vertical or horizontal connections between classrooms. In large schools, the vertical connection between the classrooms makes it possible to place students in grades 5-7 and 8-10 (11th) in separate blocks, create specialized sections that combine classrooms of academic disciplines of the natural-mathematical and humanitarian cycles. Horizontal connections between classrooms are provided in large schools when students of 2-3 adjacent classes are placed on the same floor. On the 1st floor there are rooms used by all classes: workshops, various classrooms (military, technical teaching aids and a biology laboratory); on the 2nd floor - classrooms for 4=7th grades and on the 3rd floor - for 8-10th (11th) grades.
Educational premises are not allowed to be placed in the basement or basement floors. The height of the classrooms must be at least 3 m. Each classroom and study rooms are calculated for 40 students for grades 1-8 and 36 for grades 9-10. Entrances to classrooms should be provided from the front tables and desks. The number of classrooms with entrances from the back tables or desks should not exceed 25% of the total number of classrooms.
All schools, regardless of the number of laboratories, must have at least three laboratory rooms (physics, chemistry and biology with an area of 15 m2 each), except for a school with 8 classes, where 2 laboratory rooms are allowed. Laboratory rooms should be located adjacent to the corresponding laboratories and connected to them by doors.
For the organization of labor training, the school must be equipped with: 1) a combined workshop for boys of grades 4-8 - for processing metal, wood and other types of labor with an area of 66 m2 with a utility room with an area of 16 m2; 2) tool room with an area of 16 m2; 3) a workshop for workshops for grades 9-10 with an area of 50-66 m2 with a laboratory area of 16 m2; 4) a labor office for girls in grades 4-8 for textile processing and cooking with an area of 50 m2 with a utility room of 16 m2 (for secondary schools for 50 classes - 2 rooms of 50 m2 each and a utility room of 16 m2).
Premises for labor training may be located in ground floor with mandatory natural lighting or in a separate building (in this case, a dressing room and sanitary facilities will be equipped).
The recreation area should be 0.75 m2 per student in zone I schools, 0.6 m2 in zones II-III, 0.42 m2 in the building and 0.18 m2 in the site in zone IV. Corridors with one-sided buildings with a width of at least 2.8 m can be used as recreation.
In schools with 10 classrooms, there must be an assembly hall = cinema audience (at the rate of 0.6 m2 per seat and the number of seats
in schools 20-25%, and in boarding schools - 50% of the total number of students). In schools for 8 classes, it is allowed to combine the assembly hall with the gym.
The library includes a reading room and a book depository with an area ratio of 2:1. The distance between the racks is assumed to be at least 0.9 m.
In each school, for the organization of hot meals for schoolchildren, a canteen of the appropriate capacity (Table 136) and the necessary set of premises should function. In schools for 8 = 20 classes, the canteen-preparation (for raw materials) has the following premises: a cooking room with a preparation area - 43-56 m2, a washing room - 14-21 m2, a refrigerated chamber - 5-7 m2, a pantry of dry products - 5- 9 m2, pantry of vegetables - 6.9 m2, loading and packaging - 6-9 m2, wardrobe and bathroom for staff - 7 - 11 m2. In schools for 30-50 classes they arrange a pre-cooking canteen (on semi-finished products): a pre-cooking kitchen - 55-80 m2, a washing room - 25-30 m2, a refrigerated chamber - 11-16 m2, a pantry of dry products - 10-12 m2, a loading container - 12 = 15 m2, wardrobe and bathroom for staff - 12-18 m2. Washbasins in dining rooms and buffets are provided at the rate of one tap or 0.6 m of a grooved washbasin for 20 places in the dining room.
In an eight-year school for 8 classes (with a class of 24 students), a canteen with a landing hall of 30 m2 and a utility room of 24 m2 should be organized, in elementary schools - a cubic and utility pantry.
Table 136
Daily monitoring of nutrition is carried out by a doctor and a nurse, includes monitoring the quality of incoming products, storage conditions and compliance with the deadlines for implementation, the technology of preparation and the quality of ready meals, the sanitary and anti-epidemic regime of the catering department, the organization of washing dishes, the quantitative composition of food rations. Meals for students are organized in accordance with the instructive guidelines: "Organization of public catering for students in secondary schools" (No. 1174-74), "Organization of rational nutrition for students in preparatory classes of secondary schools" (No. 2635-82).
Dining rooms are equipped with tables for 4-6-10 seats and chairs or stools. When arranging the tables, the distance between the tables and the dispensing room or the window (door) for receiving dirty dishes is 150-200 cm; between rows of tables - 100-150 cm; between tables and the wall - 40-60 cm. Tables must have a hygienic coating, easy to clean, resistant to high temperature and disinfectants (marble, plastic, etc.) Tables are washed daily with hot water, soda and soap, and after each landing they are wiped with damp, clean rags.
Issues of catering equipment, catering, washing dishes are set out in Chapter 18 "Food Hygiene". Therefore, some features for schools are highlighted here. Dinnerware can be porcelain, enameled or stainless steel. The use of aluminum is not recommended and the use of plastic dishes is prohibited. The time for using the dining room (buffet) for each class is set by a special schedule. Meals for primary school students are organized under the supervision of a teacher or high school students. Before eating, students must wash their hands with soap and dry with towels (preferably paper, electric towels).
Employees of school canteens (canteens) must undergo mandatory preventive medical examinations in accordance with the requirements of the "Instructions on mandatory preliminary upon admission to work and periodic medical examinations" (approved by the USSR Ministry of Health on 24. 12. 87, No. 4538-87; agreed with the All-Russian Central Council of Trade Unions 06. 06. 88, No. 14-4A / 2869).
Drinking fountains are maintained and cleaned regularly. In schools where there are no drinking fountains, students are provided with boiled water, which is in enameled tanks. The water in the tanks is changed daily, and glasses and mugs are washed with hot water after use.
The doctor's office should be located on the ground floor and have a length of at least 5 m to enable students to determine visual acuity. Schools with a capacity of 30 classes or more must have a dentist's office with an area of 12 m2.
The area of the vestibule with a dressing room must correspond to the norm for one student - 0.25 m2. In boarding schools designed for construction in 1A, ІB and 1D climatic subdistricts, the area of the lobby with a wardrobe dryer for clothes is taken at the rate of 0.35 m2 per student. In the lobbies of school buildings designed for construction in climatic subregions IA, ІB, 1G, vestibules with three doors are designed, in climatic regions I, II and III - with two doors, in climatic region IV - with one door.
Bathrooms consist of washrooms and latrines. The number of sanitary appliances is determined at the rate of one toilet bowl for 30 girls, one toilet bowl and one urinal for 40 boys, and one washbasin for 60 students. At the assembly hall-cinema audience, latrines and wash basins are provided: for women with the number of sanitary appliances - 1 toilet bowl and 1 wash basin - for halls with more than 160 seats; 2 toilet bowls and 1 washbasin - for halls with more than 160 seats; men's - 1 toilet bowl, 1 urinal and 1 washbasin. Toilet bowls in the latrines for students should be placed in open cabins, separated by partitions-screens with a height of at least 1.75 m from the floor, not reaching the floor by 0.2 m. The size of the cabin is 0.8X 1 m. not less than 0.6 m, between the taps of a common washbasin - 0.55 m. 11th) classes. It is not allowed to place the entrances to the latrines and wash basins for students directly from the staircases and opposite the entrances to the classrooms and sleeping quarters.
Daylight. All classrooms must have natural light. The orientation of the windows of the premises on the sides of the horizon in the buildings of boarding schools is taken according to Table. 137.
The best types of natural lighting in classrooms are lateral left-hand and tape with
Table 137
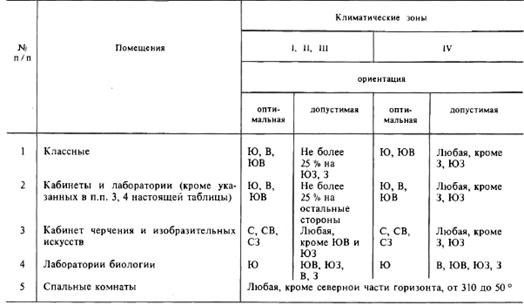
the use of sun protection devices (with a depth of training rooms of more than 6 m, a right-hand illumination device is required). The direction of the main light flux to the right, in front and behind the students is unacceptable, since the level of natural light on the working surfaces of desks and tables is reduced by 3-4 times.
Window glass should be wiped daily with a wet method from the inside and washed from the outside at least 3=4 times a year and from the side of the premises - at least 1-2 times a month.
Rationing of natural lighting is carried out according to quantitative and qualitative indicators: the first - according to SNiP P-4-79 “Natural and artificial lighting. Design standards", and the second - the ratio of brightness between the individual surfaces of the interior.
For painting desks and tables, a green range of colors is recommended - from light to dark green, as well as the color of natural wood with a reflection coefficient of 0.45, for a blackboard - dark green or Brown color with a reflection coefficient of 0.10-0.20. Walls, ceilings, floors, classroom equipment should have a matte surface to avoid glare. Interior surfaces of classrooms should be painted in warm colors; the ceiling and the upper parts of the walls are painted in White color.
Used Decoration Materials, paints, varnishes must be from among those permitted by the Ministry of Health of the USSR. Cabinets and other equipment should be installed against the rear wall of the room. You can not place indoor flowers on the windowsills. They should be placed in portable flower boxes 65-70 cm high from the floor.
Artificial lighting and electrical devices must comply with the requirements of SNiP P-4-79 “Natural and artificial lighting. Design standards ”(Table 138).
Wiring in the classrooms should provide for the possibility of separate inclusion of the 3rd row of desks and tables and local board lighting. It is hygienically justified to use a relay that automatically turns on artificial lighting when the required levels of natural light in classrooms decrease.
In all premises of the buildings of schools, boarding schools, boarding schools (dormitory buildings) hidden wiring should be provided (open wiring is allowed in kitchens, pantries, toilets and other utility rooms).
Table 138
| Room and work surface | Least illumination, | The surface to which the lighting standard applies | |
| classrooms, | |||
| study rooms: | |||
| a) tables and desks | 300 | Level surface | |
| 0.8 m | from the floor | ||
| b) blackboards | 300 | Vertical surfaces | |
| Drawing rooms (on tables) | 500 | Horizontal surfaces at the level | |
| not 0.8m from the floor | |||
| Wildlife corner | 300 | Same | |
| Workshops for metal and wood processing | 300 | » | » |
| Sewing workshops | 400 | » | » |
| Offices of service types of labor | 300 | » | » |
| pioneer rooms | 300 | » | » |
| Library | 300 | » | » |
| Doctor's office | 200 | » | » |
| teacher's room | 200 | » | » |
| Director's office | 200 | » | » |
| Bedrooms | 75 | » | » |
| Buffets | 200 | » | » |
| assembly halls | 200 | » | » |
| Sport halls | 200 | On the floor | |
| recreation | 150 | » | » |
| Lobby | 100 | » | » |
| Corridors, bathrooms, stairs | 75 | On platforms and stairs | |
To connect a slide projector, film projector, etc., in classrooms, classrooms, laboratories, rooms for organizing an extended day, two sockets are installed: one at the blackboard, the other on the wall of the room opposite from the blackboard. In the premises where children stay (with the exception of laboratories and classrooms for practical exercises), sockets are installed at a height of at least 1.5 m from the floor, switches - at a height of 1.8 m from the floor.
Artificial lighting of school premises is provided by fluorescent lamps (type LB and LE) or incandescent lamps. When illuminating with fluorescent lamps in a training room with an area of 50 m2, the following must be installed: 12 active lamps of the LPO-01-2X40 or LP0 02-2 X40 type. The blackboard is illuminated by two lamps of the LPO-12X40 type installed parallel to it (0.3 m above the top edge of the blackboard and 0.6 m towards the class in front of the blackboard). The total electrical power per class is 1040 watts. When illuminated with incandescent lamps in a training room with an area of 50 m2, 7 or 8 active light points are installed with a total capacity of 2100-
2400 W. Lamps of diffuse, mainly reflected, light distribution are used: ring SK-300, KMO-ZOO, PKRM-300.
Lamps in the classroom are arranged in two rows parallel to the line of windows at a distance of 1.5 m from the inner and outer walls, 1.2 m from the blackboard, and 1.6 m from the back wall; the distance between the lamps in rows is 2.65 m.
Lamps are cleaned at least once every 3 months (it is forbidden to involve students in cleaning lighting fixtures).
It is forbidden to use new types of lamps and lighting fixtures not permitted by the USSR Ministry of Health.
Artificial workshop lighting should be installed as general lighting or combined lighting (general and local). For general lighting, luminaires with a protective angle of 10 to 30° can be used. Sources of local lighting must have a protective angle of at least 30 ° and reflectors. In luminaires, white light lamps (LB type) should be installed, and where color discrimination is required, natural light lamps (LE). Luminaires should be installed in two rows in solid lines with a distance between rows of 3 m. working surface illumination of 300 lux, the specific electrical power should be 17 W per 1 m2 of floor area.
For local lighting, lamps with fluorescent lamps or "Alpha" type, with low voltage electric lamps (25-40 W) can be used. Lamps with the help of hinged or sliding brackets are mounted directly on the machine or on the wall near the machine so that the light falls on the workplace, and the eyes of the worker are protected from blinding by the filament of incandescent lamps.
Heating and ventilation are designed in accordance with the requirements of the SNiP chapter on heating, ventilation and air conditioning. The ventilation of classrooms is carried out by an organized supply of heated outside air in the amount of at least 16 m3/h per student. It is allowed to use a decentralized inflow of unheated outdoor air, provided that the established values of the normalized parameters of the indoor air are provided. Directly from the classrooms, natural exhaust ventilation should be provided in the amount of a single exchange of 1 hour. mechanical extraction from the electric grinder and local suction from the glue pot of grinding wheels, muffle furnaces. Independent exhaust ventilation systems are provided for classrooms and classrooms, laboratories, assembly halls, cinema audiences, sports halls, workshops, dining rooms, a first-aid post and a cinematographic complex.
In the premises of schools, the relative humidity of the air should be 40-60%, the temperature, depending on climatic conditions and the season: in classrooms and classrooms 17-20°C, in the gym 15-17°C, in metal and wood processing workshops 16 -18°С, in the locker rooms at the gym 19-23°С, in the assembly shaft, cinema audiences 17-20°С, in the library, rooms of public organizations 17-21°С, doctor's office 21-23°С, recreation 16-18 °С, in sleeping quarters 18-20 °С, in washrooms 20-23 °С, in the vestibule, wardrobe 16-19 °С, in latrines 17-21 °С, in showers not lower than 25 °С. Schools are supplied with heat from the heating networks of the CHPP. district, quarterly and group boiler houses. In case of their absence, it is allowed to install a local boiler house in a separate building in accordance with the chapter SNiP P-35-77 “Boiler installations. Design standards". In the absence of central heating, classrooms can be heated with stoves of large heat capacity (only in one-story school buildings up to 192 student places). Furnaces are fired from the corridors in the evening or early in the morning. Chimneys, in order to avoid indoor air pollution with carbon monoxide, are closed no earlier than the complete combustion of fuel and no later than 2 hours before the arrival of students.
To ensure natural ventilation of the premises, transoms are arranged. All classrooms are thoroughly ventilated during breaks (recreation - during lessons). Through ventilation in the school, the duration of which depends on the outside temperature, is carried out at the end of classes in the evening and before the start of classes in the morning, as well as in the interval between the first and second shifts (see Table 139). In each room, the opening area of the transoms and vents must be at least ‘Up to the floor area. Transoms and window vents in educational and recreational premises shall not be hammered and sealed.
Physical education lessons should be held in well-aerated gymnasiums; at an outside air temperature above 5°C and an air speed of no more than 2 m/s, it is recommended to open one or two windows in the hall on the leeward side; at a lower outside temperature and a higher air speed, one to three transoms are opened. On warm days, it is advisable to conduct classes with open transoms and windows (transoms in the latrines should not open).
In the absence of sewerage and water supply in the settlement, water supply and the method of removing sewage and waste in each case are decided in agreement with the local SES.
Table 139

Table 140
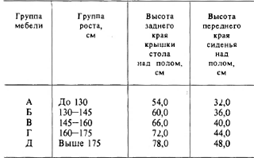
The programs of eight-year and secondary schools in chemistry and physics provide for classes and experiments with metallic mercury. Therefore, in order to prevent mercury poisoning and protect environment the necessary requirements must be observed: 1) the volume of mercury in the school should not be more than 500 cm3, 2) mercury is stored only under a layer of water in thick-walled glassware with a ground or rubber stopper in a safety enameled or plastic bath with high sides and always in places not available to students; 3) work with mercury is carried out in baths with sides; 4) pouring mercury into the sewer is strictly prohibited; 5) floors in laboratories and laboratory rooms of physics and chemistry classrooms should be without gaps; it is recommended to cover them with linoleum of a continuous sheet or hermetic sealing of seams and skirting boards; 6) laboratories should have washbasins with cold and hot water supply; 7) equipment containing mercury with an open surface is freed from mercury after operation; 8) mercury is poured into dishes that ensure its proper storage.
Before performing laboratory work in chemistry and physics, students should be instructed on measures to comply with safety regulations, special precautions when working with mercury. When mercury is spilled, immediately, as well as in order to prevent air pollution, at least once a year, the laboratory is demercurized (demercurized) with an acidified solution of potassium permanganate (per 1 liter of water, 1 g of potassium permanganate and 5 ml of hydrochloric acid, relative density 1.19). Potassium permanganate is preliminarily dissolved in a small volume of hot water, and then poured into a bottle of water and the indicated amount of acid is added. With this solution, preferably with the help of a hydro-panel, they cover the floor, walls, skirting boards and equipment with an even layer. After an hour, the solution is washed with rags.
The second method of demercurization is treatment with a 20% aqueous solution of ferric chloride. After the solution dries, all objects are washed with water. At the end of demercurization, the room is thoroughly ventilated. Metal surfaces cannot be treated with a solution of ferric chloride. If mercury vapor is detected in the air after treatment, more complex and time-consuming work is necessary: opening the floor, cleaning the underground, changing plaster, etc.
In the premises for labor training and training and production workshops, near machines and mechanisms, the work on which is associated with the release of a large amount of heat or dust (muffle furnace, grinding and grinding wheels, glue makers, etc.), provide Good work exhaust devices. The amount of air removed by ventilation is regulated by valves or shutters in the ventilation openings. The ventilation grilles are cleaned of dust every month.
Water supply. In the presence of a water supply system, cold water is supplied:
1) to washbasins, arranged one at a time in each classroom of grades 1-4, in drawing rooms and visual arts, geography and in the military cabinet; 2) to the sinks of laboratory tables in the laboratory of chemistry and to the sinks of demonstration tables in the laboratories of chemistry, physics and biology; 3) to a two-section sink in a darkroom; 4) to drain cisterns in bathrooms; 5) to drinking fountains in each recreational facility.
The supply of cold and hot water should be provided: 1) to washbasins and sinks in the offices of service types of work for the processing of fabrics and cooking for girls; 2) to the washbasins in the training workshops, teachers' room, doctor's office and treatment room;
3) to laboratory cabinets in laboratories of chemistry, physics and biology;
4) to water taps installed for household needs, one in each wash basin for students; 5) to sinks in the technical staff room and in the wildlife area; 6) to washbasins in bathrooms, to showers and appliances of personal hygiene cabins; 7) to bathrooms in dormitory buildings or in dormitory sections of boarding schools; 8) to the technological equipment of canteens and buffets.
Sanitary maintenance of premises. To combat dust, scrapers and grates for cleaning feet are placed at the entrance to the school. Every day, at the end of each shift, wet cleaning of all school premises is carried out: wet sweeping of floors, wiping desks, tables, window sills, heaters, etc. with a damp cloth. Cleaning is carried out with open windows or transoms. Wet cleaning of corridors and recreational premises is carried out after each change. The chalkboard is washed daily. Sponges dipped in water are recommended for erasing chalk.
School premises are cleaned at the following times: bedrooms - in the morning after the children wake up; classes, workshops, classrooms - at the end of the last lesson and again - at the end of the preparation of lessons and the work of circles; corridors and recreation - after each change; gaming - at the end of the day; dining room - after each meal; wardrobe (lobby) - after the start of each shift; medical premises - in the morning; assembly hall and other club premises - at the end of the day; hygienic showers - as they get dirty; bathrooms in the school building - after each break (using disinfectants).
The gym is thoroughly ventilated after each class. Wet cleaning with wiping of all equipment is carried out at least 2 times a day. Gymnastic mats are knocked out in the air at least once a week.
General cleaning of the gym and utility rooms with it is carried out at least once a week. Students are allowed to the gym only in tracksuits and sports shoes.
The bathrooms are thoroughly cleaned after each change: the floors are wiped, the toilets are washed and cleaned, the seats and handles are wiped with a cloth soaked in a disinfectant solution (2% chloramine solution or 0.5-1% solution of clarified bleach). In the absence of running water in the school, wash basins must be provided with self-leveling wash basins. Weekly conduct a thorough cleaning of the premises with wiping the panels. Once a month, a general cleaning is carried out, during which panels, floors, radiators, window sills, etc. are washed with soapy water.
It is necessary to provide for the allocation of separate cleaning equipment for cleaning bathrooms, washing floors in classrooms, washing walls, window sills, desks. Separate equipment is allocated for cleaning chemical and physical laboratories. Cleaning equipment is stored in special rooms or cabinets. Sanitary cleaning equipment is stored separately from other cleaning equipment.
Equipment of educational premises. The requirements for the size, placement of school furniture must comply with the requirements of the instructional and methodological letter "On the use of school furniture" (No. 3225-85). For the equipment of educational premises, the manufacture of furniture is provided, taking into account five groups of growth: A, B, C, D and D (Table 140). The seating of students, taking into account the growth group, makes it possible to provide a comfortable workplace for 82-86% of schoolchildren (see Table 140).
Arrangement of furniture. Group A furniture is placed first in all three (four) rows, group B is second, group C is third, etc. Workplaces in classrooms at the first and second tables (desks) in any row are assigned to students with
a significant decrease in hearing acuity, and in the row by the window - to schoolchildren with reduced visual acuity (with good correction of visual acuity with glasses, schoolchildren can sit in any row). Schoolchildren with rheumatic diseases, prone to frequent sore throats and acute inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, are given places further away from the windows. At least 2 times a year, schoolchildren sitting in the first and third (fourth) rows are changed places without violating the correspondence of the furniture numbers to their height.
Between the rows of tables (desks) and the walls of the classroom, the following established distances are observed:
In classrooms of the usual rectangular configuration: from the outer wall to the first row of tables (desks) - 0.6-0.7 m; from the inner wall to the third row of tables (desks) - 0.5-0.6 m; from the back wall to tables (desks) - 0.4-0.5 m; from the blackboard to the first tables (desks) - 2-4 m; between rows - 0.6-0.8 m;
In classrooms with a square and transverse configuration, when arranging furniture in four rows:
distance from the blackboard to the first tables (desks) - at least 3 m; from windows to the first row of tables (desks) -0.8-1 m; width of aisles between rows - not less than 0.6 m; from the last tables (desks) to cabinets located along the wall of the room - 0.9-1 m. In laboratories, the distance between rows of educational furniture is 1 m, between drafting tables in drawing rooms - 0.7 m.
Educational premises should be equipped with furniture for two or three rooms in accordance with the approximate arrangement of schoolchildren by class (Table 141). Study rooms for preparatory and first grade students are recommended to be equipped with desks.
Approximately in classrooms, preparatory rooms and 1 -
Table 141. Approximate distribution of schoolchildren by classes and furniture groups in percent
| prepare | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9th | 10th | |
| A | 95 | 70 | 40 | 15 | |||||||
| B | 5 | 30 | 60 | 75 | 70 | 35 | 10 | ||||
| IN | 10 | 30 | 60 | 70 | 55 | 30 | 15 | 10 | |||
| G | 5 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 70 | 70 | |||||
| d | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
Table 142
| Number offices | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||||||||
| 5- | 10th | 5- | 7th | 8-10th | 5- | 6th | 7th | -e | 9th-10th | |||
| (11th) | (11th) | (11th) | ||||||||||
| Group | % | PC. | % | PC. | % | PC. | % | PC. | % | PC. | % | PC. |
| B | 5 | 1 | 10 | 2 | 15 | 3 | ||||||
| IN | 40 | 8 | 60 | 12 | 15 | 3 | 65 | 13 | 35 | 7 | 10 | 2 |
| G | 45 | 9 | 30 | 6 | 70 | 14 | 20 | 4 | 55 | 11 | 70 | 14 |
| d | 10 | 2 | 15 | 3 | 10 | 2 | 20 | 4 | ||||
2 classes need furniture of two groups - A and B; 3 classes - three groups - A, B, C; 4 classes - two groups - B and C. Study rooms for schoolchildren of 5-10 (11) classes are equipped with double tables. The number of tables in each group is determined by the number of classrooms per subject (Table 142).
Study rooms for students 5-
6th and 8th-10th grades are equipped with double student tables with chairs; laboratories of physics, chemistry and biology - double laboratory tables of groups C, D, D in accordance with GOST 18314-73; for example, convenient placement of schoolchildren in grades 8-10 (11) will be provided by tables of group C in the amount of 3 pcs., G - 14 pcs., D - 3 pcs.
For the manufacture of demonstration tables, GOST 18607-73 is adopted. Various types of cabinets have been developed for storing textbooks (GOST 18666-73). Technical training aids are stored at the TCO office or directly in the classrooms in special mobile cabinets-stands. For the equipment of classrooms, a universal sliding blackboard has been developed. It consists of a main shield and four double-sided sliding shields for writing with chalk. In the classroom of the Russian language and literature, the shutters of the shields can be lined in one line, in the mathematics classroom - in a cage; a coordination grid is applied to one of the shields for drawing graphs. Foreign language classrooms are equipped with student tables in accordance with GOST 19550-74, and drafting and drawing classrooms with tables in accordance with GOST 19549-74.
Chalkboards are suspended at a height of 85 cm from the floor in grades 1-4, 95 cm in middle and senior grades. Chalkboards should have trays for holding chalk dust, trays for storing chalk, rags, holders for pointers and drawing supplies. Boards in drafting and drawing rooms can be black, and in classrooms - dark brown or green (the surface of the board cannot be varnished - it must be matte, smooth, without scratches, not shine). The gloss of the surface of the board can be reduced by rubbing a solution of ammonia (one spoon per 1 cup of water).
Organization of educational and pedagogical process. When organizing the educational regime in schools, one should be guided by the Decree of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated April 12, 1984, No. 313 "On the further improvement of the general secondary education of young people and the improvement of the working conditions of a general education school." The school day for single-shift classes should begin at 9 a.m., for two-shift classes - not earlier than 8:30 a.m. for students in grades 1-4 and 8 a.m. for secondary school students. A school day in grades 1-4 should be no more than 4 lessons, in grades 5-8 - no more than 5 lessons. The standard school curriculum sets the maximum number of hours for grades 1-3, for grade 8 - 30 hours per week, including classes in work, physical culture and art, for grades 8 = 10 (11) - 32 hours per week. Physical education classes should not exceed 2 hours per week in the 7th grade, 4 hours - in the 8th grade, 6 hours - in the 9-10th (11th) grades. Physical education classes should be held on days with the least number of lessons with a break of at least 45-60 minutes after compulsory classes.
Classes are organized according to the principle of alternating subjects and the optimal ratio during the day and week of classes in the natural-mathematical and humanitarian cycles with lessons in singing, drawing, labor and physical education. The maximum duration of the lessons is 45 minutes (in the 1st grade it is recommended up to 35 minutes), breaks - 10 minutes. One of the breaks (second or third), when students are provided with hot meals, should have a duration of 30 minutes (or two breaks of 20 minutes each).
Homework is given to students, taking into account the possibility of doing it within the limits: in the 1st grade - up to 1 hour, in the 2nd grade - up to 11/2 hours, in the 3rd-4th - up to 2 hours, in the 5th-6th - up to 21 / h, at 7 am - up to 3 h, at 8-10 (11 th) - up to 4 h.
The educational and pedagogical process in preparatory classes should be organized in accordance with the guidelines "Organization of training sessions and extended day regimes in preparatory classes of general education schools" (No. 2487-81).
The use of technical teaching aids (screen-sound, screen and sound) in the educational process is carried out taking into account " methodological recommendations on the use of technical teaching aids in the educational work of general education schools” (M., 1982). Each pair of headphones (such as TON-2, etc.) must be equipped with individual volume controls (the volume level near the student's ear is within 40-45 dB).
Organization of labor training for students in grades 1-7. Defined by "The main directions of the reform of general education and vocational schools" (1984), by the Decree of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the USSR Council of Ministers of April 12, 1984 "On improving labor education, training, vocational guidance for schoolchildren and organizing their socially useful, productive work" (No. 314) and is carried out taking into account the “Sanitary and hygienic requirements for the organization of labor training for students in grades 1-7 (No. 3216-85).
Organization and mode of classes for students in grades 1-4. Labor classes are held in classrooms for 1 academic hour (45 minutes) - 2 times a week (duplication of lessons is unacceptable). The total duration of practical work for students in grades 1-2 should not exceed 20-25 minutes of lesson time, for students in grades 3-4 - 30-35 minutes.
In the classroom, work should alternate between different types of activities and tasks. Explanations of the teacher should be carried out at the beginning of the lesson and after completing a certain part of the task. Continuous execution duration labor actions for schoolchildren is limited: for students of the 1st grade - no more than 5 minutes; for students of 2-3 grades - no more
4-7 min; for students of the 4th grade - no more than 10 minutes when working with paper, cardboard, fabric and 4-5 minutes when working with wood and wire. During labor training of students of the 1st grade, after each period of work, 2-3-minute breaks follow for rest and additional explanations by the teacher. For students in grades 2-4, every 15 minutes of the lesson, 3-minute physical education breaks follow.
Organization and mode of classes for students in grades 5-7. Labor classes are held in training workshops once a week in the form of double lessons according to the scheme: theoretical part, practical work, organized breaks and the final part (practical work 60-65% of the class time).
In the process of independent work of schoolchildren, it is necessary to take organized 3-minute breaks. The duration of the interrupted performance of the main labor operations is regulated: for students of the 5th grade, the optimal duration of carpentry operations is 8 minutes, plumbing - 6 minutes (but not more than 10 minutes); for students of the 6th grade, the optimal time for carpentry operations is 11 minutes, for locksmith operations - 9 minutes (but not more than 13 minutes); for students of the 7th grade, this time is 12, 10 (16 minutes), respectively. The optimal duration of continuous work on electric sewing machines should be 5-10 minutes for schoolchildren of the 4th grade; 6th-7th grade - 7-12 min. Permissible duration, respectively, no more than 12 and 15 minutes. When students perform tasks, one should not regulate the pace of work that is uniform for everyone and limit spontaneous micropauses. For students of grades 5-7, the class schedule provides for: a change between the first and second hours of classes lasting 8 = 15 minutes and organized breaks in the time of practical work, which for students of grade 5 should be held every 12 minutes of work, for students 6th grade - after 15-18 minutes of work, for students of 7th grade - after 20 minutes of work. In the classroom sewing business, cooking, electrical engineering, designing for students in grades 5-7, a change of 10-15 minutes should be organized between the first and second hours and in the middle of each hour of classes - breaks of 5 minutes (physical education breaks).
Labor training of students in grades 8-10 (11) is carried out in accordance with the "List of medical contraindications for work and industrial training of adolescents in various professions" ( graduate School, vol. 1-IX, 1984) and is controlled, guided by the "Sanitary and hygienic requirements for the organization of the regime and conditions for teaching schoolchildren in interschool educational and production plants and in the workshops of basic enterprises" (No. 3215-85).
The total duration of labor lessons for schoolchildren (theoretical and practical classes) should not exceed 4 hours per day for students in grades 8-9, and 6 hours per day for students in grades 10-11. The duration of practical work of students should not exceed 70-75% of the time of classes. Students must be provided with personal protective equipment: overalls, safety shoes, eye protection (glasses, masks) and hearing protection (anti-noise). On days of the week that combine classes in general education subjects at school with labor training, the total duration of the workload of schoolchildren in grades 8-10 (11) should not exceed 6 hours a day. In the mode of these days, 10-minute breaks should be provided after the theoretical part (preferably physical education breaks), as well as a 30-minute break after 2 practical classes. During these 2 hours, 10-minute breaks should also be taken: in the 8th grade - after 30 minutes, in the 9th - after 45 minutes of work. In the presence of adverse production factors (noise, vibration, dustiness, etc.), physical education pauses are held outside industrial premises.
The production rates for schoolchildren aged 14 should not exceed 40% of the hourly rate of adults, for adolescents aged 15-16 - no more than 60%, and for 17-year-olds - no more than 80%.
When performing work, it is necessary to observe the norms for carrying heavy loads (no more): boys 14 years old - 6 kg, 15 years old - 8.2 kg, 16 years old - 12 kg, 17 years old - 16.4 kg; girls - respectively 6; 6.8; 8 and 9 kg.
The duration of such work should not exceed 1/3 of the working time.
Hygienic requirements for the organization of training conditions in the Criminal Procedure Code and at the workplaces of basic enterprises. Training workshops of the CPC and training workshops of basic enterprises must meet sanitary and hygienic requirements in accordance with the following documents:
1. Decrees of the State Committee of the USSR on Labor and Social Affairs "On the list of industries, professions and work with difficult and harmful working conditions, which prohibit the use of labor of persons under 18 years of age" (No. 283 / P-9 of 10.09.80) and “On Approval of the List of Industries, Professions and Works with Difficult and Harmful Working Conditions where the Use of Women's Labor is Prohibited” (No. 240/11-10-3 dated 25.07.78);
2. SNiP and P-66-78 “Vocational and secondary specialized educational institutions. Design standards”; SNiP P-L-65-73 “Comprehensive schools and boarding schools. Design standards”; SNiP P-4-79 “Natural and artificial lighting. Design standards”; CH-245-71 " Sanitary standards design of industrial enterprises.
3.GOST 12.1.003-83 "SSBT. Noise, general safety requirements”; GOST 12.1.00576 "SSBT. Work area air. General sanitary and hygienic requirements”; GOST 12.1.007-76 "SSBT. Harmful substances. Classification and general safety requirements”. "Guidelines for the prevention of adverse effects of industrial noise on the body of adolescents" (No. 2410-81).
Natural and artificial lighting. All classrooms (classrooms, classrooms, workshops) must have natural lighting. With a small depth of classrooms (up to 6 m), a lateral left-side illumination is provided, with a greater depth, a right-side illumination device is required. For workshops with large laying depths the best system lighting should be considered two-sided and combined (lateral left-hand and top). Walls, study tables and equipment should be painted in a matte light color range with a reflectance of at least 0.45, the ceiling and upper parts of the walls should be painted white. The color of the premises of the metal and woodworking shops should be a calm green and yellow spectrum with a reflection coefficient of 0.60. To emphasize individual equipment, it should be painted in a more intense color.
The level of artificial lighting on work surfaces in classrooms and classrooms should be at least 300 lux; in locksmith workshops at workplaces - 500 lux and be created by a general lighting system. When performing accurate visual work of 1-4 categories, combined lighting is necessary, while the level of general lighting should be 10% of the normalized illumination, but not less than 150 lux.
Artificial lighting of classrooms is created by lamps with fluorescent lamps of the LPO-01-2X40 / D-01, LPO-02-4X40 / A-01, LPO-10-2X65, LS-002-2X65 types. The blackboard is illuminated by two mirror lamps of the LPO-12-IX40 type installed parallel to it. For general lighting of educational workshops with normal environmental conditions, lamps of the LSO 02-2X40, L 2010M-2X40 (2X80), LSP 02-2X40 (2X65), LSP 06-2X80, LPO 01-2X40, LPO 13-2X40, LPO series should be used 02-2X40. For industrial premises with adverse environmental conditions - series PVL-2X40 (2X80), PVL 02-2X40, LVP 31-4X80, LVP 33-2X80. For local lighting when performing tool work - lamps with incandescent lamps of the NKS1 series, for grinding machines - lamps of the LKS-01 series.
The normalized noise parameter for adolescents aged 16-17 is the limiting spectrum of 65 dBA (PS-65). When the normative noise parameter increases, breaks for students are mandatory
8-9th grades after 50 minutes, for students of 10-11th grades - after 1.5 hours of work, while limiting the duration of work in a noisy environment and using personal noise protection equipment (headphones, earplugs). With noise parameters PS-95 and above, teenagers are not allowed to undergo industrial training and practice.
The sanitary regime must be observed in the premises: daily wet cleaning, ventilation of the premises before lessons and during breaks, weekly cleaning of the premises using detergents and disinfectants, cleaning of window panes, lighting fittings, etc.
The socially useful productive work of schoolchildren includes: self-service, work on the improvement of the school estate, manufacturing and repair educational equipment, inventory, participation in the repair of the school building, work on the educational and experimental site, construction works and etc.
Classes should start 1 hour after the end of the lessons according to the schedule (lunch and rest time).
The duration of labor is 30 minutes for students in grades 2-4; 1 hour - for students in grades 5-7; 2 hours - for students in grades 8-9 and 3 hours a day - for students in grades 10 (11).
Only healthy students of grades 2-10 (11) should be involved in socially useful work.
Children and adolescents should not be involved in work:
1) not appropriate for age and associated with great physical exertion (students of grades 2-4 - for mopping, washing clothes by hand or machines; teenagers of grades 5-8 - for washing bed and underwear by hand, loading and unloading heavy objects, rubbing the floor, etc.);
2) life-threatening: throwing snow from the roof and roadways of streets, repairing and maintaining the electrical network, preparing ice on rivers and lakes, washing and wiping lighting fixtures and window panes on any floor, servicing a boiler room, carrying out ongoing disinfection, disinfestation and deratization , as well as to work related to the use of pesticides;
3) dangerous in epidemiological terms: cleaning of bathrooms, washrooms, common areas, cleaning and removal of waste, etc.
For auxiliary work in the kitchen (cutting bread, washing dishes, filling drinking tanks, etc.) only students from the age of 14 who have undergone a medical examination as employees of food enterprises can be involved.
Students perform socially useful work only in special clothes (overalls, dressing gowns, aprons, scarves). Equipment must be appropriate for the height and age of the students.
Washing floors, radiators and panels should be done only in the presence of warm water (20-35 ° C).
To work with household machines and appliances (vacuum cleaners, electric polishers, washing machines) students only from 14 years old are allowed. Carrying weights within the normal range (up to 4 kg) should take no more than 1/3 of their working time. After work, students are provided with conditions for observing the rules of personal hygiene (warm water, soap, towels).
Involving students in the collection of secondary raw materials requires enhanced sanitary control in accordance with the "Sanitary rules for the collection of secondary raw materials by schoolchildren" (No. 2398-81). Students are allowed to collect scrap metal, waste paper and glassware. Students in grades 3-4 can only collect waste paper. High school students can collect secondary raw materials in institutions (except for medical ones), shops, and enterprises. It is forbidden to collect raw materials from apartments, yards, markets, landfills. Carts, stretchers, nets, bags, etc., corresponding to the age capabilities of schoolchildren and meeting safety regulations, must be allocated for the transportation of the collected raw materials. Students must be provided with gloves. Storage of raw materials is allowed in sheds or adapted, but necessarily isolated rooms. Secondary raw materials must be removed in a timely manner. Prior to the collection of secondary raw materials, the principal of the school is obliged, with the help of medical workers, to organize conversations in classes about the rules of personal hygiene, the prevention of infectious diseases and worms, as well as safety rules.
Sanitary and hygienic assessment of places of physical education lessons (“Sanitary rules for maintaining places of physical culture and sports lessons”, No. 1567-76). The gym is planned at the rate of 4 m2 per person.
A skating rink on natural water bodies must have an ice thickness of at least 16-18 cm, and a bulk rink - at least 6 cm. The number of skaters at the same time is allowed, based on the calculation of 10 m2 per young man and 8 m2 per child. At temperatures below minus 15 ° C in calm weather and at - 8-10 ° C in strong winds, children are not allowed on the skating rink.
Pools for swimming in flowing water bodies are located either upstream (at a distance of at least 100 m from the place of wastewater discharge, places for bathing livestock, ship moorings, laundry, etc.), or downstream (at least 2 km from source of pollution), taking into account the nature of the effluent and the results of the sanitary analysis of water. Water flow - no more than 0.5 m / s. The water surface area in flowing water bodies is at least 5 m2 per adult and 4 m2 per child, and in stagnant water bodies - at least 8 m2 per person. For those who cannot swim, pools are fenced off at the rate of 3 m2 per visitor (depth for children 0.5-0.8 m, for adults 1.2-1.4 m).
artificial pools. The capacity of the pool with a size of 15X25 m is no more than 75 people for simultaneous swimming, and for sports activities - no more than 35 people; for pools measuring 20x50 m - no more than 200 and 50 people, respectively. The water entering the pool must meet the requirements drinking water(GOST 2874-82 "Drinking water. Hygienic requirements and quality control"). The content of residual chlorine in the pool water is within 0.2-0.3 mg per 1 liter of water, and the titer of Escherichia coli is at least 100 ml. Each visitor to the pool pre-washes with hot water and soap under the shower and passes through a flowing foot bath (for outdoor pools 1 horn for 3 people, for closed 1 horn for 2 people of one shift).
Basketball court for children 11-14 years old should have dimensions of 7X 15 m; the ring is placed at a height of 280 cm; for children 15 years and older, respectively, 26X14 and 305 cm. The volleyball court for children under 12 years old has dimensions of 15X7.5 m, for children 15 years old and older, 18X9 m.
Sports entertainment and sports activities are carried out in the following temperature conditions (Table 143).
The organization of physical education in schools and boarding schools provides for gymnastics until
Table 143
lessons, physical education lessons, physical education lessons, mass physical culture and sports sectional work during extracurricular time, tourism and hardening. Monitoring the health of those involved in physical exercises and sports is mandatory and consists of regular medical examinations: 1) primary - before starting physical exercises, hardening and sports; 2) planned - repeated; 3) additional - before participating in competitions and before resuming physical exercises after breaks.
During the primary medical examination, a group is determined for physical education, taking into account health, physical development and functional capabilities of the body (Table 144).
Table 144
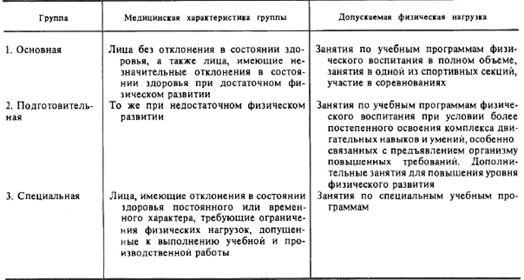
Students of a special group are subject to dispensary observation in medical and physical education dispensaries, medical control rooms (compliance with physical education standards is excluded).
The recruitment of groups is carried out by a doctor with the participation of a physical education teacher. The size of each group is 15-20 people. If possible, the following age groups should be distinguished: from 7 to 10 years old - junior, from 11 to 13 years old - middle, from 14 years old and older - senior.
To conduct classes with children, teachers with higher or secondary physical education who have undergone special training should be allowed.
After illnesses, operations, injuries, students are temporarily exempted from physical education classes and sports training.
Out-of-school work on physical education is built in the form of classes in sports sections and in children's sports schools, where medical control over the state of health and load is carried out by the medical staff of the organization.
Schools and after-school groups provide for the allocation of premises at the rate of 20% of the total number of students in grades 1-4 and 10% of students in grades 5-6 (SNiP P-L 65-73). In extended day schools, students are from 8:30 a.m. to
18-19 hours, provided with two meals a day. In connection with the need to organize a differentiated regime for students of different classes, the possibility of sectional placement of classes, daytime sleep (for students in grades 1-2 and children with poor health) should be provided. Mandatory 3-3 "/g-hour stay in the air for students in grades 1-2 and 2-2" / 2-hour for students in grades 3-8. Physical education of students is widely organized: morning exercises, physical culture pauses during training sessions, short (20-25 minutes) physical exercise, outdoor games, work of sports sections.
Schools with an extended day are equipped with additional furniture (new types of easily moved and folded furniture are provided), built-in wardrobes for storing students' change of clothes and washing supplies.
font size
HYGIENIC REQUIREMENTS FOR EDUCATIONAL CONDITIONS FOR SCHOOLCHILDREN IN VARIOUS TYPES OF MODERN GENERAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS-... Relevant in 2017
SANITARY RULES AND REGULATIONS
SANITARY RULES AND REGULATIONS
1. Designed:
Scientific Center for the Health of Children, Adolescents and Youth of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences (N.N. Kuindzhi, B.Z. Voronova, V.I. Belyavskaya, G.M. Sapozhnikova, M.I. Stepanova, Z.I. Sazanyuk, M.A. Polenova, V. V. Butrov);
2.1.6. The service radius from the house to educational institutions located in the II and III building-climatic zones should be no more than 0.5 km of walking distance; in the I climatic region (I subzone) for students of primary and secondary school age (I - II levels of education) - 0.3 km, for older students (III level) - 0.4 km; in the I climatic region (II subzone) for students of primary and secondary school age - 0.4 km, for older students - 0.5 km.
It is allowed to place educational institutions at a distance of transport accessibility: for students of the 1st stage - 15 minutes (one way), for students of the 2nd and 3rd levels - no more than 30 minutes (one way).
2.1.7. In rural areas, the location of general educational institutions should provide for students of the 1st stage the radius of accessibility of no more than 2 km on foot and no more than 15 minutes. (one way) for transport services.
For students of levels II and III, the radius of walking distance should not exceed 4 km, and with transport services - no more than 30 minutes.
The maximum radius of service for students of II-III steps should not exceed 15 km.
2.1.8. Transport services are subject to students living at a distance of more than 3 km from the school.
The transportation of rural schoolchildren is carried out by special school transport.
2.2.3. The territory of the site must be fenced with a 1.5 m high fence and green spaces along it.
2.2.4. The site must be landscaped at the rate of at least 50% of its area.
2.3.14. The optimal dimensions of the students' working area depend on the visibility angle (associated with the distance from the board to 1 side rows - desks). It should be at least 35 degrees for students of the II-III stage of the school and at least 45 degrees for students of 6-7 years old.
2.3.23. During the construction and reconstruction of modern educational institutions, preference should be given to recreational facilities of the hall type.
2.3.24. The medical center of a general educational institution should include the following premises: a doctor's office with a length of at least 7 m (to determine the acuity of hearing and vision of students) with an area of at least 14 square meters. m; Dentist's office with an area of 12 sq. m, equipped with a fume hood; treatment room with an area of 14 sq. m; psychologist's office with an area of 10 sq. m.
: Due to the loss of force SNiP 2.08.02-89, one should be guided by the SNiP 31-06-2009 adopted instead
Heat supply of buildings should be provided from CHP, district or local boiler houses. Steam heating is not allowed.
As heating devices, radiators, tubular heating elements built into concrete panels can be used, and convectors with casings can also be used. Heating appliances should be enclosed with removable wooden grates, located under window openings and have temperature controllers. It is not allowed to install fences made of chipboards and other polymeric materials. The average surface temperature of heating devices should not exceed 80 degrees Celsius.
2.5.2. When designing air heating combined with ventilation in a school building, automatic control of systems should be provided to maintain the calculated levels of temperature and relative air humidity in the range of 40 - 60% in the room during working hours.
In the locker room of the gym - 19 - 23 degrees Celsius;
In doctors' offices - 21 - 23 degrees Celsius;
In recreation - 16 - 18 degrees Celsius;
In the library - 17 - 21 degrees Celsius;
In the lobby and cloakroom - 16 - 19 degrees Celsius.
2.5.7. Physical education lessons should be held in well-aerated halls. To do this, it is necessary to open one or two windows on the leeward side during classes in the hall at an outdoor temperature above +5 degrees Celsius and a light wind. At lower temperatures and higher air speeds, classes in the hall should be held with open transoms, and cross-ventilation should be carried out during breaks in the absence of students.
When the air temperature in the room reaches 15 - 14 degrees Celsius, the ventilation of the hall should be stopped.
2.5.8. In the premises of educational institutions, the relative humidity of the air should be in the range of 40 - 60%.
In classrooms, predominantly fluorescent lighting should be designed using lamps: LB, LHB, LEC. The use of incandescent lamps is allowed (in this case, the illumination standards are reduced by 2 steps of the illumination scale).
It is forbidden to use fluorescent lamps and incandescent lamps in the same room. The use of new types of lamps and fixtures must be coordinated with local sanitary and epidemiological supervision centers.
2.9.6. In order to facilitate the process of adaptation of children to the requirements of the school in the 1st grade, a "stepped" mode of training sessions with a gradual increase in the teaching load should be used:
In September - 3 lessons of 35 minutes duration;
From the second quarter - 4 lessons of 35 minutes each;
From the second half of the year, in accordance with clause 2.9.2.
For students in the 1st grade, additional weekly holidays are established throughout the year.
After classes with VDT, it is necessary to carry out gymnastics for the eyes, which is performed by students at the workplace (Appendix 3).
2.9.14. In the classroom, work should alternate tasks of various nature. It is unacceptable in the lesson to perform one type of activity throughout the entire time of independent work.
The total duration of practical work should not exceed 20-25 minutes for students in grades 1-2, and 30-35 minutes for students in grades 3-4.
The duration of continuous work with paper, cardboard, fabric should be no more than 5 minutes for students in grades 1, 2 - 3 - 5 - 7 minutes, 4 - 10 minutes, and when working with wood and wire - no more 45 minutes.
The duration of practical work in labor lessons for students in grades 5-7 should not exceed 65% of the class time. The duration of continuous work on basic labor operations should be no more than 10 minutes for students in grade 5, 12 minutes for grade 6, and 16 minutes for grade 7 students.
2.9.15. The school schedule of lessons should be drawn up separately for compulsory and optional classes. Extracurricular activities should be scheduled on the days with the fewest compulsory lessons.
There is a 45-minute break between the start of optional classes and the last lesson of compulsory classes.
2.9.16. Conducting double lessons in elementary school is prohibited. For students in grades 5-9, dual lessons are allowed for laboratory, test work, labor lessons, physical education for the intended purpose (skiing, swimming).
Double lessons in basic and specialized subjects for students in grades 5-9 are allowed provided that they are carried out after a physical education lesson or a dynamic pause of at least 30 minutes.
In grades 10-11, double lessons are allowed in basic and specialized subjects.
2.9.17. When scheduling lessons, it is necessary to alternate during the day and week for younger students the main subjects with music, art, labor, physical education lessons, and for middle-aged and older students - subjects of natural, mathematical and humanitarian cycles.
2.9.18. The school schedule of lessons should be built taking into account the course of the daily and weekly curve of the mental performance of students (Appendix 6).
2.9.19. The duration of breaks between lessons for students of all types of educational institutions should be at least 10 minutes, a long break (after 2 or 3 lessons) - 30 minutes: instead of one big break, it is allowed to arrange two breaks of 20 minutes each after 2 and 3 lessons.
Changes must be carried out with the maximum use of fresh air, in outdoor games.
When conducting a daily dynamic pause, it is allowed to extend the big break up to 45 minutes, of which at least 30 minutes are allotted for the organization of motor active activities of students on the school sports ground, in the gym or in recreations equipped with simulators.
2.9.20. Homework is given to students, taking into account the possibility of their completion within the following limits: in the 1st grade (from the second half of the year) - up to 1 hour, in the 2nd - up to 1.5 hours, in the 3rd - 4th - up to 2 hours, at 5 - 6 - up to 2.5 hours, at 7 - 8 - up to 3 hours, at 9 - 11 - up to 4 hours.
2.9.21. The work of extended day groups should be built in accordance with the Methodological Guidelines "Organization and mode of operation of extended day groups".
In extended day groups, the duration of a walk for younger students should be at least 2 hours, for students in grades 5-8 - at least 1.5 hours.
Self-training should begin at 16:00. The duration of self-studying is determined by the class of training in accordance with clause 2.9.20.
The best combination of activities for children in extended day groups is their physical activity in the air before self-training (walking, outdoor and sports games, socially useful work in the school area), and after self-training - participation in emotional activities (classes in circles, games, visiting entertainment events, preparing and holding amateur concerts, quizzes, etc.).
2.10.1. All educational institutions must be staffed with qualified personnel of paramedical workers, pediatricians.
2.10.2. Students of any educational institution must be provided with medical examinations in accordance with Order N 186/272 of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation (Appendix 7).
2.10.3. In all types of educational institutions, a comprehensive rehabilitation of children with deviations in health should be organized, with the inclusion of psychological and pedagogical correction in its structure.
2.10.4. In the absence of a medical worker, the school management concludes an agreement with a nearby polyclinic on medical care for children.
2.10.5. All school employees must undergo mandatory preventive examinations in accordance with current orders.
2.10.6. When children with chronic diseases enter their school, the administration and medical staff of educational institutions with in-depth training should explain to parents that studying in such schools is an additional risk factor for the health of a sick child.
2.10.7. When deciding on the issue of exemption from the final certification of graduates of grades 9, 11 (12), one should be guided by the Order of the Ministry of Health and Medical Industry of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation N 268/146 dated 18.07.94.
2.11.1. During the period of epidemiological well-being in institutions, daily wet cleaning of the premises is carried out using soda, soap or synthetic detergents.
Cleaning of classrooms and other educational and auxiliary premises is carried out after the end of the lessons with open windows or transoms. If the school has two shifts, cleaning is done twice. They wash the floors, wipe the places where dust accumulates (window sills, radiators, etc.).
Once a month, a general cleaning of the premises is carried out using not only detergents, but also disinfectants. For these purposes, use a 0.5 - 1% solution of bleach, chloramine or calcium hypochlorite, 0.2% solution of sulfochloranthin, 3% ampholan solution, 1% (according to DV) solution of polysept, 1% (according to DV) solution of peramine, 3 % (according to DV) hydrogen peroxide solution with detergent.
Windows outside and inside and window openings are washed 2 times a year (in spring and autumn).
Common areas (toilets, canteen, canteen and medical office) are always cleaned with disinfectants.
Sanitary equipment is subject to daily disinfection, regardless of the epidemiological situation. Toilet seats, cistern handles and door handles are washed with warm soapy water. Sinks, toilet bowls are cleaned with quaches or brushes with cleaning and disinfecting agents: Shine-2, Sanita, Belka, PCHD, Desef, Desus, Sanitary, etc., - in accordance with the instructions on the label or wiped twice with a rag soaked in one of the disinfectants ( Appendix 8).
2.11.2. The dining room is cleaned after each visit by its children (breakfast, lunch, afternoon tea). After each meal, the tables are washed with hot water and soap or soda.
Washing of dishes is carried out mechanically or manually.
With the manual method of washing dishes, a three-cell bath is used. The tableware freed from food residues is washed with a brush in water having 50 degrees Celsius, with the addition of detergents (1 bath). After that, the dishes are immersed in one of the disinfectant solutions (0.2% solution of chloramine, sodium or calcium hypochlorite) - 2 baths, rinsed with hot running water at a temperature of 65 degrees Celsius (3 baths) and dried in special cabinets or grates.
Glassware after mechanical cleaning is washed using approved detergents (1 bath), rinsed with hot running water (2 baths) and dried on special grids.
Cutlery after mechanical cleaning and washing with detergents (1 bath) is rinsed with hot running water (2 baths) and disinfected by a physical method in air sterilizers for 2-3 minutes. Clean cutlery is stored in metal cassettes in a vertical position with the handles up.
2.11.3. During quarantine, the order of dish processing processes changes. First, after being freed from food debris, the dishes are immersed in one of the disinfectant solutions listed in Appendix 8, or boiled in a 2% soda solution for 15 minutes. After that, the dishes are washed, rinsed with hot water and dried.
When using a dishwasher, the dishes are processed according to the regime specified in the documentation for the machine.
2.11.4. Washcloths, brushes for washing dishes, rags for wiping tables after use are boiled for 15 minutes in water with the addition of soda or soaked in a disinfectant solution (0.5% chloramine solution for 30 minutes), then rinsed, dried and stored in a special labeled container.
2.11.5. Food remains are disinfected by boiling for 15 minutes. or covered with bleach or any of the following: heat-resistant bleaching lime 200 g/kg, or NGK, or DOSHA 100 g/kg.
2.11.6. In the premises of the catering unit (kitchens, pantries, etc.), the rules for storing food and food waste must be observed and the fight against flies, cockroaches and rodents must be carried out.
2.11.7. In the medical office, in addition to disinfecting the premises and furnishings, it is necessary to disinfect reusable medical instruments by immersion in one of the solutions specified in the Appendix, or use physical disinfection methods (boiling, dry hot air), patient care items are disinfected by wiping or immersion into a disinfectant solution (Appendix 8).
2.11.8. In cases where sterility is required, disposable products must be used.
2.11.9. During the quarantine period, all rooms where there were children from the quarantined class are subject to daily disinfection.
When carrying out disinfection, special attention is paid to the processing of objects that play a decisive role in the transmission of this information. With drip infections - frequent airing of classrooms (at each change), thorough removal of dust in the premises, disinfection of dishes; for intestinal infections - disinfection of dishes, surfaces of dining tables, sanitary equipment, washing hands with soap and water after each visit to the toilet and before eating.
2.11.10. In order to detect pediculosis, medical personnel need to conduct examinations of children at least 4 times a year after each vacation and monthly selectively (four to five classes). Examinations (of the hairy part of the body and clothing) are carried out in a well-lit room, using a magnifying glass and fine combs. After each inspection, the comb is doused with boiling water or wiped with a 70-degree alcohol solution.
2.11.11. The site is cleaned daily. Garbage is collected in metal bins with lockable lids. They are located at a distance of at least 25 m from the main building on a concrete or asphalt base. Waste bins are cleaned when they are 2/3 full. After emptying, the bins are disinfected. Disinfection of garbage bins, garbage pits, dustbins is carried out by irrigation with a 10% solution of bleach (or heat-resistant whitewash), a 5% solution of NGK or a 7% solution of VGK with a disinfection time of 60 minutes. Garbage is poured with one of the solutions: 10% solution of bleach in a ratio of 2:1 for 120 minutes, 20% chloride-lime milk 2:1 for 60 minutes, 5% solution of NGK 2:1 for 120 minutes.
2.11.12. In order to prevent the breeding of flies and destroy them in the development phase in the waste, once every 5 to 10 days, the waste collection sites are treated with one of the means proposed by the methodological guidelines for the fight against flies.
There should be no stray animals on school grounds.
2.12.1. Requirements for the diet of students.
For students of all educational institutions, a one-time hot meal (breakfast) should be organized. At the request of parents, students can also be provided with lunch.
Students of extended day groups should be provided at the place of study with two hot meals a day (breakfast and lunch), and for a long stay at school, and an afternoon snack.
2.12.2. The organization and diet of students in educational institutions are subject to mandatory coordination with the bodies of the state sanitary and epidemiological supervision.
2.12.3. When catering for schoolchildren, the following documents should be followed:
SanPiN 42-123-5777-91 "Sanitary rules for catering establishments, including confectionery shops and enterprises producing soft ice cream";
SanPiN 42-123-4147-86 "Conditions, terms of storage of especially perishable products";
Guidelines for the organization of rational nutrition of students in secondary schools.
2.12.4. About cases of food poisoning and acute intestinal infections among students and staff at the school, it is necessary to inform the state sanitary and epidemiological supervision authorities in a timely manner.
2.12.5. In the nutrition of students of educational institutions it is forbidden to use:
Flask, barrel, unpasteurized milk without heat treatment (boiling);
Cottage cheese and sour cream in its natural form without heat treatment (cottage cheese is used in the form of casseroles, cheesecakes, cheesecakes; sour cream is used in the form of sauces and in the first dish 5-10 minutes before readiness);
Milk and curdled milk "samokvas" in its natural form, as well as for making cottage cheese;
Green peas without heat treatment;
Pasta with minced meat (navy style), pancakes with meat, jelly, okroshka, pate, minced herring, jellied dishes (meat and fish);
Drinks, fruit drinks without heat treatment, kvass;
Macaroni with chopped egg, scrambled eggs;
Cream pastries and cakes;
Deep-fried pies, donuts;
Unknown powders as dough rippers.
2.12.6. Requirements for compliance with the rules of personal hygiene by employees of the catering department.
Healthy persons who have undergone a medical examination in accordance with the current orders and instructions, as well as those who have attended a hygiene training course with passing a test, are allowed to work at the catering unit.
Control over compliance with the deadlines for passing medical examinations rests with the school health worker.
Each employee must have a personal medical book, which includes the results of medical examinations, information about infectious diseases, and the passing of the sanitary minimum.
The staff of the catering establishment is obliged to observe the following rules of personal hygiene:
Come to work in clean clothes and shoes;
Leave outerwear, headgear, personal items in the dressing room;
Cut nails short;
Before starting work, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water, put on clean sanitary clothes in a specially designated place, after visiting the toilet, wash your hands thoroughly with soap, preferably disinfectant;
If there are signs of a cold or intestinal dysfunction, as well as suppuration, cuts, burns, inform the administration and contact a medical institution for treatment;
Report all cases of intestinal infections in the worker's family.
When preparing dishes, culinary and confectionery products, wear jewelry, varnish your nails, fasten your sanitary clothing with pins;
Eating, smoking in the workplace. Eating and smoking are allowed in a specially designated room or place.
Every day, before the start of the shift, the health worker conducts an inspection of open surfaces of the body for the presence of pustular diseases in all workers. Persons with pustular skin diseases, festering cuts, burns, abrasions, as well as catarrhs of the upper respiratory tract are not allowed to work, but are transferred to another job. The results of the inspections are recorded in the journal of the established form.
Each catering unit should have a first aid kit with a set of medicines for first aid.
Annex 1
(mandatory)
| - Desk | 1 - 2 pcs. |
| - Chairs | 4 - 6 pcs. |
| - Screen | 1 PC. |
| - Couch | 1 PC. |
| - Stationery cabinet | 1 - 2 pcs. |
| - Pharmacy cabinet | 1 PC. |
| - Medical table with a glass cover: a) with a set of grafting tools | 1 PC. |
| b) with funds for emergency care | 1 PC. |
| - Refrigerator (for vaccines and medicines) | 1 PC. |
| - Washbasin (washbasin) | 1 PC. |
| - Bucket with pedal lid | 1 PC. |
| - Medical scales | 1 PC. |
| - Height meter | 1 PC. |
| - Spirometer | 1 PC. |
| - Manual dynamometer | 1 PC. |
| - Table lamp for ophthalmological and otolaryngological examinations | 1 PC. |
| - Table for determining visual acuity, placed in the Rotta apparatus | 1 PC. |
| - Tonometer | 1 PC. |
| - Phonendoscope | 2 pcs. |
| - Bix is small | 2 pcs. |
| - Bix big | 2 pcs. |
| - Rubber harness | 4 - 6 pcs. |
| - Disposable syringes with 2.0 needles | 10 pieces. |
| 5,0 | 10 pieces. |
| 10,0 | 5 pieces. |
| - Tweezers | 1 PC. |
| - Medical thermometer | 20 - 25 pcs. |
| - Scissors | 2 pcs. |
| - Rubber heating pad | 1 - 2 pcs. |
| - Ice bubble | 1 - 2 pcs. |
| - Reniform tray | 5 pieces. |
| - Metal spatula | 40 pcs. |
| - Tires (Kramer, Dieterichs, plastic, for upper limbs) | 10 pieces. |
| - Stretcher | 1 PC. |
| - Tube quartz | 1 PC. |
| - Glasses in children's frames (Drr 56 - 58 mm) with lenses of 1 diopter | 1 PC. |
| - Polychromatic tables for the study of color perception E.B. Rabkin | 1 PC. |
| - Wooden plantograph (can be made in the school workshop) | 1 PC. |
| - Mat (1 m x 1.5 m) | 1 PC. |
School classes, combining mental, static, dynamic loads on individual organs and systems and on the whole organism as a whole, require FM in class to relieve local fatigue and FM of the general impact.
FM to improve cerebral circulation.
1. Starting position (ip) - sitting on a chair. 1 - 2 - take your head back and gently tilt back, 3 - 4 - tilt your head forward, do not raise your shoulders. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is slow.
2. I.p. - sitting, hands on the belt. 1 - head turn to the right, 2 - ip, 3 - head turn to the left, 4 - ip Repeat 6 - 8 times. The pace is slow.
3. I.p. - standing or sitting, hands on the belt. 1 - swing your left hand over your right shoulder, turn your head to the left. 2 - ip, 3 - 4 - the same with the right hand. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is slow.
FM to relieve fatigue from the shoulder girdle and arms.
1. I.p. - standing or sitting, hands on the belt. 1 - right hand forward, left up. 2 - change the position of the hands. Repeat 3-4 times, then relax down and shake your hands, tilt your head forward. The pace is average.
2. I.p. - standing or sitting, hands with the back on the belt. 1 - 2 - bring your elbows forward, tilt your head forward. 3 - 4 - elbows back, bend. Repeat 6-8 times, then arms down and shake relaxed. The pace is slow.
3. I.p. - sitting, hands up. 1 - clench your hands into a fist. 2 - unclench the brushes. Repeat 6-8 times, then relax your arms down and shake your hands. The pace is average.
FM to relieve fatigue from the body.
1. I.p. - stand legs apart, hands behind the head. 1 - sharply turn the pelvis to the right. 2 - sharply turn the pelvis to the left. During turns, the shoulder girdle should remain motionless. Repeat 6 - 8 times. The pace is average.
2. I.p. - stand legs apart, hands behind the head. 1 - 3 - circular movements of the pelvis in one direction. 4 - 6 - the same in the other direction. 7 - 8 - hands down and shake your hands relaxed. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is average.
3. I.p. - stand legs apart. 1 - 2 - tilt forward, the right hand slides down along the leg, the left, bending, along the body up. 3 - 4 - ip, 5 - 8 - the same in the other direction. Repeat 6 - 8 times. The pace is average.
FM of the general impact are completed from exercises for different muscle groups, taking into account their tension in the process of activity.
A set of exercises FM for younger students in the classroom with elements of writing.
1. Exercises to improve cerebral circulation.
I.p. - sitting, hands on the belt. 1 - turn the head to the right, 2 - ip, 3 - turn the head to the left, 4 - ip, 5 - gently tilt the head back, 6 - ip, 7 - tilt the head forward. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is slow.
2. Exercises to relieve fatigue from the small muscles of the hand.
I.p. - sitting, hands raised up. 1 - clench the brushes into a fist, 2 - unclench the brushes. Repeat 6-8 times, then relax your arms down and shake your hands. The pace is average.
3. Exercises to relieve fatigue from the muscles of the body.
I.p. - stand legs apart, hands behind the head. 1 - sharply turn the pelvis to the right. 2 - sharply turn the pelvis to the left. During turns, the shoulder girdle should remain motionless. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is average.
4. Exercises to mobilize attention.
I.p. - standing, arms along the body. 1 - right hand on the belt, 2 - left hand on the belt, 3 - right hand on the shoulder, 4 - left hand on the shoulder, 5 - right hand up, 6 - left hand up, 7 - 8 - clapping hands above the head, 9 - lower the left hand on the shoulder, 10 - the right hand on the shoulder, 11 - the left hand on the belt, 12 - the right hand on the belt, 13 - 14 - clapping hands on the hips. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace - 1 time slow, 2 - 3 times - medium, 4 - 5 - fast, 6 - slow.
1. Blink quickly, close your eyes and sit quietly, slowly counting to 5. Repeat 4-5 times.
3. Stretch your right hand forward. Follow with your eyes, without turning your head, the slow movements of the index finger of the outstretched hand to the left and right, up and down. Repeat 4-5 times.
4. Look at the index finger of the outstretched hand at the expense of 1 - 4, then look into the distance at the expense of 1 - 6. Repeat 4 - 5 times.
5. At an average pace, do 3 - 4 circular movements with your eyes to the right side, the same amount to the left side. After relaxing the eye muscles, look into the distance at the expense of 1 - 6. Repeat 1 - 2 times.
| Classes | Daily amount of time (h) | Cultural and recreational activities | Physical education lessons per week (h) | Extra-curricular forms of classes per week, sports sections of physical education circles, general physical education groups (h) | School events | Self. physical education at least (min.) | ||||
| gymnastics before training sessions (min.) | physical education minutes at the lessons (min.) | moving changes (min.) | sport. hour in extended day (h) | |||||||
| participation in competitions in studies. year (times) | days of health and sports | |||||||||
| I | 2 | 5 - 6 | 5 | 15 - 20 | 1 | 2 | 1,10 | 6 - 8 | Monthly | 10 - 15 |
| II | 2 | 5 - 6 | 5 | 15 - 20 | 1 | 2 | 1,30 | 6 - 8 | -" | 15 - 20 |
| III | 2 | 5 - 6 | 5 | 15 - 20 | 1 | 2 | 1,30 | 6 - 8 | -" | 15 - 20 |
| IV | 2 | 5 - 6 | 5 | 15 - 20 | 1 | 2 | 1,30 | 6 - 8 | -" | 15 - 20 |
| V | 2 | 5 - 7 | 5 | 35 - 45 | 1 | 2 | 1,30 | 8 - 9 | -" | 20 - 25 |
| VI | 2 | 5 - 7 | 5 | 35 - 45 | 1 | 2 | 1,30 | 8 - 9 | -" | 20 - 25 |
| VII | 2 | 6 - 8 | 5 | 35 - 45 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 8 - 9 | -" | 20 - 25 |
| VIII | 2 | 6 - 8 | 5 | 35 - 45 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 8 - 9 | -" | 20 - 25 |
| IX | 2 | 6 - 8 | 35 - 45 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 8 - 9 | -" | 25 - 30 | |
| X | 2 | 6 - 8 | 15 - 20 | 2 | 2 | 10 | -" | 25 - 30 | ||
| XI | 2 | 6 - 8 | 15 - 20 | 2 | 2 | 10 | -" | 30 - 35 | ||
Note. The duration of the combined lessons is reduced to 40 minutes, the last lessons - to 35 minutes.
In the 1st grade, the duration of the lessons is 30 minutes in the first half of the year, and 35 minutes in the second.
The second break (20 min.) is used for feeding children, the third (20 min.) - for outdoor games.
In option 2, in the first grade, after the 3rd lesson, a 2.5-hour break is held, during which lunch, sleep, and games are organized. In conditions of full combination, lessons of physical education, labor, singing, drawing are held.
Modern scientific research has established that the biorhythmological optimum of mental performance in children of school age falls on the interval of 10-12 hours. During these hours, the greatest efficiency of assimilation of the material is noted at the lowest psychophysiological costs of the body.
Therefore, in the schedule of lessons for younger students, the main subjects should be taught in 2-3 lessons, and for middle-aged and older students - in 2, 3, 4 lessons.
The mental performance of students is not the same on different days of the school week. Its level increases towards the middle of the week and remains low at the beginning (Monday) and at the end (Friday) of the week.
Therefore, the distribution of the study load during the week should be built in such a way that its largest volume falls on Tuesday and (or) Wednesday. On these days, the school schedule should include either the most difficult subjects, or subjects of medium and light difficulty, but in greater numbers than on the other days of the week.
Presentation of new material test papers should be carried out at 2 - 4 lessons in the middle of the school week.
Subjects that require a lot of time for home preparation should not be grouped on the same day of the school schedule.
| Item | Number of points |
| Mathematics, Russian language (for national schools) | 11 |
| Foreign language | 10 |
| Physics chemistry | 9 |
| Story | 8 |
| Mother tongue, literature | 7 |
| Natural science, geography | 6 |
| Physical training | 5 |
| Work | 4 |
| Drawing | 3 |
| Drawing | 2 |
| Singing | 1 |
Addition to the table I.G. Sivkov can serve as the data of a survey of students of modern educational institutions, which include computer science, specialized disciplines, and new subjects for them among the most difficult subjects. These items should be evaluated at least 10 points.
With a properly designed lesson schedule, the highest number of points per day for the sum of all subjects should fall on Tuesday and (or) Wednesday. Such a distribution of the weekly study load should be sought when drawing up a schedule for older students.
For junior and middle-aged students, the study load should be distributed in a weekly cycle in such a way that its greatest intensity (according to the sum of points per day) falls on Tuesday and Thursday, while Wednesday was a somewhat lighter day.
The schedule is incorrect when the highest number of points per day is on the last days of the week or when it is the same on all days of the week.
Annex 7
(mandatory)
extraction
from the Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation,
Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation
dated June 30, 1992 N 186/272
| Tipping periods | Pre-medical stage (screening and laboratory examination) | Medical and pedagogical stage | Specialized stage | |
| pediatrician | teacher, psychologist | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Before entering preschool | The average health worker of a medical and preventive institution | Inspection with data analysis screening - test and laboratory examination. Distribution by health groups | Recommendations on the adaptation regime in a preschool institution | Neurologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedic surgeon, dentist, speech therapist (from 3 years old), psychiatrist and other specialists according to indications |
| One year before starting school | Inspection with data analysis screening - test and laboratory examination | Determination of functional readiness for learning at school | Neurologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedic surgeon, dentist, according to indications speech therapist, psychiatrist | |
| Before entering school | Middle health worker of a preschool institution | Inspection with data analysis screening - test and laboratory examination. Distribution into medical groups for physical education | Definition of functional readiness for school | |
| End of first year | School nurse | Recommendations for recovery in the summer holidays | Assessment of adaptation to learning at school, recommendations for the holidays | Neurologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedic surgeon, dentist, psychiatrist, speech therapist |
| Transition to subject education | School nurse | Assessment of neuropsychic and physical development, determination of the biological age of the child and compliance with the passport | Adaptation assessment | |
| Pubertal period (14 - 15 years) | School nurse | Neurologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedic surgeon, dentist, psychiatrist, speech therapist and gynecologist according to indications | ||
| Before graduating from an educational institution (10 - 11 cl. 16 - 17 years old) | School nurse | Medical and professional consultation, transfer of information on young men of pre-conscription age to military registration and enlistment offices | Teacher, psychologist Medical and professional consultation | Neurologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedic surgeon, dentist, psychiatrist, speech therapist and gynecologist according to indications |
Annex 8
(mandatory)
In real Sanitary regulations References are made to the following documents:
1. Law of the RSFSR "On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population".
2. RF Law "On Education".
3. "Regulations on state sanitary and epidemiological regulation", approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of June 5, 1994, N 625.
4. Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation "Improving the system of medical support for children in educational institutions" dated 30.06.92, N 186/272.
5. Classifier of sanitary-hygienic and epidemiological regulatory and methodological documents, approved by the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of the Russian Federation on 04/09/93.
6. Guide R 1.1.004-94 "State system of sanitary-epidemiological regulation of the Russian Federation. General requirements for the construction, presentation and execution of sanitary-hygienic and epidemiological regulatory and methodological documents", approved by the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of the Russian Federation on 09.02.94.
"Sanitary and hygienic rules and norms for the organization of education for children from the age of six", approved by the USSR Ministry of Health and the USSR Ministry of Education in 1986.
15. SanPiN 42-123-4147-86 "Conditions, terms of storage of especially perishable products", approved by the USSR Ministry of Health in 1986
16. SanPiN 42-123-5777-91 "Sanitary rules for catering establishments, including confectionery shops and enterprises producing soft ice cream", approved by the USSR Ministry of Health in 1991.
17. Guidelines for the organization of rational nutrition of students in secondary schools, approved by the Ministry of Trade of the USSR on 28.12.85, N 315.